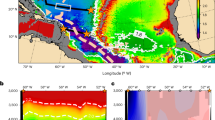
Abstract
A LARGE amount of momentum is transferred to the Southern Ocean by strong westerly winds. Analytical and numerical models have suggested that transient eddies may be important in transporting this momentum away from the region of wind forcing, either horizontally1or vertically downwards where it is balanced by bottom topographic drag2–5. There are, however, few long-term in situ observations of horizontal eddy momentum flux6–8, and no large-scale measurements of vertical eddy fluxes, to test these models. As a result, the momentum balance of the Antarctic circumpolar current (ACC) remains uncertain, and the role of eddies controversial. Here we use Geosat satellite altimeter data to resolve directional eddy kinetic energy and horizontal eddy momentum flux in the ACC on fine spatial and temporal scales. The complex spatial distribution of surface eddy momentum flux is strongly influenced by bottom topography. The horizontal eddy momentum flux tends generally to concentrate the mean flow, although some regions of divergence are observed. Our results show that the zonally averaged horizontal eddy momentum flux from transient eddies is an order of magnitude too small, and in the wrong direction to directly balance the eastward momentum input from wind1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gill, A. E. J. Fluid Mech. 32, 465–488 (1968).
Munk, W. H. & Palmen, E. Tellus 3, 53–55 (1951).
McWilliams, J. C., Holland, W. R. & Chow, J. H. S. Dynam. Atmos. Oceans 2, 213–291 (1978).
Wolff, J.-O., Maier-Reimer, E. & Olbers, D. J. J. phys. Oceanogr. 21, 236–264 (1991).
Johnson, G. C. & Bryden, H. L. Deep Sea Res. 36, 39–53 (1989).
Piola, A. R., Figueroa, H. A. & Bianchi, A. A. J. geophys. Res. 92, 5101–5114 (1987).
Bryden, H. L. & Heath, R. A. Prog. Oceanogr. 14, 65–87 (1985).
Luyten, J. et al. Woods Hole Oceanogr. Inst. Tech. Rep. WHO1-90-30 (1990).
Chelton, D. B., Schlax, M. G., Witter, D. L. & Richman, J. G. J. geophys. Res. 95, 17877–17903 (1990).
Van Gysen, H., Coleman, R., Morrow, R. A., Hirsch, B. & Rizos, C. J. geophys. Res. 97, 2265–2277 (1992).
Parke, M. E., Stewart, R. H., Farless, D. L. & Cartwright, D. E. J. geophys. Res. 92, 11693–11707 (1987).
Sciremammano, F. Jr. J. phys. Oceanogr. 9, 221–226 (1979).
Inoue, M. J. phys. Oceanogr. 15, 1157–1181 (1985).
Daniault, N. & Menard, Y. J. geophys. Res. 90, 11877–11899 (1985).
Patterson, S. L. J. phys. Oceanogr. 15, 865–884 (1985).
Treguier, A. M. & McWilliams, J. C. J. phys. Oceanogr. 20, 321–343 (1990).
Sandwell, D. T. & Zhang, B. J. geophys. Res. 94, 17971–17984 (1989).
Tai, C.-K. & White, W. B. J. phys. Oceanogr. 20, 1761–1777 (1990).
Coleman, R. Austr. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 35, 619–633 (1984).
Mulhearn, P. J. J. phys. Oceanogr. 17, 1148–1155 (1987).
Nishida, H. & White, W. B. J. phys. Oceanogr. 12, 160–170 (1982).
Schmitz, W. J. J. phys. Oceanogr. 12, 208–210 (1982).
Trenberth, K. E., Large, W. G. & Olsen, J. G. J. phys. Oceanogr. 20, 1742–1760 (1990).
Gordon, A. L. & Molinelli, E. J. Southern Ocean Atlas: Thermohaline and Chemical Distributions and the Atlas Data Set (Columbia Univ. Press, New York, 1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morrow, R., Church, J., Coleman, R. et al. Eddy momentum flux and its contribution to the Southern Ocean momentum balance. Nature 357, 482–484 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/357482a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/357482a0
This article is cited by
-
Geostrophic current estimation using altimeter data at ground track crossovers in the northwest Pacific Ocean
Frontiers of Earth Science (2013)
-
Ocean eddy momentum fluxes at the latitudes of the Gulf Stream and the Kuroshio extensions as revealed by satellite data
Ocean Dynamics (2010)
-
Dynamics of sea-surface temperature anomalies in the Southern Ocean diagnosed from a 2D mixed-layer model
Climate Dynamics (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.