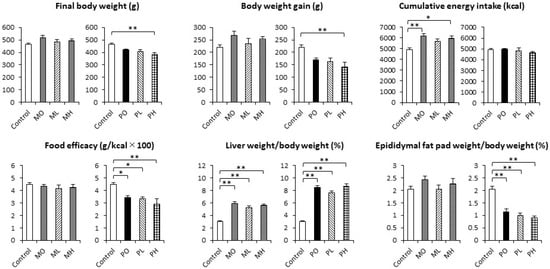
The ozone (O
3) variations in southeast China are largely different between mountainous forest areas located inland, and lowland urban areas located near the coast. Here, we selected these two kinds of areas to compare their similarities and differences in surface O
3 variability from diurnal to seasonal scales. Our results show that in comparison with the lowland urban areas (coastal areas), the mountainous forest areas (inland areas) are characterized with less human activates, lower precursor emissions, wetter and colder meteorological conditions, and denser vegetation covers. This can lead to lower chemical O
3 production and higher O
3 deposition rates in the inland areas. The annual mean of 8-h O
3 maximum concentrations (MDA8 O
3) in the inland areas are ~15 μg·m
−3 (i.e. ~15%) lower than that in the coastal areas. The day-to-day variation in surface O
3 in the two types of the areas is rather similar, with a correlation coefficient of 0.75 between them, suggesting similar influences on large scales, such as weather patterns, regional O
3 transport, and background O
3. Over 2016–2020, O
3 concentrations in all the areas shows a trend of “rising and then falling”, with a peak in 2017 and 2018. Daily MDA8 O
3 correlates with solar radiation most in the coastal areas, while in the inland areas, it is correlated with relative humidity most. Diurnally, during the morning, O
3 concentrations in the inland areas increase faster than in the coastal areas in most seasons, mainly due to a faster increase in temperature and decrease in humidity. While in the evening, O
3 concentrations decrease faster in the inland areas than in the coastal areas, mostly attributable to a higher titration effect in the inland areas. Seasonally, both areas share a double-peak variation in O
3 concentrations, with two peaks in spring and autumn and two valleys in summer and winter. We found that the valley in summer is related to the summer Asian monsoon that induces large-scale convections bringing local O
3 upward but blocking inflow of O
3 downward, while the one in winter is due to low O
3 production. The coastal areas experienced more exceedance days (~30 days per year) than inland areas (~5-10 days per year), with O
3 sources largely from the northeast. Overall, the similarities and differences in O
3 concentrations between inland and coastal areas in southeastern China are rather unique, reflecting the collective impact of geographic-related meteorology, O
3 precursor emissions, and vegetation on surface O
3 concentrations.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT