Abstract
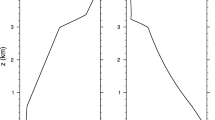
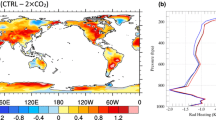
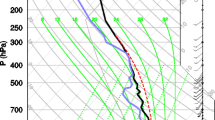
This paper presents application of the EULAG model combined with a sophisticated double-moment warm-rain microphysics scheme to the model intercomparison case based on RICO (Rain in Cumulus over Ocean) field observations. As the simulations progress, the cloud field gradually deepens and a relatively sharp temperature and moisture inversions develop in the lower troposphere. Two contrasting aerosol environments are considered, referred to as pristine and polluted, together with two contrasting subgridscale mixing scenarios, the homogeneous and the extremely inhomogeneous mixing. Pristine and polluted environments feature mean cloud droplet concentrations around 40 and 150 mg−1, respectively, and large differences in the rain characteristics. Various measures are used to contrast evolution of macroscopic cloud field characteristics, such as the mean cloud fraction, the mean cloud width, or the height of the center of mass of the cloud field, among others. Macroscopic characteristics appear similar regardless of the aerosol characteristics or the homogeneity of the subgrid-scale mixing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, B.A. (1989), Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness, Science 245,4923, 1227–1230, DOI: 10.1126/science.245.4923.1227.
Arabas, S., H. Pawlowska, and W.W. Grabowski (2009), Effective radius and droplet spectral width from in-situ aircraft observations in trade-wind cumuli during RICO, Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L11803, DOI: 10.1029/2009GL038257.
Bony, S., and J.-L. Dufresne (2005), Marine boundary layer clouds at the heart of tropical cloud feedback uncertainties in climate models, Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L20806, DOI: 10.1029/2005GL023851.
Brenguier, J.-L., and W.W. Grabowski (1993), Cumulus entrainment and cloud droplet spectra: A numerical model within a two-dimensional dynamical framework, J. Atmos. Sci. 50,1, 120–136, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1993)050〈0120:CEACDS〉2.0.CO;2.
Chosson, F., J.-L. Brenguier, and M. Schröder (2004), Radiative impact of mixingprocesses in boundary layer clouds. In: Proc. 14 Int. Conf. on Clouds and Precipitation, Bologna, Italy, International Association of Meteorology and Atmospheric Sciences, 371–374.
Chosson, F., J.-L. Brenguier, and L. Schüller (2007), Entrainment-mixing and radiative transfer simulation in boundary-layer clouds, J. Atmos. Sci. 64,7, 2670–2682, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3975.1.
Gerber, H.E., G.M. Frick, J.B. Jensen, and J.G. Hudson (2008), Entrainment, mixing, and microphysics in trade-wind cumulus, J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 86A, 87–106, DOI: 10.2151/jmsj.86A.87.
Grabowski, W.W. (2006), Indirect impact of atmospheric aerosols in idealized simulations of convective-radiative quasi-equilibrium, J. Climate 19,18, 4664–4682, DOI: 10.1175/JCLI3857.1.
Grabowski, W.W., and T.L. Clark (1991), Cloud-environment interface instability: Rising thermal calculations in two spatial dimensions, J. Atmos. Sci. 48,4, 527–546, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1991)048〈0527:CIIRTC〉2.0.CO;2.
Grabowski, W.W., and T.L. Clark (1993), Cloud-environment interface instability, Part II: Extension to three spatial dimensions, J. Atmos. Sci. 50,4, 555–573, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1993)050〈0555:CEIIPI〉2.0.CO;2.
Grabowski, W.W., and P.K. Smolarkiewicz (1990), Monotone finite difference approximations to the advection-condensation problem, Mon. Weather Rev. 118,10, 2082–2098, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118〈2082: MFDATT〉2.0.CO;2.
Grabowski, W.W., and P.K. Smolarkiewicz (1996), Two-time-level semi-Lagrangian modeling of precipitating clouds, Mon. Weather Rev. 124,3, 487–497, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(1996)124〈0487:TTLSLM〉2.0.CO;2.
Grabowski, W.W., X. Wu, M.W. Moncrieff, and W.D. Hall (1998), Cloud-resolving modeling of cloud systems during Phase III of GATE. Part II: Effects of resolution and the third spatial dimension, J. Atmos. Sci. 55,21, 3264–3282, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1998)055〈3264:CRMOCS〉2.0.CO;2.
Grabowski, W.W., P. Bechtold, A. Cheng, R. Forbes, C. Halliwell, M. Khairoutdinov, S. Lang, T. Nasuno, J. Petch, W.-K. Tao, R. Wong, X. Wu, and K.-M. Xu (2006), Daytime convective development over land: A model intercomparison based on LBA observations, Quart. J. Roy. Met. Soc. 132,615, 317–344, DOI: 10.1256/qj.04.147.
Koren, I., O. Altaratz, G. Feingold, Z. Levin, and T. Reisin (2009), Cloud’s Center of Gravity — a compact approach to analyze convective cloud development, Atmos. Chem. Phys. 9,1, 155–161, DOI: 10.5194/acp-9-155-2009.
Margolin, L.G., P.K. Smolarkiewicz, and Z. Sorbjan (1999), Large-eddy simulations of convective boundary layers using nonoscillatory differencing, Physica D 133,1–4, 390–397, DOI: 10.1016/S0167-2789(99)00083-4.
Morrison, H., and W.W. Grabowski (2007), Comparison of bulk and bin warm-rain microphysics models using a kinematic framework, J. Atmos. Sci. 64,8, 2839–2861, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3980.
Morrison, H., and W.W. Grabowski (2008), Modeling supersaturation and subgridscale mixing with two-moment bulk warm microphysics, J. Atmos. Sci. 65,3, 792–812, DOI: 10.1175/2007JAS2374.1.
Pincus, R., and M.B. Baker (1994), Effect of precipitation on the albedo susceptibility of clouds in the marine boundary layer, Nature 372, 250–252, DOI: 10.1038/372250a0.
Prusa, J.M., P.K. Smolarkiewicz, and A.A. Wyszogrodzki (2008), EULAG, a computational model for multiscale flows, Comput. Fluids 37,9, 1193–1207, DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2007.12.001.
Siebesma, A.P., C.S. Bretherton, A. Brown, A. Chlond, J. Cuxart, P.G. Duynkerke, H. Jiang, M. Khairoutdinov, D. Lewellen, C.-H. Moeng, E. Sanchez, B. Stevens, and D.E. Stevens (2003), A large eddy simulation intercomparison study of shallow cumulus convection, J. Atmos. Sci. 60,10, 1201–1219, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(2003)60〈1201:ALESIS〉2.0.CO;2.
Slawinska, J., W.W. Grabowski, H. Pawlowska, and A.A. Wyszogrodzki (2008), Optical properties of shallow convective clouds diagnosed from a bulk-microphysics large-eddy simulation, J. Climate 21,7, 1639–1647, DOI: 10.1175/2007JCLI1820.1.
Slawinska, J., W.W. Grabowski, H. Pawlowska, and H. Morrison (2011), Droplet activation and mixing in large-eddy simulation of a shallow cumulus field, J. Atmos. Sci., DOI: 10.1175/JAS-D-11-054.1
Smolarkiewicz, P.K., and L.G. Margolin (1997), On forward-in-time differencing for fluids: An Eulerian/semi-Lagrangian nonhydrostatic model for stratified flows, Atmos. Ocean Sp. 35,1, 127–152.
Stevens, B. (2007), On the growth of layers of nonprecipitating cumulus convection, J. Atmos. Sci. 64,8, 2916–2931, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3983.1.
Stevens, B., and A. Seifert (2008), Understanding macrophysical outcomes of microphysical choices in simulations of shallow cumulus convection, J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 86A, 143–162, DOI: 10.2151/jmsj.86A.143.
Stevens, B., A.S. Ackerman, B.A. Albrecht, A.R. Brown, A. Chlond, J. Cuxart, P.G. Duynkerke, D.C. Lewellen, M.K. Macvean, R.A.J. Neggers, E. Sanchez, A.P. Siebesma, and D.E. Stevens (2001), Simulations of trade wind cumuli under a strong inversion, J. Atmos. Sci. 58,14, 1870–1891, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(2001)058〈1870:SOTWCU〉2.0.CO;2.
Twomey, S. (1974), Pollution and the planetary albedo, Atmos. Environ. 8,12, 1251–1256, DOI: 10.1016/0004-6981(74)90004-3.
Twomey, S. (1977), The influence of pollution on the shortwave albedo of clouds, J. Atmos. Sci. 34,7, 1149–1152, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1977)034〈1149: TIOPOT〉2.0.CO;2.
van Zanten, M.C., B. Stevens, L. Nuijens, A.P. Siebesma, A. Ackerman, F. Burnet, A. Cheng, F. Couvreux, H. Jiang, M. Khairoutdinov, Y. Kogan, D.C. Lewellen, D. Mechem, K. Nakamura, A. Noda, B.J. Shipway, J. Slawinska, S. Wang, and A. Wyszogrodzki (2011), Controls on precipitation and cloudiness in simulations of trade-wind cumulus as observed during RICO, J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 3, M06001, DOI: 10.1029/2011MS000056.
Warner, J. (1955), The water content of cumuliform cloud, Tellus 7,4, 449–457, DOI: 10.1111/j.2153-3490.1955.tb01183.x.
Warner, J. (1968), Areduction in rainfall associated with smoke from sugar-cane fires — An inadvertent weather modification?, J. Appl. Meteor. 7,2, 247–251, DOI: 10.1175/1520-0450(1968)007〈0247:ARIRAW〉2.0.CO;2.
Xue, H., and G. Feingold (2006), Large-eddy simulations of trade wind cumuli: Investigation of aerosol indirect effects, J. Atmos. Sci. 63,6, 1605–1622, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3706.1.
Zhao, M., and P.H. Austin (2005a), Life cycle of numerically simulated shallow cumulus clouds. Part I: Transport, J. Atmos. Sci. 62,5, 1269–1290, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3414.1.
Zhao, M., and P.H. Austin (2005b), Life cycle of numerically simulated shallow cumulus clouds. Part II: Mixing dynamics, J. Atmos. Sci. 62,5, 1291–1310, DOI: 10.1175/JAS3415.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabowski, W.W., Slawinska, J., Pawlowska, H. et al. Macroscopic impacts of cloud and precipitation processes in shallow convection. Acta Geophys. 59, 1184–1204 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-011-0038-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11600-011-0038-9