Abstract
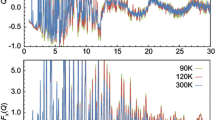
Neutron total scattering measurements from powdered samples of cristobalite have been used to determine the local structure in both the tetragonal and cubic phases. The results for the cubic phase show directly that the Si–O bonds are tilted at an angle of around 17° to the unit cell [111] direction. It is striking that the structure of β-cristobalite over the range 5–10 Å is closer to that of silica glass than α-cristobalite, which suggests that the local structure of β-cristobalite is not likely to consist of domains with the structure of α-cristobalite. The measurements show a small thermal expansion of the Si–O bonds over the temperature range 570–950 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 23, 1996 /Revised, accepted January 12, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dove, M., Keen, D., Hannon, A. et al. Direct measurement of the Si–O bond length and orientational disorder in the high-temperature phase of cristobalite. Phys Chem Min 24, 311–317 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050043
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050043