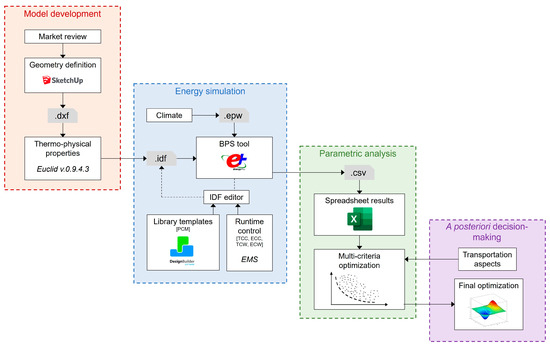
Our preliminary research proposed the cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1 (
CYP7A1) and hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex beta subunit (
HADHB) genes as candidates for association with milk-production traits in dairy cattle because of their differential expression across different lactation stages in the liver tissues of Chinese Holstein cows and their potential roles in lipid metabolism. Hence, we identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the
CYP7A1 and
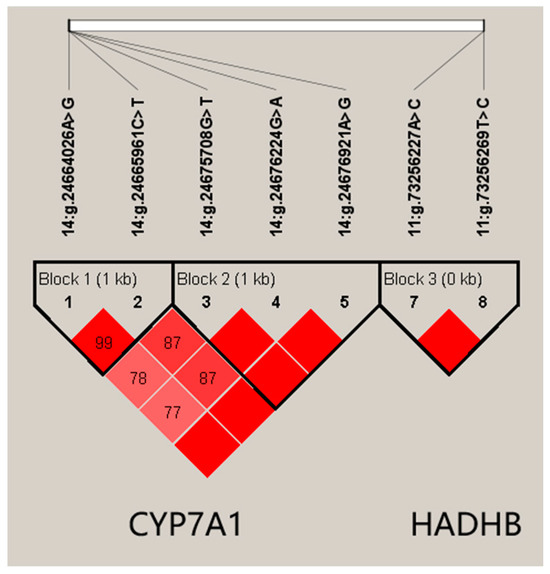
HADHB genes and validated their genetic effects on milk-production traits in a Chinese Holstein population with the goal of providing valuable genetic markers for genomic selection (GS) in dairy cattle, This study identified five SNPs, 14:g.24676921A>G, 14:g.24676224G>A, 14:g.24675708G>T, 14:g.24665961C>T, and 14:g.24664026A>G, in the
CYP7A1 gene and three SNPs, 11:g.73256269T>C, 11:g.73256227A>C, and 11:g.73242290C>T, in
HADHB. The single-SNP association analysis revealed significant associations (
p value ≤ 0.0461) between the eight SNPs of
CYP7A1 and
HADHB genes and 305-day milk, fat and protein yields. Additionally, using Haploview 4.2, we found that the five SNPs of
CYP7A1 formed two haplotype blocks and that the two SNPs of
HADHB formed one haplotype block; notably, all three haplotype blocks were also significantly associated with milk, fat and protein yields (
p value ≤ 0.0315). Further prediction of transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) based on Jaspar software (version 2023) showed that the 14:g.24676921A>G, 14:g.24675708G>T, 11:g.73256269T>C, and 11:g.73256227A>C SNPs could alter the 5′ terminal TFBS of the
CYP7A1 and
HADHB genes. The 14:g.24665961C>T SNP caused changes in the structural stability of the mRNA for the
CYP7A1 gene. These alterations have the potential to influence gene expression and, consequently, the phenotype associated with milk-production traits. In summary, we have confirmed the genetic effects of
CYP7A1 and
HADHB genes on milk-production traits in dairy cattle and identified potential functional mutations that we suggest could be used for GS of dairy cattle and in-depth mechanistic studies of animals.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT