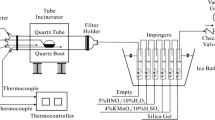
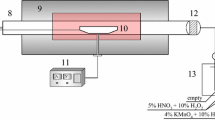
Abstract
Effects of interactions among chlorine (Cl), sulfur (S), phosphorus (P), and minerals on thallium (Tl) distributions were simulated using thermodynamic equilibrium conditions during the sludge co-combustion. Our results showed that Tl mainly existed in the forms of Tl2O3(s) and Tl(g) and did not react with SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, Fe2O3, and TiO2. Cl generated TlCl(g) and Tl(g) which in turn promoted Tl volatilization. S produced Tl2SO4(s), thus inhibiting Tl volatilization. P existence had no influence on Tl volatilization. With the couplings of Cl + S, S + P, and Cl + S + P, the reactions between single minerals and Tl were mainly controlled by S but P and Cl. With the Cl + P coupling, Cl controlled the reactions between the minerals and Tl, while P and the minerals had no significant impact. With the coupled minerals of SiO2 + CaO + Al2O3, S exerted a more influence than did Cl and P on the distributions of Tl, thus preventing Tl emissions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Li, C., Jin, Y., Nie, Y., Li, J.: Comparison of the fixation effects of heavy metals by cement rotary kiln co-processing and cement based solidification/stabilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 165(1–3), 1179–1185 (2009)
Bujak, J.: Thermal treatment of medical waste in a rotary kiln. J. Environ. Manage. 162, 139–147 (2015)
Cai, H., Zou, H., Liu, J., Xie, W., Kuo, J., Buyukada, M., Evrendilek, F.: Thermal degradations and processes of waste tea and tea leaves via TG-FTIR: combustion performances, kinetics, thermodynamics, products and optimization. Bioresource. Technol. 268, 715–725 (2018)
Guo, F., Zhong, Z., Xue, H., Zhong, D.: Migration and distribution of heavy metals during co-combustion of sedum plumbizincicola and coal. Waste. Biomass. Valori. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9955-4
Arena, U.: Process and technological aspects of municipal solid waste gasification. a review. Waste. Manage. 32(4), 625–639 (2012)
Liu, J., Zhuo, Z., Xie, W., Kuo, J., Lu, X., Buyukada, M., Evrendilek, F.: Interaction effects of chlorine and phosphorus on thermochemical behaviors of heavy metals during incineration of sulfur-rich textile dyeing sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 351, 897–911 (2018)
Lv, D., Zhu, T., Liu, R., Lv, Q., Sun, Y., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Zhang, F.: Effects of co-processing sewage sludge in cement kiln on NOx, NH3 and PAHs emissions. Chemosphere. 159, 595–601 (2016)
Richards, G., Agranovski, I.E.: Dioxin-like pcb emissions from cement kilns during the use of alternative fuels. J. Hazard. Mater. 323(Pt B), 698–709 (2017)
Liu, J., Zeng, J., Sun, S., Huang, S., Kuo, J., Chen, N.: Combined effects of FeCl3 and CaO conditioning on SO2, HCl and heavy metals emissions during the DDSS incineration. Chem. Eng. J. 299, 449–458 (2016)
Liu, J.Y., Huang, L., Sun, S., Ning, X., Kuo, J., Sun, J., Wang, Y., Xie, W.: Thermodynamic equilibrium calculations on Cd transformation during sewage sludge incineration. Water Environ. Res. 88(6), 548–556 (2016)
Liu, J., Fu, J., Sun, S., Ning, X., Wang, Y., Chen, T., Luo, G., Xie, W., Yang, Z., Zhuo, Z.: Effect of different sulfides on cadmium distribution during sludge combustion based on experimental and thermodynamic calculation approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 22(2), 1113–1126 (2014)
Gupta, R.K., Majumdar, D., Trivedi, J.V., Bhanarkar, A.D.: Particulate matter and elemental emissions from a cement kiln. Fuel. Process. Technol. 104, 343–351 (2012)
Liu, J., Xie, C., Xie, W., Zhang, X., Chang, K., Sun, J., Kuo, J., Xie, W., Liu, C., Sun, S., Buyukada, M., Evrendilek, F.: Arsenic partitioning behavior during sludge co-combustion: thermodynamic equilibrium simulation. Waste. Biomass. Valori. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0248-3
Yang, Y., Xue, J., Huang, Q.: Studies on the solidification mechanisms of Ni and Cd in cement clinker during cement kiln co-processing of hazardous wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 57, 138–143 (2014)
Clarke, L.B., Sloss, L.L.: Trace Elements Emission from Coal Combustion and Gasification (1992)
Saha, A.: Thallium toxicity: a growing concern. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 9(2), 53–56 (2005)
Shi, Y.Z., Liu, Q.: Development for the determination method of heavy metals in sewage sludge and materialsfrom the co-processing in cement kiln. Zhongguo Shuini. (05), 70–74 (2013) (In Chinese)
Antonia López-Antón, M., Spears, A., Díaz-Somoano, D., Diaz, M., Rosa, L., Martínez-Tarazona, M.: Enrichment of thallium in fly ashes in a Spanish circulating fluidized-bed combustion plant. Fuel. 146, 51–55 (2015)
Luan, J. D., Li, R. D., Zhang, Z. H., Li, Y. L., Zhao, Y.: Influence of chlorine, sulfur and phosphorus on the volatilization behavior of heavy metals during sewage sludge thermal treatment. Waste. Manag. Res. 31(10), 1012–1018 (2013)
Antón, M.A., Spears, D.A., Somoano, M.D., Tarazona M.: Thallium in coal: analysis and environmental implications. Fuel. 105, 13–18 (2013)
Zhou, H., Sun, J., Meng, A., Li, Q., Zhang, Y.: Effects of sorbents on the partitioning and speciation of Cu during municipal solid waste incineration. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 22(11–12), 1347–1351 (2014)
Liu, J., Fu, J., Ning, X., Sun, S., Wang, Y., Xie, W., Huang, S., Zhong, S.: An experimental and thermodynamic equilibrium investigation of the Pb, Zn, Cr, Cu, Mn and Ni partitioning during sewage sludge incineration. J. Environ. Sci. (China). 35, 43–54 (2015)
Nzihou, A., Stanmore, B.: The fate of heavy metals during combustion and gasification of contaminated biomass-a brief review. J. Hazard. Mater. 256–257, 56–66 (2013)
Liu, J.Y., Huang, S.J., Sun, S.Y., Ning, X.A., He, R.Z., Li, X.M., Chen, T., Luo, G.Q., Xie, W.M., Wang, Y.J., Zhuo, Z.X., Fu, J.W.: Effects of sulfur on lead partitioning during sludge incineration based on experiments and thermodynamic calculations. Waste. Manag. 38, 336–348 (2015)
Liu, J., Zhuo, Z., Sun, S., Xie, W., Lu, S., Sun, J., Kuo, J., Yujie, W.: Thermal behavior of Cd during sludge incineration: experiments and thermodynamic equilibrium model. Water Environ. Res. 88(12), 2245–2256 (2016)
Fraissler, G., Jöller, M., Mattenberger, H., Brunner, T., Obernberger, I.: Thermodynamic equilibrium calculations concerning the removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge ash by chlorination. Chem. Eng. Process. 48(1), 152–164 (2009)
Saqib, N., Backstrom, M.: Trace element partitioning in ashes from boilers firing pure wood or mixtures of solid waste with respect to fuel composition, chlorine content and temperature. Waste. Manag. 34(12), 2505–2519 (2014)
Dirk Verhulst, A., Buekens, A., And, P.J.S., Eriksson, G.: Thermodynamic behavior of metal chlorides and sulfates under the conditions of incineration furnaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30(1), 50–56 (1996)
Ndiba, P., Axe, L., Boonfueng, T.: Heavy metal immobilization through phosphate and thermal treatment of dredged sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(3), 920–926 (2008)
Lin, M., Ning, X., Liang, X., Wei, P., Wang, Y., Liu, J.: Study of the heavy metals residual in the incineration slag of textile dyeing sludge. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 45(4), 1814–1820 (2014)
Soria, J., Gauthier, D., Flamant, G., Rodriguez, R., Mazza, G.: Coupling scales for modelling heavy metal vaporization from municipal solid waste incineration in a fluid bed by CFD. Waste. Manage. 43, 176–187 (2015)
Liu, J., Liu, C., Zhuo, Z., Xie, C., Dang, X., Zhang, X., Kuo, J., Chang, K., Sun, J., Sun, S., Buyukada, M., Evrendilek, F.: Thermodynamic behaviors of Cu in interaction with chlorine, sulfur, phosphorus and minerals during sewage sludge co-incineration. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 26(5), 1160–1170 (2018)
Liu, J.Y., Sun, S.Y., Xu, Y.B., Xie, W.M., Chen, T., Chen, M.T.: Heavy metals characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of municipal sewage sludge from Guangzhou for agriculture process. Huanjing Kexue Xuebao. 29(12), 2545–2556 (2009) (In Chinese)
Folgueras, M.B., Díaz, R.M., Xiberta, J., Prieto, I.: Volatilisation of trace elements for coal–sewage sludge blends during their combustion. Fuel. 82(15–17), 1939–1948 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Guangdong Special Support Program for Training High Level Talents (No.2014TQ01Z248), the Scientific and Technological Planning Project of Guangzhou, China (No.2016201604030058; 201704030109) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2017A050501036; 2017A040403063; 2017A040403044). We are grateful to Lv Jun for his enthusiastic help with the numerical simulations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhang, J., Sun, G. et al. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Simulations of Thallium Distributions in Interactions with Chlorine, Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Minerals During Sludge Co-combustion. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 1251–1259 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0454-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0454-z