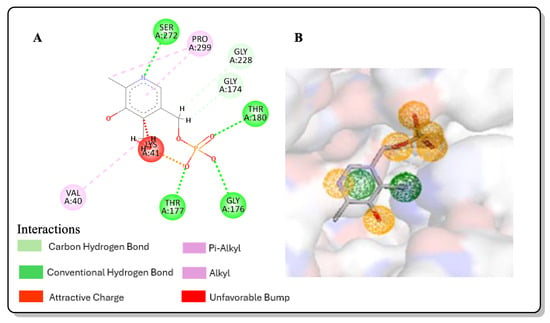
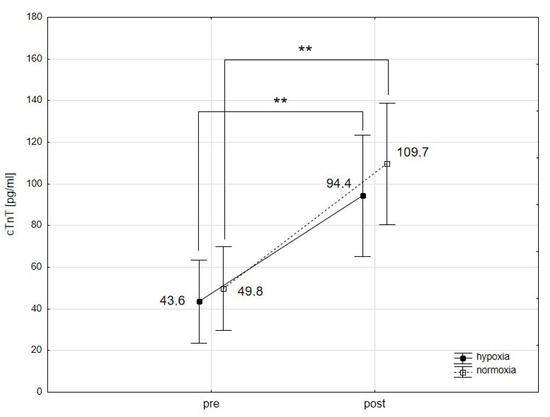
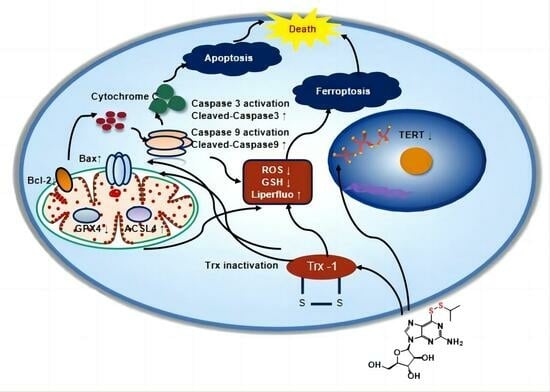
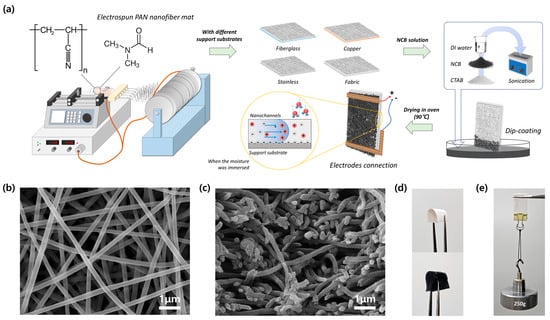
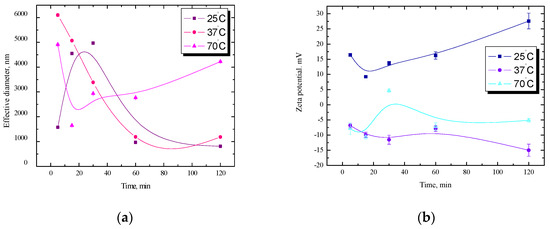
The inhibition of
O-acetyl sulphydrylase synthase isoforms has been reported to represent a promising approach for the development of antibiotic adjuvants. This occurs via the organism developing an unpaired oxidative stress response, causing a reduction in antibiotic resistance in vegetative and swarm cell populations. This consequently increases the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics at lower doses. This study aimed to predict potential inhibitors of
Salmonella typhimurium ortho acetyl sulphydrylase synthase (
StOASS), which has lower binding energy than the cocrystalized ligand pyridoxal 5 phosphate (PLP), using a computer-aided drug design approach including pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, and in silico ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity) evaluation. The screening and molecular docking of 4254 compounds obtained from the PubChem database were carried out using AutoDock vina, while a post-screening analysis was carried out using Discovery Studio. The best three hits were compounds with the PubChem IDs 118614633, 135715279, and 155773276, possessing binding affinities of −9.1, −8.9, and −8.8 kcal/mol, respectively. The in silico ADMET prediction showed that the pharmacokinetic properties of the best hits were relatively good. The optimization of the best three hits via scaffold hopping gave rise to 187 compounds, and they were docked against
StOASS; this revealed that lead compound
1 had the lowest binding energy (−9.3 kcal/mol) and performed better than its parent compound 155773276. Lead compound
1, with the best binding affinity, has a hydroxyl group in its structure and a change in the core heterocycle of its parent compound to benzimidazole, and pyrimidine introduces a synergistic effect and consequently increases the binding energy. The stability of the best hit and optimized compound at the
StOASS active site was determined using RMSD, RMSF, radius of gyration, and SASA plots generated from a molecular dynamics simulation. The MD simulation results were also used to monitor how the introduction of new functional groups of optimized compounds contributes to the stability of ligands at the target active site. The improved binding affinity of these compounds compared to PLP and their toxicity profile, which is predicted to be mild, highlights them as good inhibitors of
StOASS, and hence, possible antimicrobial adjuvants.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT