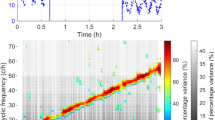
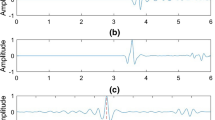
Abstract
Correlations of seismic noise are commonly used to monitor temporal variations of relative seismic velocity in period ranges from 1 s up to 100 s. Of particular interest is the detection of small changes in the order of 0.01–0.1 % in propagation speeds. Measuring such small differences can, however, be significantly biased by temporal variations in the properties of the noise sources within the corresponding frequency band. Using synthetic data, we show that apparent relative velocity variations might appear only due to changes in the amplitude and frequency content caused by source variations. Removing such unwanted effects by applying narrow bandpass filters in the preprocessing restricts the high-resolution analysis of any signal due to Gabor’s uncertainty limit, i.e., the correlation function suffers a limited resolution to time delay estimates for small correlation times, low-frequency ranges, and in narrow frequency bands. Better understanding of spatiotemporal noise source properties and the theoretical limitations of time–frequency analysis is critical for accurate and reliable passive monitoring.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baig AM, Campillo M, Brenguier F (2009) Denoising seismic noise cross correlations. J Geophys Res 114:2156–2202. doi: 10.1029/2008JB006085
Bensen GD, Ritzwoller MH, Barmin MP, Levshin AL, Lin F, Moschetti MP, Shapiro NM, Yang Y (2007) Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophys J Int 169:1239–1260
Bindi D, Marzorati S, Parolai S, Strollo A, Jäkel KH (2009) Empirical spectral ratios estimated in two deep sedimentary basins using microseisms recorded by short-period seismometers. Geophys J Int 176:175–184
Brenguier F, Shapiro NM, Campillo M, Ferrazzini V, Duputel Z, Coutant O, Nercessian A (2008a) Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise. Nat Geosci 1:126–130
Brenguier F, Campillo M, Hadziioannou C, Shapiro NM, Nadeau RM, Larose E (2008b) Postseismic relaxation along the San Andreas fault at Parkfield from continuous seismological observations. Science 321:1478–1481
Bromirski PD, Duennebier FK, Stephen RA (2005) Mid‐ocean microseisms. Geochem Geophys Geosys 6:Q04009. doi: 10.1029/2004GC000768
Campillo M, Paul A (2003) Long-range correlations in the diffuse seismic coda. Science 299:547–549
Carter GC (1987) Coherence and time delay estimation. Proc IEEE 75:236–255
Chen JH, Froment B, Liu QY, Campillo M (2010) Distribution of seismic wave speed changes associated with the 12 May 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake. Geophys Res Lett 37:L18302. doi:10.1029/2010GL044582
Clarke D, Zaccarelli L, Shapiro NM, Brenguier F (2011) Assessment of resolution and accuracy of the Moving Window Cross Spectral technique for monitoring crustal temporal variations using ambient seismic noise. Geophys J Int 186:867–882
Cohen L (1989) Time–frequency distributions—a review. Proc IEEE 77:941–981
Cooley JW, Tukey JW (1965) An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series. Math Comput 19:297–301
Cupillard P, Stehly L, Romanowicz B (2011) The one-bit noise correlation: a theory based on the concepts of coherent and incoherent noise. Geophys J Int 184:1397–1414
Derode A, Tourin A, Fink M (1999) Ultrasonic pulse compression with one-bit time reversal through multiple scattering. J Appl Phys 85:6343–6352
Derode A, Larose E, Campillo M, Fink M (2003) How to estimate the Green’s function of a heterogeneous medium between two passive sensors? Application to acoustic waves. Appl Phys Lett 83:3054–3056
Draganov D, Campman X, Thorbecke J, Verdel A, Wapenaar K (2009) Reflection images from ambient seismic noise. Geophysics 74:A63–A67
Duputel Z, Ferrazzini V, Brenguier F, Shapiro N, Campillo M, Nercessian A (2009) Real time monitoring of relative velocity changes using ambient seismic noise at the Piton de la Fournaise volcano (La Réunion) from January 2006 to June 2007. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 184:164–173
Ekström G, Abers GA, Webb SC (2009) Determination of surface‐wave phase velocities across USArray from noise and Aki’s spectral formulation. Geophys Res Lett 36:L18301. doi: 10.1029/2009GL039131
Evans JR, Followill F, Hutt CR, Kromer RP, Nigbor RL, Ringler AT, Steim JM, Wielandt E (2010) Method for calculating self-noise spectra and operating ranges for seismographic inertial sensors and recorders. Seismol Res Lett 81:640–646
Fichtner A (2014) Source and processing effects on noise correlations. Geophys J Int 197:1527–15331
Froment B, Campillo M, Roux P, Gouédard P, Verdel A, Weaver RL (2010) Estimation of the effect of nonisotropically distributed energy on the apparent arrival time in correlations. Geophysics 75:85–93
Froment B, Campillo M, Chen JH, Liu QY (2013) Deformation at depth associated with the 12 May 2008 MW 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake from seismic ambient noise monitoring. Geophys Res Lett 40:78–82
Gabor D (1946) Theory of communication. Part 1: the analysis of information. J Inst Electr Eng 93:429–441
Gouédard P, Roux P, Campillo M, Verdel A (2008) Convergence of the two-point correlation function toward the Green’s function in the context of a seismic-prospecting data set. Geophysics 73:47–53
Guillier B, Atakan K, Chatelain JL, Havskov J, Ohrnberger M, Cara F, Duval AM, Zacharopoulos S, Teves-Costa P, the SESAME Team (2008) Influence of instruments on the H/V spectral ratios of ambient vibrations. Bull Earthq Eng 6:3–31
Hadziioannou C, Larose E, Coutant O, Roux P, Campillo M (2009) Stability of monitoring weak changes in multiply scattering media with ambient noise correlation: laboratory experiments. J Acoust Soc Am 125:3688–3695
Hadziioannou C, Larose E, Baig A, Roux P, Campillo M (2011) Improving temporal resolution in ambient noise monitoring of seismic wave speed. J Geophys Res 116:B07304. doi:10.1029/2011JB008200
Hanasoge SM, Branicki MM (2013) Interpreting cross-correlations of one-bit filtered seismic noise. Geophys J Int 195:1811–1830
Herbers THC, Guza RT (1994) Wind-wave nonlinearity observed at the seafloor, part I: forced-wave energy. J Phys Oceanogr 21:1740–1761
Hillers G, Campillo M, Ma KF (2014a) Seismic velocity variations at TCDP are controlled by MJO driven precipitation pattern and high fluid discharge properties. Earth Planet Sci Lett 391:121–127
Hillers G, Retailleau L, Campillo M, Inbal A, Ampuero JP, Nishimura T (2014b) In-situ observations of velocity changes in response to tidal deformation from analysis of the high-frequency ambient field. J Geophys Res 120:210–225. doi:10.1002/2014JB011318
Hobiger M, Wegler U, Shiomi K, Nakahara H (2012) Coseismic and postseismic elastic wave velocity variations caused by the 2008 Iwate–Miyagi Nairiku earthquake, Japan. J Geophys Res 117:B09313. doi: 10.1029/2012JB009402
Hobiger M, Wegler U, Shiomi K, Nakahara H (2014) Single-station cross-correlation analysis of ambient seismic noise: application to stations in the surroundings of the 2008 Iwate–Miyagi Nairiku earthquake. Geophys J Int 198:90–109
Jenkins GM, Watts DG (1968) Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden-Day, San Francisco
Kibblewhite AC, Ewans KC (1985) Wave–wave interactions, microseisms, and infrasonic ambient noise in the ocean. J Acoust Soc Am 78:981–994
Larose E, Margerin L, Derode A, van Tiggelen B, Campillo M, Shapiro N, Paul A, Stehly L, Tanter M (2006) Correlation of random wave fields: an interdisciplinary review. Geophysics 71:SI11–SI21
Lau NC (1988) Variability of the observed midlatitude storm tracks in relation to low-frequency changes in the circulation pattern. J Atmos Sci 45:2718–2743
Liu Z, Huang J, Li J (2010) Comparison of four techniques for estimating temporal change of seismic velocity with passive image interferometry. Earthq Sci 23:511–518
Lobkis OI, Weaver RL (2003) Coda-wave interferometry in finite solids: recovery of p-to-s conversion rates in an elastodynamic billiard. Phys Rev Lett 90:254302
Maeda T, Obara K, Yukutake Y (2010) Seismic velocity decrease and recovery related to earthquake swarms in a geothermal area. Earth Planets Space 62:685
Marzorati S, Bindi D (2006) Ambient noise levels in north central Italy. Geochem Geophys Geosys 7:Q09010. doi: 10.1029/2006GC001256
McNamara DE, Buland RP (2004) Ambient noise levels in the continental United States. Bull Seismol Soc Am 94:1517–1527
Meier U, Shapiro NM, Brenguier F (2010) Detecting seasonal variations in seismic velocities within Los Angeles basin from correlations of ambient seismic noise. Geophys J Int 181:985–996
Mosser B, Appourchaux T (2009) On detecting the large separation in the autocorrelation of stellar oscillation times series. Astron Astrophys 508:877–887
Obermann A, Planès T, Larose E, Sens-Schönfelder C, Campillo M (2013) Depth sensitivity of seismic coda waves to velocity perturbations in an elastic heterogeneous medium. Geophys J Int 194:372–382
Ohmi S, Hirahara K, Wada H, Ito K (2008) Temporal variations of crustal structure in the source region of the 2007 Noto Hanto Earthquake, central Japan, with passive image interferometry. Earth Planets Space 60:1069
Parolai S, Cara F, Bindi D, Pacor F (2009) Empirical site-specific response-spectra correction factors for the Gubbio basin (central Italy). Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 29:546–552
Poupinet G, Ellsworth WL, Frechet J (1984) Monitoring velocity variations in the crust using earthquake doublets: an application to the Calaveras Fault. California J Geophys Res 89:5719–5731
Quazi A (1981) An overview on the time delay estimate in active and passive systems for target localization. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 29:527–533
Ratdomopurbo A, Poupinet G (1995) Monitoring a temporal change of seismic velocity in a volcano: application to the 1992 eruption of Mt. Merapi (Indonesia). Geophys Res Lett 22:775–778
Richter T, Sens-Schönfelder C, Kind R, Asch G (2014) Comprehensive observation and modeling of earthquake and temperature-related seismic velocity changes in Northern Chile with passive image interferometry. J Geophys Res 119:4747–4765
Rivet D, Campillo M, Shapiro NM, Cruz‐Atienza V, Radiguet M, Cotte N, Kostoglodov V (2011) Seismic evidence of nonlinear crustal deformation during a large slow slip event in Mexico. Geophys Res Lett 38:L08308. doi: 10.1029/2011GL047151
Roux P, Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Kuperman WA, Fehler MC (2005) P‐waves from cross‐correlation of seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 32:L19303. doi: 10.1029/2005GL023803
Roxburgh IW, Vorontsov SV (2006) The autocorrelation function of stellar p-mode measurements and its diagnostic properties. Mon Not R Astron Soc 369:1491–1496
Sabra KG, Gerstoft P, Roux P, Kuperman WA, Fehler MC (2005) Extracting time-domain Greens function estimates from ambient seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 32:L03310. doi: 10.1029/2004GL021862
Seats KJ, Lawrence JW, Prieto GA (2012) Improved ambient noise correlation functions using Welch’ s method. Geophys J Int 188:513–523
Sens‐Schönfelder C, Wegler U (2006) Passive image interferometry and seasonal variations of seismic velocities at Merapi Volcano, Indonesia. Geophys Res Lett 33:L21302. doi: 10.1029/2006GL027797
Shapiro NM, Campillo M, Stehly L, Ritzwoller MH (2005) High-resolution surface-wave tomography from ambient seismic noise. Science 307:1615–1618
Snieder R, Grêt A, Douma H, Scales J (2002) Coda wave interferometry for estimating nonlinear behavior in seismic velocity. Science 295:2253–2255
Stehly L, Campillo M, Shapiro NM (2006) A study of the seismic noise from its long‐range correlation properties. J Geophys Res 111:B10306. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004237
Stehly L, Cupillard P, Romanowicz B (2011) Towards improving ambient noise tomography using simultaneously curvelet denoising filters and SEM simulations of seismic ambient noise. Compt Rendus Geosci 343:591–599
Stephen RA, Spiess FN, Collins JA, Hildebrand JA, Orcutt JA, Peal KR, Vernon FL, Wooding FB (2003) The ocean seismic network pilot experiment. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 4(10):1092. doi:10.1029/2002GC000485
Stutzmann E, Roult G, Astiz L (2000) GEOSCOPE station noise levels. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90:690–701
Takagi R, Okada T, Nakahara H, Umino N, Hasegawa A (2012) Coseismic velocity change in and around the focal region of the 2008 Iwate–Miyagi Nairiku earthquake. J Geophys Res 117:6315. doi: 10.1029/2012JB009252
Tsai VC, Moschetti MP (2010) An explicit relationship between time-domain noise correlation and spatial autocorrelation (SPAC) results. Geophys J Int 182:454–460
Ueno T, Saito T, Shiomi K, Enescu B, Hirose H, Obara K (2012). Fractional seismic velocity change related to magma intrusions during earthquake swarms in the eastern Izu peninsula, central Japan. J Geophys Res 117:B12305. doi: 10.1029/2012JB009580
Ugalde A, Gaite B, Villaseñor A (2014) Temporal variations of seismic velocity at Paradox Valley, Colorado, using passive image interferometry. Bull Seismol Soc Am 104:1088–1099
Wang B, Zhu P, Chen Y, Niu F, Wang B (2008) Continuous subsurface velocity measurement with coda wave interferometry. J Geophys Res 113:B12313. doi: 10.1029/2007JB005023
Wapenaar K, Fokkema J (2006) Green’s function representations for seismic interferometry. Geophysics 71:SI33–SI46
Weaver RL, Lobkis OI (2005) Fluctuations in diffuse field–field correlations and the emergence of the Green’s function in open systems. J Acoust Soc Am 117:3432–3439
Weaver RL, Hadziioannou C, Larose E, Campillo M (2011) On the precision of noise correlation interferometry. Geophys J Int 185:1384–1392
Wegler U, Sens‐Schönfelder C (2007) Fault zone monitoring with passive image interferometry. Geophys J Int 168:1029–1033
Wegler U, Nakahara H, Sens‐Schönfelder C, Korn M, Shiomi K (2009) Sudden drop of seismic velocity after the 2004 Mw 6.6 mid‐Niigata earthquake, Japan, observed with passive image interferometry. J Geophys Res 114:B06305. doi: 10.1029/2008JB005869
Xu ZJ, Song X (2009) Temporal changes of surface wave velocity associated with major Sumatra earthquakes from ambient noise correlation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:14207–14212
Zaccarelli L, Shapiro NM, Faenza L, Soldati G, Michelini A (2011) Variations of crustal elastic properties during the 2009 L’Aquila earthquake inferred from cross‐correlations of ambient seismic noise. Geophys Res Lett 38:L24304. doi: 10.1029/2011GL049750
Zhan Z, Tsai VC, Clayton RW (2013) Spurious velocity changes caused by temporal variations in ambient noise frequency content. Geophys J Int 194:1574–1581
Acknowledgments
We thank Nori Nakata and two anonymous reviewers for their precious comments that significantly improved the manuscript. For the field experiment, the instruments were provided by the Geophysical Instrumental Pool Potsdam. K. Fleming kindly improved our English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilz, M., Parolai, S. On the use of the autocorrelation function: the constraint of using frequency band-limited signals for monitoring relative velocity changes. J Seismol 20, 921–934 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-016-9571-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-016-9571-y