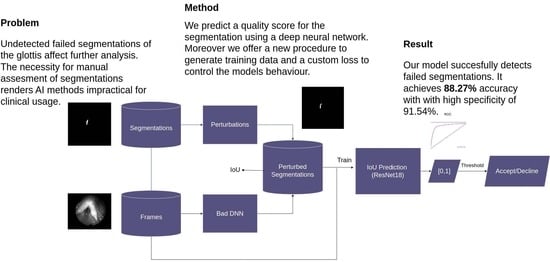
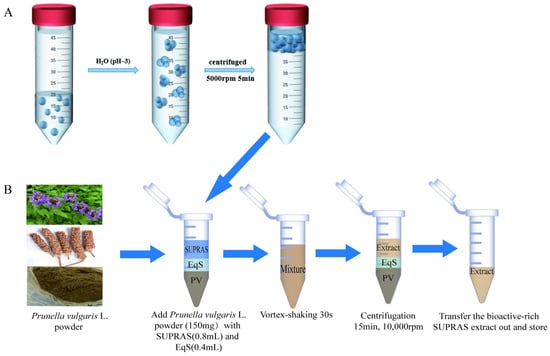
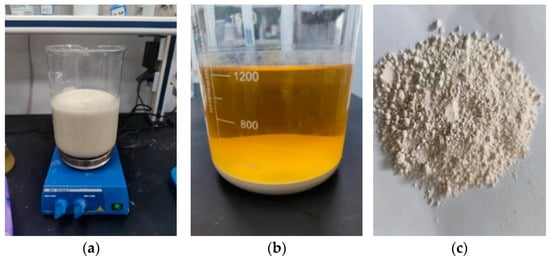
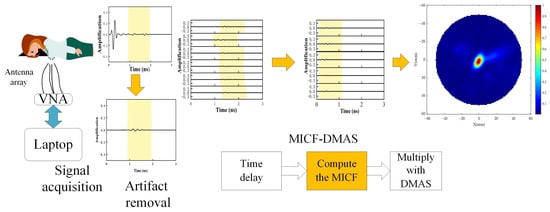
Open AccessArticle
Salvage Ablative Radiotherapy for Isolated Local Recurrence of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma following Definitive Surgery
by
Edward Christopher Dee, Victor C. Ng, Eileen M. O’Reilly, Alice C. Wei, Stephanie M. Lobaugh, Anna M. Varghese, Melissa Zinovoy, Paul B. Romesser, Abraham J. Wu, Carla Hajj, John J. Cuaron, Danny N. Khalil, Wungki Park, Kenneth H. Yu, Zhigang Zhang, Jeffrey A. Drebin, William R. Jarnagin, Christopher H. Crane and Marsha Reyngold
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(9), 2631; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13092631 (registering DOI) - 30 Apr 2024
Abstract
Introduction: The rate of isolated locoregional recurrence after surgery for pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) approaches 25%. Ablative radiation therapy (A-RT) has improved outcomes for locally advanced disease in the primary setting. We sought to evaluate the outcomes of salvage A-RT for isolated locoregional recurrence
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The rate of isolated locoregional recurrence after surgery for pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) approaches 25%. Ablative radiation therapy (A-RT) has improved outcomes for locally advanced disease in the primary setting. We sought to evaluate the outcomes of salvage A-RT for isolated locoregional recurrence and examine the relationship between subsequent patterns of failure, radiation dose, and treatment volume.
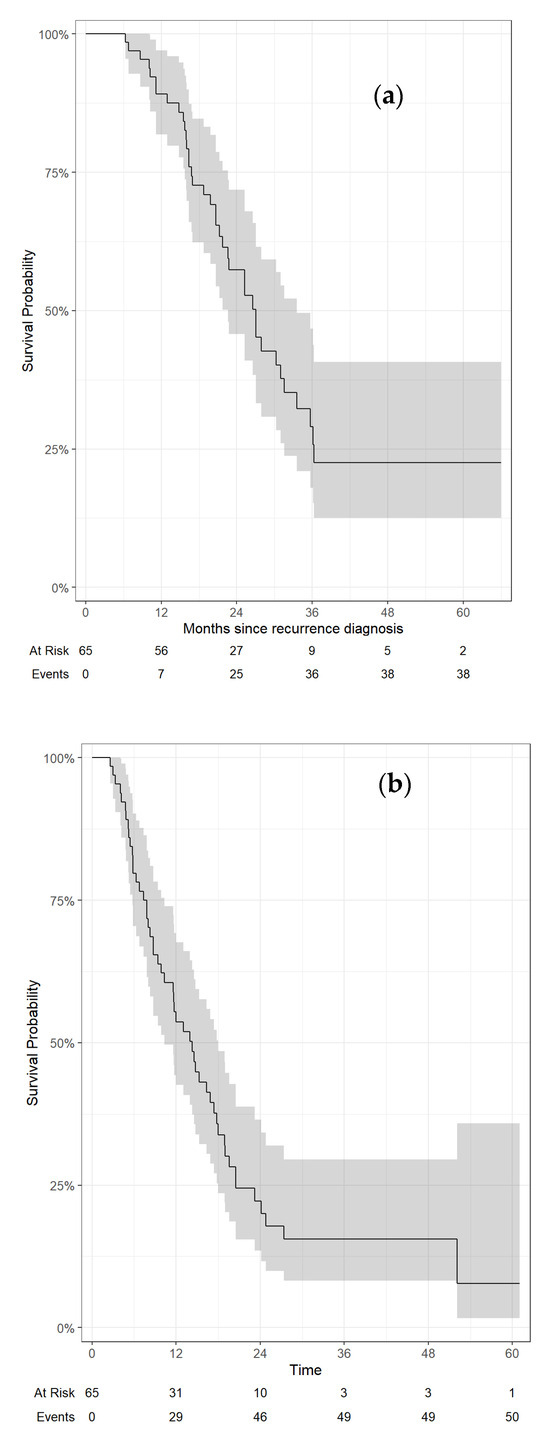
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of all consecutive participants who underwent A-RT for an isolated locoregional recurrence of PDAC after prior surgery at our institution between 2016 and 2021. Treatment consisted of ablative dose (BED10 98–100 Gy) to the gross disease with an additional prophylactic low dose (BED10 < 50 Gy), with the elective volume covering a 1.5 cm isotropic expansion around the gross disease and the circumference of the involved vessels. Local and locoregional failure (LF and LRF, respectively) estimated by the cumulative incidence function with competing risks, distant metastasis-free and overall survival (DMFS and OS, respectively) estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method, and toxicities scored by CTCAE v5.0 are reported. Location of recurrence was mapped to the dose region on the initial radiation plan.
Results: Among 65 participants (of whom two had two A-RT courses), the median age was 67 (range 37–87) years, 36 (55%) were male, and 53 (82%) had undergone pancreaticoduodenectomy with a median disease-free interval to locoregional recurrence of 16 (range, 6–71) months. Twenty-seven participants (42%) received chemotherapy prior to A-RT. With a median follow-up of 35 months (95%CI, 26–56 months) from diagnosis of recurrence, 24-month OS and DMFS were 57% (95%CI, 46–72%) and 22% (95%CI, 14–37%), respectively, while 24-month cumulative incidence of in-field LF and total LRF were 28% (95%CI, 17–40%) and 36% (95%CI 24–48%), respectively. First failure after A-RT was distant in 35 patients (53.8%), locoregional in 12 patients (18.5%), and synchronous distant and locoregional in 10 patients (15.4%). Most locoregional failures occurred in elective low-dose volumes. Acute and chronic grade 3–4 toxicities were noted in 1 (1.5%) and 5 patients (7.5%), respectively.
Conclusions: Salvage A-RT achieves favorable OS and local control outcomes in participants with an isolated locoregional recurrence of PDAC after surgical resection. Consideration should be given to extending high-dose fields to include adjacent segments of at-risk vessels beyond direct contact with the gross disease.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT