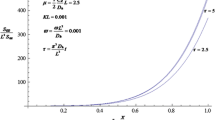
Abstract
In this paper we consider the shot-noise model of streamflow series. We show how design discharge can be obtained by the stochastic intensity of thinned Poisson processes describing the peaks over a threshold. The main result concerns the stationary distribution of peaks. We derive an explicit expression for this limit distribution in terms of its Laplace transform. Approximation formulas are developed making use of the saddle point method for the asymptotic evaluation of contour integrals and the Post-Widder formula for inversion of Laplace transforms. We illustrate this methods on the case of Gamma-distributed shots. The stationary peak distribution is used to approximate the maximum value distribution for larger time intervals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I. A. (eds.) 1965: Handbook of mathematical functions. New York: Dover Publications Inc.
Bernier, J. 1970: Inventaire des modelés de processus stochastiques applicables à lar description des débits journaliers des riviers. Rev. Int. Statist. Inst. 38, 49–70
Bodo, B. A.; Thompson, M. E.; Unny T. E. 1987: A review on stochastic differential equations in hydrology. Stoch. Hydrol. and Hydraul. 1, 81–101
Brémaud, P. 1981: Point processes and queues. Martingale dynamics. Springer Series in Statistics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Daniels, H. E. 1954: Saddlepoint approximations in statistics. Ann. Math. Statist. 25, 631–650
Daniels, H. E. 1960: Approximate solutions of Green's type for univariate stochastic processes. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B22, 376–401
Davies, B.; Martin, B. 1979: Numerical inversion of the Laplace transform: a survey and comparison of methods. J. Comp. Phys. 33, 1–32
Devroye, L. 1986: An automatic method for generating random variates with a given characteristic function. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 46/4, 698–719
Hutton, J. L. 1986: Non-negative time series and shot-noise processes as models for dry rivers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London
Hutton, J. L. 1990: Non-negative time series models for dry river flow. J. Appl. Prob. 27, 171–182
Kingman, J. F. C. 1964: On doubly stochastic Poisson processes. Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 60, 923–930
Koch, R. W. 1985: A stochastic streamflow model based on physical principles. Water Resour. Res. 21/4, 545–553
O'Connell, P. E.; Jones, D. A. 1979: Some experience with the development of models for the stochastic simulation of daily flows. In E. A. Mc Bean (ed.) Inputs for Risk Analysis in Water Systems. Fort Collins, Colorado: Water Resources Publications
Rice, J. 1977: On generalized shot-noise. Adv. Appl. Prob 9, 553–565
Rosbjerg, D. 1985: Estimation in partial duration series with independent and dependent peak values. J. Hydrol. 76, 183–195
Snyder, D. L. 1975: Random point processes. New York: J.Wiley.
Todorovic, P.; Woolhiser, D. A. 1987: A shot-noise model of streamflow. In V. P. Singh (ed.) Flood Hydrology. Dortrecht: D. Reidel Publ.
Treiber, B.; Plate, E. 1975: A Stochastic model for the simulation of daily flows. Int. Symposium and Workshops on the Application of Mathematical Models in Hydrology and Water Resource Systems, Bratislava
Vervaat, W. 1979: On a stochastic difference equation and a representation of non-negative infinitely divisible random variables. Adv. Appl. Prob. 11, 750–783
Weiss, G. 1977: Shot noise models for the generation of synthetic streamflow data. Water Resour. Res. 13/1, 101–108
Widder, D. V. 1946: The Laplace transform. Princetown Univ. Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konecny, F. On the shot-noise streamflow model and its applications. Stochastic Hydrol Hydraul 6, 289–303 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581622
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581622