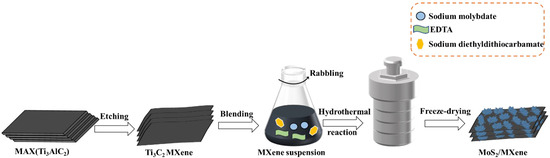
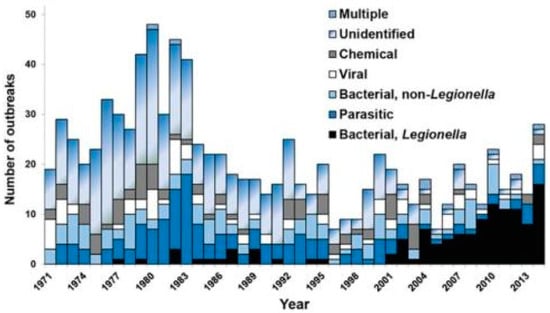
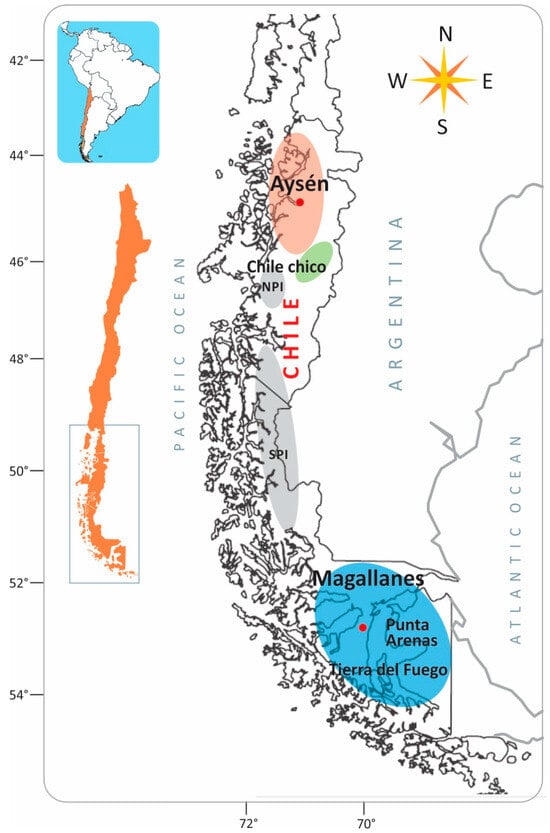
In contrast to “frank” pathogens, like
Salmonella entrocolitica,
Shigella dysenteriae, and
Vibrio cholerae, that always have a probability of disease, “opportunistic” pathogens are organisms that cause an infectious disease in a host with a weakened immune system and rarely in a healthy host. Historically, drinking water treatment has focused on control of frank pathogens, particularly those from human or animal sources (like
Giardia lamblia,
Cryptosporidium parvum, or
Hepatitis A virus), but in recent years outbreaks from drinking water have increasingly been due to opportunistic pathogens. Characteristics of opportunistic pathogens that make them problematic for water treatment include: (1) they are normally present in aquatic environments, (2) they grow in biofilms that protect the bacteria from disinfectants, and (3) under appropriate conditions in drinking water systems (e.g., warm water, stagnation, low disinfectant levels, etc.), these bacteria can amplify to levels that can pose a public health risk. The three most common opportunistic pathogens in drinking water systems are
Legionella pneumophila,
Mycobacterium avium, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This report focuses on these organisms to provide information on their public health risk, occurrence in drinking water systems, susceptibility to various disinfectants, and other operational practices (like flushing and cleaning of pipes and storage tanks). In addition, information is provided on a group of nine other opportunistic pathogens that are less commonly found in drinking water systems, including
Aeromonas hydrophila,
Klebsiella pneumoniae,
Serratia marcescens,
Burkholderia pseudomallei,
Acinetobacter baumannii,
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia,
Arcobacter butzleri, and several free-living amoebae including
Naegleria fowleri and species of
Acanthamoeba. The public health risk for these microbes in drinking water is still unclear, but in most cases, efforts to manage
Legionella, mycobacteria, and
Pseudomonas risks will also be effective for these other opportunistic pathogens. The approach to managing opportunistic pathogens in drinking water supplies focuses on controlling the growth of these organisms. Many of these microbes are normal inhabitants in biofilms in water, so the attention is less on eliminating these organisms from entering the system and more on managing their occurrence and concentrations in the pipe network. With anticipated warming trends associated with climate change, the factors that drive the growth of opportunistic pathogens in drinking water systems will likely increase. It is important, therefore, to evaluate treatment barriers and management activities for control of opportunistic pathogen risks. Controls for primary treatment, particularly for turbidity management and disinfection, should be reviewed to ensure adequacy for opportunistic pathogen control. However, the major focus for the utility’s opportunistic pathogen risk reduction plan is the management of biological activity and biofilms in the distribution system. Factors that influence the growth of microbes (primarily in biofilms) in the distribution system include, temperature, disinfectant type and concentration, nutrient levels (measured as AOC or BDOC), stagnation, flushing of pipes and cleaning of storage tank sediments, and corrosion control. Pressure management and distribution system integrity are also important to the microbial quality of water but are related more to the intrusion of contaminants into the distribution system rather than directly related to microbial growth. Summarizing the identified risk from drinking water, the availability and quality of disinfection data for treatment, and guidelines or standards for control showed that adequate information is best available for management of
L. pneumophila. For
L. pneumophila, the risk for this organism has been clearly established from drinking water, cases have increased worldwide, and it is one of the most identified causes of drinking water outbreaks. Water management best practices (e.g., maintenance of a disinfectant residual throughout the distribution system, flushing and cleaning of sediments in pipelines and storage tanks, among others) have been shown to be effective for control of
L. pneumophila in water supplies. In addition, there are well documented management guidelines available for the control of the organism in drinking water distribution systems. By comparison, management of risks for
Mycobacteria from water are less clear than for
L. pneumophila. Treatment of
M. avium is difficult due to its resistance to disinfection, the tendency to form clumps, and attachment to surfaces in biofilms. Additionally, there are no guidelines for management of
M. avium in drinking water, and one risk assessment study suggested a low risk of infection. The role of tap water in the transmission of the other opportunistic pathogens is less clear and, in many cases, actions to manage
L. pneumophila (e.g., maintenance of a disinfectant residual, flushing, cleaning of storage tanks, etc.) will also be beneficial in helping to manage these organisms as well.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT