Abstract
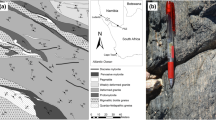
In the present study we investigate the microstructural development in mullite, quartz and garnet in an anatectic migmatite hosted within a Grenvillian-age shear zone in the Aravalli–Delhi Fold Belt. The migmatite exhibits three main deformation structures and fabrics (S1, S2, S3). Elongated garnet porphyroblasts are aligned parallel to the metatexite S2 layers and contain crenulation hinges defined by biotite–sillimanite–mullite–quartz (with S1 axial planar foliation). Microstructural evidence and phase equilibrium relations establish the garnet as a peritectic phase of incongruent melting by breakdown of biotite, sillimanite ± mullite and quartz at peak P–T of ~ 8 kbar, 730 °C along a tight-loop, clockwise P–T path. Monazite dating establishes that the partial melting occurred between ~ 1000 and 870 Ma. The absence of subgrains and systematic crystal lattice distortions in these garnets despite their elongation suggests growth pseudomorphing pre-existing 3-D networks of S1 biotite aggregates rather than high-temperature crystal plastic deformation which is noted in the S1 quartz grains that exhibit strong crystallographic preferred orientation (CPO), undulatory extinction and subgrains. Mode-I fractures in these garnet porphyroblasts induced by high melt pressure during late stage of partial melt crystallization are filled by retrograde biotite–sillimanite. Weak CPO and non-systematic crystal lattice distortions in the coarse quartz grains within the S2 leucosome domains indicate these crystallized during melt solidification without later crystal plastic deformation overprint. In the later stages of deformation (D3), strain was mostly accommodated in the mullite–biotite–sillimanite-rich restite domains forming S3 which warps around garnet and leucosome domains; consequently, fine-grained S3 quartz does not exhibit strong CPOs.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S, Urai JL (2012) Discrete element modelling of boudinage: Insights on rock rheology, matrix flow, and evolution of geometry. J Geophys Res 117:B01407
Arzi AA (1978) Critical phenomena in the rheology of partially molten rocks. Tectonophysics 74:173–184
Ashworth JR (1985) Migmatites. Blackie, Glasgow
Auzanneau E, Schmidt MW, Vielzeuf D, Connolly JAD (2010) Titanium in phengite: a geobarometer for high temperature eclogites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 159:1–24
Beaumont C, Nguyen MH, Jamieson RA, Ellis S (2006) Crustal flow modes in large hot orogens, in channel flow, ductile extrusion and exhumation in continental collision zones, vol 268. Law RD, Searle MP, Godin L (ed) Geological Society of London Special Publication, pp 91–145
Behrmann J, Mainprice D (1987) Deformation mechanisms in a high-temperature quartz feldspar mylonite evidence for superplastic flow in the lower continental-crust. Tectonophysics 140:297–305
Benisek A, Kroll H, Cemic L (2004) New developments in two-feldspar thermometry. Am Mineral 89:1496–1504
Berger A, Kalt A (1999) Structures and melt fractions as indicators of rheology in cordierite-bearing migmatites of the Bayerische Wald (Variscan Belt, Germany). J Petrol 40:1699–1719
Bestmann M, Prior DJ (2003) Intragranular dynamic recrystallization in naturally deformed calcite marble: diffusion accommodated grain boundary sliding as a result of subgrain rotation recrystallization. J Struct Geol 25:1597–1613
Bhattacharya A, Mohanty L, Maji A, Sen SK, Raith M (1992) Non-ideal mixing in the phlogopite-annite boundary: constraints from experimental data on Mg–Fe partitioning and a reformulation of the biotite-garnet geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petr 111:87–93
Bhowmik SK, Bernhardt HJ, Dasgupta S (2010) Grenvillian age high-pressure upper amphibolite–granulite metamorphism in the Aravalli–Delhi Mobile Belt, North-western India: new evidence from monazite chemical age and its implication. Precambrian Res 178:168–184
Brodie KH, Rutter EH (2000) Deformation mechanisms and rheology: why marble is weaker than quartzite. J Geol Soc London 157:1093–1096
Brown M (2001) Orogeny, migmatites and leucogranites: a review. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Earth Planet Sci) 110:313–336
Brown M (2002) Retrograde processes in migmatites and granulites revisited. J Metamorph Geol 20:25–40
Buick IS, Allen C, Pandit M, Rubatto D, Hermann J (2006) The Proterozoic magmatic and metamorphic history of the Banded Gneiss Complex, central Rajasthan, India: LA-ICP-MS U–Pb zircon constraints. Precambrian Res 151:119–142
Buick IS, Clark C, Rubatto D, Hermann J, Pandit MK, Hand M (2010) Constraints on the Proterozoic evolution of the Aravalli–Delhi Orogenic belt (NW India) from monazite geochronology and mineral trace element geochemistry. Lithos 120:511–528
Blumenfeld P, Mainprice D, Bouchez JL (1986) C-slip in quartz from subsolidus deformed granite. Tectonophysics 127:97–115
Cavalcante GCG, Egydio-Silva M, Vauchez A, Camps P, Oliveira E (2013) Strain distribution across a partially molten middle crust: Insights from the AMS mapping of the Carlos Chagas Anatexite, Araçuaí belt (East Brazil). J Struct Geol 55:79–100
Coggon R, Holland TJB (2002) Mixing properties of phengitic micas and revised garnet-phengite thermobarometers. J Metamorph Geol 20:683–696
Connolly JAD (2005) Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: a tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 236:524–541
Cyprych D, Piazolo S, Wilson CJ, Luzin V, Prior DJ (2016) Rheology, microstructure and crystallographic preferred orientation of matrix containing a dispersed second phase: Insight from experimentally deformed ice. Earth Planet Sci Lett 449:272–281
Dasgupta S, Sengupta P, Guha D, Fukuoka M (1991) A refined garnet–biotite Fe–Mg exchange geothermometer and its application in amphibolites and granulites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 109:130–137
Deb M, Thorpe RI (2004) Geochronological constraints in the Precambrian geology of Rajasthan and their metallogenic implications. In: Deb M, Goodfellow WD (eds) Sediment-hosted Lead –Zinc Sulphide Deposits; Attributes and Models of Some Major Deposits in India, Australia and Canada. Narosa, New Delhi, pp 246 –263
Deb M, Thorpe RI, Cumming GL, Wagner PA (1989) Age, source and Strati-graphic implications of Pb isotope data for conformable, sediment-hosted, base-metal deposits in the Proterozoic Aravalli–Delhi Orogenic Belt, Northwestern India. Precambrian Res 43:1–22
Engi M, Wersin P (1987) Derivation and application of a solution model for calcic garnet. Schweizerische Mineralogische und Petrographische Mitteilunger 67:53–73
Ferry JM, Spear FS (1978) Experimental calibration of the partitioning of Fe and Mg between biotite and garnet. Contrib Mineral Petrol 66:113–117
Guernina S, Sawyer EW (2003) Large-scale melt-depletion in granulite terranes: an example from the Archean Ashuanipi Subprovince of Quebec. J Metamorph Geol 21:181–201
Gupta SN, Arora YK, Mathur RK, Iqballuddin BP, Sahai TN, Sharma SB (1980) Lithostratigraphic Map of the Aravalli Region. Scale 1:100,000. Geological Survey of India, Calcutta
Gupta P, Mathur YK, Iqbaluddin BP, Sahai TN, Sharma SB (1997) Lithostratigraphic map of the Aravalli region, southern Rajasthan and northeastern Gujarat. Geological Survey of India Publications, Jaipur
Hasalová P, Schulmann K, Lexa O, Štípská P, Hrouda F, Ulrich S, Haloda J, Týcová P (2008) Origin of migmatites by deformation-enhanced melt infiltration of orthogneiss: a new model based on quantitative microstructural analysis. J Metamorph Geol 26:29–53
Hasalová P, Weinberg RF, Macre C (2011) Microstructural evidence for magma confluence and reusage of magma pathways: implications for magma hybridization, Karakoram Shear Zone in NW India. J Metamorph Geol 29:875–900
Hazarika P, Upadhyay D, Mishra B (2013) Contrasting geochronological evolution of the Rajpura–Dariba and Rampura–Agucha metamorphosed Zn–Pb deposit, Aravalli–Delhi Belt, India. J Asian Earth Sci 73:429–439
Heron AM (1953) Geology of central Rajasthan. Mem Geol Surv India 79:339
Holdaway MJ (2000) Application of new experimental and garnet Margules data to the garnet–biotite geothermometer. Am Mineral 85:881–892
Holland TJB, Powell R (1998) An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J Metamorph Geol 16:309–343
Holland T, Powell R (2001) Calculation of phase relations involving haplogranitic melts using an internally consistent thermodynamic dataset. J Petrol 42:673–683
Ji SC, Martignole J (1994) Ductility of garnet as an indicator of extremely high-temperature deformation. J Struct Geol 16:985–996
Ji SC, Saruwatari K, Mainprice D, Wirth R, Xu Z, Xia B (2003) Microstructures, petrofabrics and seismic properties of ultra high-pressure eclogites from Sulu region, China: implications for rheology of subducted continental crust and origin of mantle reflections. Tectonophysics 370:49–76
Kelsey D, White R, Powell R (2005) Calculated phase equilibria in K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O for silica-undersaturated sapphirine-bearing mineral assemblages. J Metamorph Geol 23:217–239
Kilian R, Heilbronner R, Stünitz H (2011) Quartz grain size reduction in a granitoid rock and the transition from dislocation to diffusion creep. J Struct Geol 33:1265–1284
Kleinschrodt R, Duyster JP (2002) HT-deformation of garnet: an EBSD study on granulites from Sri Lanka, India and the Ivrea Zone. J Struct Geol 24:1829–1844
Kleinschrodt R, McGrew A (2000) Garnet plasticity in the lower continental crust: implications for deformation mechanisms based on microstructures and SEM-electron channeling pattern analysis. J Struct Geol 22:795–809
Komoróczi A, Abe S, Urai JL (2013) Meshless numerical modeling of brittle–viscous deformation: first results on boudinage and hydrofracturing using a coupling of discrete element method (DEM) and smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Comput Geosci 17:373–390
Kretz R (1983) Symbols for rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 68:277–279
Law RD (2014) Deformation thermometry based on quartz c-axis fabrics and recrystallization microstructures: a review. J Struct Geol 66:129–161
Ludwig KR (2001) User manual for Isoplot/Ex ver. 2.49: A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronol Centre Spec Publ 1a:1–56
Mainprice D, Bascou J, Cordier P, Tommasi A (2004) Crystal preferred orientations of garnet: comparison between numerical simulations and electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) measurements in naturally deformed eclogites. J Struct Geol 26:2089–2102
Menegon L, Nasipuri P, Stünitz H, Behrens H, Ravna E (2011) Dry and strong quartz during deformation of the lower crust in the presence of melt. J Geophys Res 116:B10410
Nasipuri P, Bhattacharya A, Das S (2009) Metamorphic reactions in dry and aluminous granulites: a Perple_X P–T pseudosection analysis of the influence of effective reaction volume. Contrib Mineral Petrol 157:301–311
Ojha MK, Mishra B, Hazarika P, Jeyagopal AV, Yadav GS (2016) EPMA monazite geochronology of the basement and supracrustal rocks within the Pur-Banera basin, Rajasthan: evidence of Columbia breakup in Northwestern India. J Asian Earth Sci 117:284–303
Passchier CW, Trouw RAJ (2005) Microtectonics. Springer, Berlin, p. 366
Paterson MS (1987) Problems in the extrapolation of laboratory rheological data. Tectonophysics 133:33–43
Petrìk I, Konečný P (2009) Metasomatic replacement of inherited metamorphic monazite in a biotite-garnet granite from the NízkeTatry Mountains, Western Carpathians, Slovakia: chemical dating and evidence for disequilibrium melting. Am Mineral 94:957–974
Piazolo S, Jaconelli P (2013) Sillimanite deformation mechanisms within a Grt–Sil–Bt gneiss: effect of pre-deformation grain orientations and characteristics on mechanism, slip-system activation and rheology. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 394:189–213
Piazolo S, Bestmann M, Spiers C, Prior DJ (2006) Temperature dependent grain boundary migration mechanisms: insights from insitu experiments. Tectonophysics 427:55–71
Prior DJ, Boyle AP, Brenker F, Cheadle MC, Day A, Lopez G, Peruzzo L, Potts GJ, Reddy S, Spiess R, Timms NE, Trimby P, Wheeler J, Zetterstrom L (1999) The application of electron backscatter diffraction and orientation contrast imaging in the SEM to textural problems in rocks. Am Mineral 84:1741–1759
Prior DJ, Wheeler J, Brenker FE, Harte B, Matthews M (2000) Crystal plasticity of natural garnet: new microstructural evidence. Geology 28:1003–1006
Prior DJ, Wheeler J, Peruzzo L, Spiess R, Storey C (2002) Some garnet microstructures: an illustration of the potential of orientation maps and misorientation analysis in microstructural studies. J Struct Geol 24:999–1011
Raja Rao CS (1976) Precambrian sequences of Rajasthan. Misc Publ Geol Surv India 23:497–516
Rimsa A, Whitehouse MJ, Piazolo S (2007) Brittle fracturing and fracture healing of zircon: integrated cathodoluminescence, U–Th–Pb and REE study. Am Mineral 92:1213–1224
Roy AB (2000) Structural investigation of the Rampura- Agucha Mine and Neighbourhood. Hindustan Zinc Ltd. Project Report, p 30 (unpublished)
Roy AB, Jakhar SR (2002) Geology of Rajasthan (Northwest India) Precambrian to recent. Scientific Publishers, Jodhpur
Rutter E, Neumann DHK (1995) Experimental deformation of partially molten Westerly granite under fluid absent conditions, with implications for the extraction of granitic magmas. J Geophys Res 100:15697–15715
Saha L, Bhowmik SK, Fukuoka M, Dasgupta S (2008) Contrasting episodes of regional granulite facies metamorphism in enclaves and host gneisses from the Aravalli-Delhi Mobile Belt, NW India. J Petrol 49:107–128
Sawyer EW (2001) Melt segregation in the continental crust: distribution and movement of melt in anatectic rocks. J Metamorph Geol 19:291–309
Sawyer EW (2008) Atlas of migmatites, vol 9. Mineralogical Associations of Canada Special Publication, p 387
Schmid S (1982) Microfabric studies as indicators of deformation mechanisms and microfabric studies as indicators of deformation mechanisms and flow laws operative in mountain building. In: Hsu K (ed) Mountain building processes. Academic Press, London, pp 95–110
Smith JR, Piazolo S, Daczko NR, Evans L (2015) The effect of pre-tectonic reaction and annealing extent on behaviour during subsequent deformation: insights from paired shear zones in the lower crust of Fiordland, New Zealand. J Metamorph Geol 33:557–577
Song WJ, Ree JH (2007) Effect of mica on the grain size of dynamically recrystallized quartz in a quartz-muscovite mylonite. J Struct Geol 29:1872–1881
Spear FS (1993) Metamorphic phase equilibria and pressure-temperature-time paths. Mineralogical Society America Monograph, Book Crafters, Chelsea
Storey CD, Prior DJ (2005) Plastic deformation and recrystallization of garnet: a mechanism to facilitate diffusion creep. J Petrol 46:2593–2613
Stüwe K (1997) Effective bulk composition change due to cooling: a model predicting complexities in retrograde reaction textures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 129:43–52
Stüwe K (2007) Geodynamics of the lithosphere: quantitative description of geological problems, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, p 493
Svahnberg H, Piazolo S (2010) The initiation of strain localisation in plagioclase-rich rocks: insights from detailed microstructural analyses. J Struct Geol 32:1404–1416
Takeda Y–T, Obata M (2003) Some comments on the rheologically critical melt percentage. J Struct Geol 25:813–818
Tomascak PB, Krogstad EJ, Walker RJ (1998) Sm-Nd isotope systematics and the derivation of granitic pegmatites in southwestern Maines. Can Mineral 36:327–337
Tretiakova IG, Belousova EA, Malkovets VG, Griffin WL, Piazolo S, Pearson NJ, O’Reilly SW, Nishido H (2016) Recurrent magmatic activity on a lithosphere-scale structure: crystallization and deformation in kimberlitic zircons. Gondwana Res 42:126–132
Venables JA, Harland CJ (1973) Electron back-scattering patterns–a new technique for obtaining crystallographic information in the SEM. Philos Mag 27:1193–1200
Vigneresse JL, Barbey P, Cuney M (1996) Rheological transitions during partial melting and crystallization with application to felsic magma segregation and transfer. J Petrol 37:1579–1600
Webb G, Powell R, McLaren S (2015) Phase equilibria constraints on the melt fertility of crustal rocks: the effect of subsolidus water loss. J Metamorph Geol 33:147–165
White RW, Powell R (2002) Melt loss and the preservation of granulite facies mineral assemblages. J Metamorph Geol 20:621,632
White RW, Powell R (2010) Retrograde melt-residue interaction and the formation of near-anhydrous leucosomes in migmatites. J Metamorph Geol 28:579–597
White RW, Powell R, Holland TJB (2001) Calculation of partial melting equilibria in the system Na2O–CaO–K2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O (NCKFMASH). J Metamorph Geol 19:139–153
White RW, Powell R, Holland TJB (2007) Progress relating to calculations of partial melting equilibria for metapelites. J Metamorph Geol 25:511–527
Whitney D, Teyssier C, Vanderhaeghe O (2004) Gneiss domes and crustal flow. Geol Soc Am Spec Papers 380:15–330
Acknowledgements
LS acknowledges Faculty Initiation Grant, IIT Roorkee for conducting field work and for the analytical costs. LS also acknowledges Dr. M. Satyanarayanan, NGRI, Hyderabad, India, for XRF analyses and Ms. Jyothirmayee Palaparthi for compiling the figures. SP acknowledges the Australian Research Council through her Future Fellowship (FT1101100070) for financial support. The authors thank one anonymous reviewer and Kåre Kullerud for their constructive reviews and Prof. Dullo for helpful editorship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Fig. 11.
a, b T–MH2O pseudosections at 6 and 8 kbar, respectively, showing stability fields of different minerals under water-deficient and water-fluxed conditions. High modal percentages of melt are observed in garnet–sillimanite–bioite–feldspar–quartz–melt-bearing fields. Bulk compositions for C0 and C1 (in molar proportions) are, respectively, SiO2:Al2O3:FeO:MgO:CaO:Na2O:K2O:H2O = 62.68:12.56:6.77:10.99:1.49:1.49: 3.77:0.26 and 41.18:8.25:4.45:7.22:0.98:0.98:2.47:34.46
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, A., Piazolo, S., Saha, L. et al. Deformation behavior of migmatites: insights from microstructural analysis of a garnet–sillimanite–mullite–quartz–feldspar-bearing anatectic migmatite at Rampura–Agucha, Aravalli–Delhi Fold Belt, NW India. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 107, 2265–2292 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-018-1598-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-018-1598-6