No CrossRef data available.
Lithium and Potassium Absorption, Differential Thermal, and Infrared Properties of Some Montmorillonites
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 January 2024
Abstract
Investigations are underway concerning inter-relations of X-ray analyses of chemically treated samples, infrared absorption and DTA for a group of 28 montmorillonite samples. Results to date generally support Greene-Kelly’s LiCl test for evaluation of the proportion of tetrahedral and octahedral layer charge in montmorillonite. Decrease in expandable characteristics of the montmorillonites owing to K+-saturation is much more closely related to the total layer charge than to charge distribution in tetrahedral or octahedral layers.
As the tetrahedral charge increases and the octahedral charge decreases, the infrared absorption band at 11.95µ is replaced by one at 11.35–11.5µ, and the absorption band at 9.2µ decreases or disappears.
Most DTA dehydroxylation peak temperatures are related to charge distribution as follows:
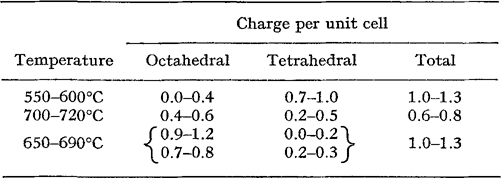
- Type
- General Session
- Information
- Clays and Clay Minerals (National Conference on Clays and Clay Minerals) , Volume 13 , February 1964 , pp. 275
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Clay Minerals Society 1964




