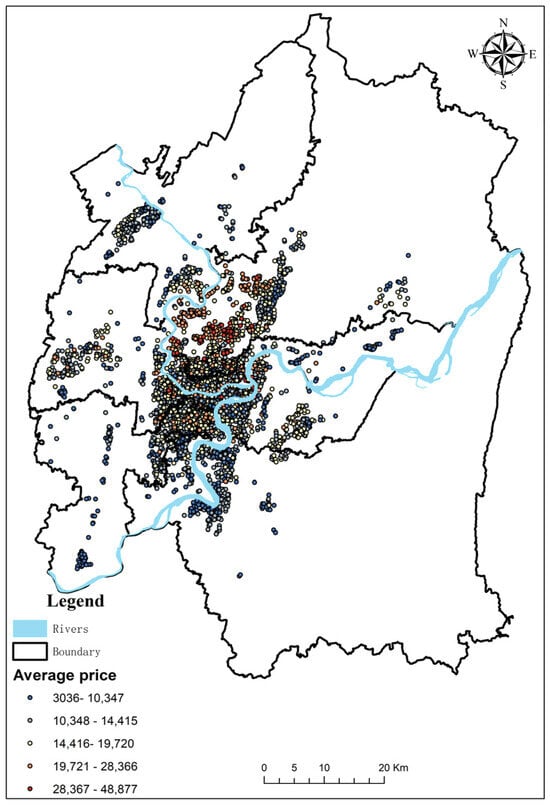
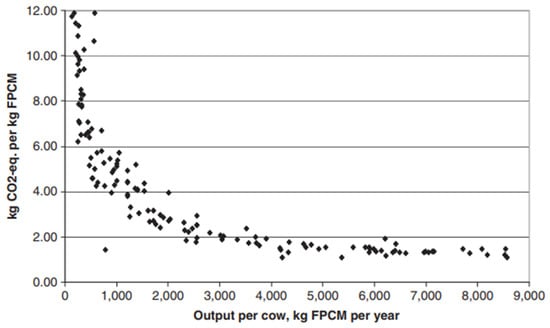
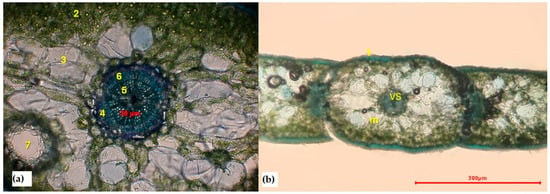
The adaptive potential of plants in urban environments, responding to factors like air pollution, electromagnetic radiation, and specific microclimates, remains insufficiently understood. Our study focused on two evergreen
Cupressaceae family species,
Thuja occidentalis L. and
Platycladus orientalis L. Franco, which are commonly found
[...] Read more.
The adaptive potential of plants in urban environments, responding to factors like air pollution, electromagnetic radiation, and specific microclimates, remains insufficiently understood. Our study focused on two evergreen
Cupressaceae family species,
Thuja occidentalis L. and
Platycladus orientalis L. Franco, which are commonly found in Kazakhstan’s urban landscapes. Conducted in Almaty, one of Kazakhstan’s most polluted cities, our comparative analysis examined the anatomical features, photosynthetic activity, and secondary metabolite composition of these conifers. Both species exhibited xeromorphic traits, such as submerged stomata, resin passages, and a prominent leaf cuticle.
T. occidentalis displayed higher photosynthetic activity values (quantum yield of photosystem II (YII), electron transport rate (ETR), and quantum yield of non-photochemical quenching (Y(NPQ))) than
P. orientalis, while
P. orientalis exhibited a higher quantum yield of non-regulated energy dissipation in PSII (Y(NO)) values. Chemical analysis revealed 31 components in
T. occidentalis and 33 in
P. orientalis, with
T. occidentalis containing three times more thujone (16.42% and 5.18%, respectively) and a higher monosaccharide content (17.33% and 6.98%, respectively).
T. occidentalis also contained 14.53% steroids, whereas
P. orientalis showed no steroid presence. The cytotoxic activity of essential oils was determined by the survival of
Artemia salina aquatic crustaceans, whereas tested essential oils from both species exhibited acute lethal toxicity to
A. salina aquatic crustaceans across all tested concentrations. The connection between physiological traits, adaptation strategies, and cytotoxic effects offers a comprehensive view of the ecological and pharmacological importance of these two observed conifer species, highlighting their diverse roles in urban environments, as well as their potential medical uses.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
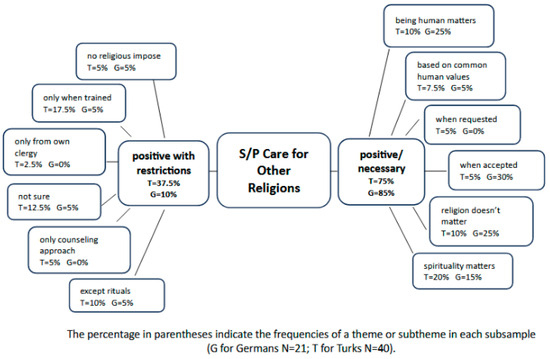
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT