Abstract
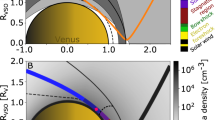
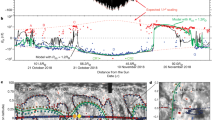
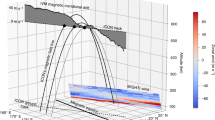
THE abrupt termination of the daytime ionosphere of Venus at about 500 km observed with the Mariner V two-frequency occultation experiment provides an extremely interesting picture of the direct interaction of the solar wind with a planetary ionosphere1,2. It has been suggested that a pseudo-magnetopause is formed by magnetic fields carried along by the solar wind and forced to pile up on the topside of the highly conducting planetary ionosphere3,4. This magnetic obstacle then interacts with the superalfvénic and supersonic solar wind to form a bow shock; evidence for such a bow shock has been obtained by experiments on Mariner V and Venera IV (refs. 2 and 5).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mariner Stanford Group, Science, 158, 1678 (1967).
Bridge, H. S., Lazarus, A. J., Snyder, C. W., Smith, E. J., Davis, L., Coleman, P. J., and Jones, D. E., Science, 158, 1669 (1967).
Dessler, A. J., in Atmospheres of Mars and Venus (edit. by Brandt, J. C., and McElroy, M. B.), 241 (Gordon and Breach, 1968).
Johnson, F. S., J. Atmos. Sci., 25, 658 (1968).
Dolginov, S. S., Yeroshenko, E. G., and Zhuzgov, L. N., Kosmich. Issled., 6, 561 (1968).
Spreiter, J. R., and Alksne, A. Y., Revs. Geophys., 7, 11 (1969).
McElroy, M. B., J. Geophys. Res., 74, 29 (1969).
Herman, J. R., and Chandra, S., Planet. Space Sci., 17, 815 (1969).
Barth, C. A., Wallace, L., and Pearce, J. B., J. Geophys. Res., 73, 2541 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BAUER, S., HARTLE, R. & HERMAN, J. Topside Ionosphere of Venus and its Interaction with the Solar Wind. Nature 225, 533–534 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/225533a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/225533a0
This article is cited by
-
9. The venus ionosphere and solar wind interaction
Space Science Reviews (1977)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.