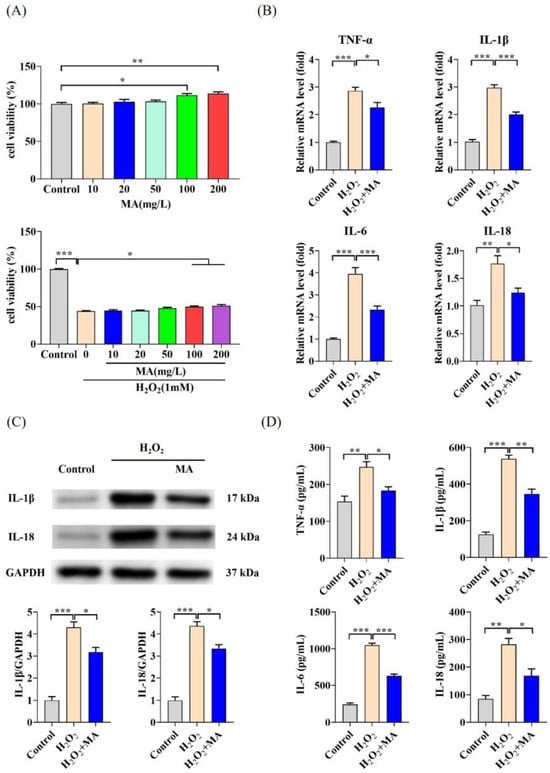
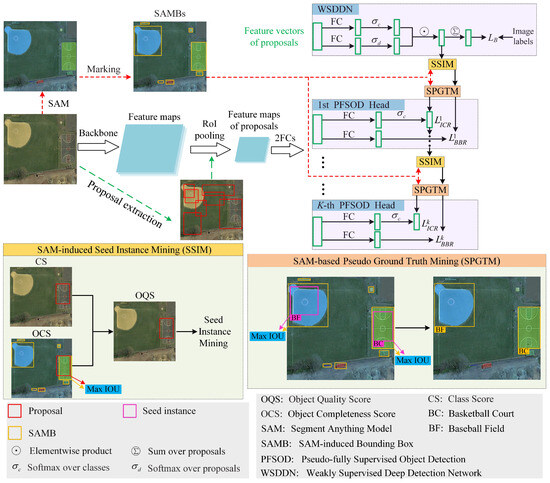
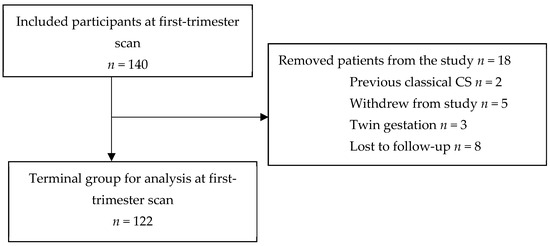
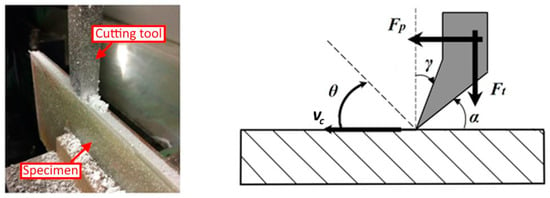
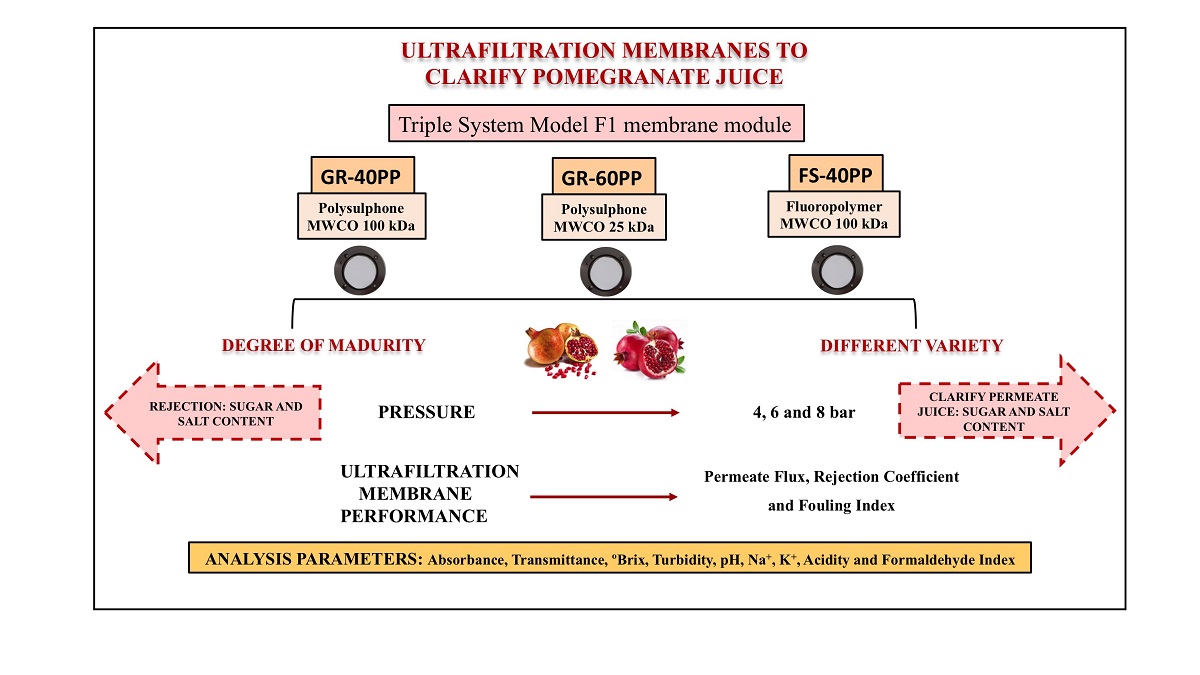
Their unique physicochemical properties and multi-enzymatic activity make CeO
2 nanoparticles (CeO
2 NPs) the most promising active component of the next generation of theranostic drugs. When doped with gadolinium ions, CeO
2 NPs constitute a new type of contrast agent for magnetic
[...] Read more.
Their unique physicochemical properties and multi-enzymatic activity make CeO
2 nanoparticles (CeO
2 NPs) the most promising active component of the next generation of theranostic drugs. When doped with gadolinium ions, CeO
2 NPs constitute a new type of contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging, possessing improved biocatalytic properties and a high level of biocompatibility. The present study is focused on an in-depth analysis of the enzyme-like properties of gadolinium-doped CeO
2 NPs (CeO
2:Gd NPs) and their antioxidant activity against superoxide anion radicals, hydrogen peroxide, and alkylperoxyl radicals. Using an anion-exchange method, CeO
2:Gd NPs (~5 nm) with various Gd-doping levels (10 mol.% or 20 mol.%) were synthesized. The radical-scavenging properties and biomimetic activities (namely SOD- and peroxidase-like activities) of CeO
2:Gd NPs were assessed using a chemiluminescent method with selective chemical probes: luminol, lucigenin, and L-012 (a highly sensitive luminol analogue). In particular, gadolinium doping has been shown to enhance the radical-scavenging properties of CeO
2 NPs. Unexpectedly, both bare CeO
2 NPs and CeO
2:Gd NPs did not exhibit SOD-like activity, acting as pro-oxidants and contributing to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Gadolinium doping caused an increase in the pro-oxidant properties of nanoscale CeO
2. At the same time, CeO
2:Gd NPs did not significantly inhibit the intrinsic activity of the natural enzyme superoxide dismutase, and CeO
2:Gd NPs conjugated with SOD demonstrated SOD-like activity. In contrast to SOD-like properties, peroxidase-like activity was observed for both bare CeO
2 NPs and CeO
2:Gd NPs. This type of enzyme-like activity was found to be pH-dependent. In a neutral medium (pH = 7.4), nanoscale CeO
2 acted as a prooxidant enzyme (peroxidase), while in an alkaline medium (pH = 8.6), it lost its catalytic properties; thus, it cannot be regarded as a nanozyme. Both gadolinium doping and conjugation with a natural enzyme were shown to modulate the interaction of CeO
2 NPs with the key components of redox homeostasis.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT