Abstract
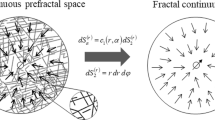
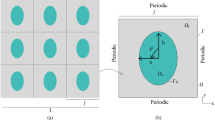
Electrokinetic and electroosmotic couplings can play important roles in water and ions transport in charged porous media. Electroosmosis is the phenomena explaining the water movement in a porous medium subjected to an electrical field. In this work, a new model is obtained through a new up-scaling procedure, considering the porous medium as a bundle of tortuous capillaries of fractal nature. From the model, the expressions for the electroosmosis pressure coefficient, the relative electroosmosis pressure coefficient, the maximum back pressure, the maximum flow rate, the flow rate-applied back pressure relation and the product of the permeability and formation factor of porous media are also obtained. The sensitivity of the relative electroosmosis pressure coefficient is then analyzed and explained. The model predictions are then successfully compared with published datasets. Additionally, we deduce an expression for the relative streaming potential coefficient and then compare it with a previously published model and experimental data from a dolomite rock sample. We find a good agreement between those models and experimental data, opening up new perspectives to model electroosmotic phenomena in porous media saturated with various fluids.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandopadhyay, A., DasGupta, D., Mitra, S.K., Chakraborty, S.: Electro-osmotic flows through topographically complicated porous media: role of electropermeability tensor. Phys. Rev. E 87, 033006 (2013)
Bernabe, Y., Revil, A.: Pore-scale heterogeneity, energy dissipation and the transport properties of rocks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 1529–1532 (1995)
Bertolini, L., Coppola, L., Gastaldi, M., Redaelli, E.: Electroosmotic transport in porous construction materials and dehumidification of masonry. Constr. Build. Mater. 23, 254–263 (2009)
Bolève, A., Crespy, A., Revil, A., Janod, F., Mattiuzzo, J.L.: Streaming potentials of granular media: influence of the dukhin and reynolds numbers. J. Geophys. Res. 112, B08204 (2007)
Bruell, C.J., Segall, B.A., Walsh, M.T.: Electroosomotic removal of gasoline hydrocarbons and TCE from clay. J. Environ. Eng. 118, 68–83 (1992)
Bruus, H.: Theoretical Microfluidics, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2008)
Cai, J.C., Hu, X.Y., Standnes, D.C., You, L.J.: An analytical model for spontaneous imbibition in fractal porous media including gravity. Colloids Surf. A Physicocem. Eng. Asp. 414, 228–233 (2012a)
Cai, J.C., You, L.J., Hu, X.Y., Wang, J., Peng, R.H.: Prediction of effective permeability in porous media based on spontaneous imbibition effect. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C (2012b). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129183112500544
Casagrande, L.: Stabilization of soils by means of electroosmotic state-of-art. J. Boston Soc. Civ. Eng. ASCE 69, 255–302 (1983)
Cherubini, A., Garcia, B., Cerepi, A., Revil, A.: Streaming potential coupling coefficient and transport properties of unsaturated carbonate rocks. Vadose Zone J. 17, 180030 (2018)
Davis, J., James, R., Leckie, J.: Surface ionization and complexation at the oxide/water interface. I. computation of electrical double layer properties in simple electrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 63, 480–499 (1978)
Feder, J., Aharony, A.: Fractals in Physics. North Holland, Amsterdam (1989)
Friedman, S.P.: Soil properties influencing apparent electrical conductivity: a review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 46, 45–70 (2005)
Ghanbarian, B., Hunt, A., Ewing, R.P., Sahimi, M.: Tortuosity in porous media: a critical review. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 77, 1461–1477 (2013)
Gierst, L.: Double layer and electrode kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 88, 4768–4768 (1966)
Glover, P., Zadjali, I.I., Frew, K.A.: Permeability prediction from MICP and NMR data using an electrokinetic approach. Geophysics 71, F49–F60 (2006)
Glover, P.W.J., Déry, N.: Streaming potential coupling coefficient of quartz glass bead packs: dependence on grain diameter, pore size, and pore throat radius. Geophysics 75, F225–F241 (2010)
Glover, P.W.J., Walker, E.: Grain-size to effective pore-size transformation derived from electrokinetic theory. Geophysics 74(1), E17–E29 (2009)
Good, B.T., Bowman, C.N., Davis, R.H.: An effervescent reaction micropump for portable microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 6, 659–666 (2006)
Guarracino, L., Jougnot, D.: A physically based analytical model to describe effective excess charge for streaming potential generation in water saturated porous media. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 123, 52–65 (2018)
Han, S.-J., Kim, S.-S., Kim, B.-I.: Electroosmosis and pore pressure development characteristics in lead contaminated soil during electrokinetic remediation. Geosci. J. 8, 85 (2004)
Hu, G., Li, D.: Multiscale phenomena in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 3443–3454 (2007)
Hu, X., Hu, S., Jin, F., Huang, S.: Physics of Petroleum Reservoirs. Springer, Berlin (2017)
Hunter, R.J.: Zeta Potential in Colloid Science. Academic, New York (1981)
Israelachvili, J.: Intermolecular and Surface Forces. Academic Press, New York (1992)
Jaafar, M.Z., Vinogradov, J., Jackson, M.D.: Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with high salinity NACL brine. Geophys. Res. Lett. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL040549
Jacob, H.M., Subirm, B.: Electrokinetic and Colloid Transport Phenomena. Wiley, New York (2006)
Jardani, A., Revil, A., Boleve, A., Crespy, A., Dupont, J.-P., Barrash, W., Malama, B.: Tomography of the Darcy velocity from self-potential measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L24403 (2007)
Jougnot, D., Linde, N., Revil, A., Doussan, C.: Derivation of soil-specific streaming potential electrical parameters from hydrodynamic characteristics of partially saturated soils. Vadose Zone J. 11, 272–286 (2012)
Jougnot, D., Mendieta, A., Leroy, P., Maineult, A.: Exploring the effect of the pore size distribution on the streaming potential generation in saturated porous media, insight from pore network simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 124, 5315–5335 (2019)
Jurin, J.: Ii. an account of some experiments shown before the royal society; with an enquiry into the cause of the ascent and suspension of water in capillary tubes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 30, 739–747 (1719)
Katz, A.J., Thompson, A.H.: Fractal sandstone pores: implications for conductivity and pore formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 1325–1328 (1985)
Kirby, B.: Micro and Nanoscale Fluid Mechanics: Transport in Microfluidic Devices. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010)
Larue, O., Wakeman, R., Tarleton, E., Vorobiev, E.: Pressure electroosmotic dewatering with continuous removal of electrolysis products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 61, 4732–4740 (2006)
Leroy, P., Maineult, A.: Exploring the electrical potential inside cylinders beyond the Debye–Hückel approximation: a computer code to solve the Poisson–Boltzmann equation for multivalent electrolytes. Geophys. J. Int. 214, 58–69 (2018)
Leroy, P., Revil, A.: A triple-layer model of the surface electrochemical properties of clay minerals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 270, 371–380 (2004)
Levine, S., Marriott, J., Neale, G., Epstein, N.: Theory of electrokinetic flow in fine cylindrical capillaries at high zeta-potentials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 52, 136–149 (1975)
Li, S.X., Pengra, D.B., Wong, P.Z.: Onsager’s reciprocal relation and the hydraulic permeability of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 51, 5748–5751 (1995)
Liang, M., Yang, S., Miao, T., Yu, B.: Analysis of electroosmotic characters in fractal porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 127, 202–209 (2015)
Liang, M., Yang, S., Yu, B.: A fractal streaming current model for charged microscale porous media. J. Electrostat. 72, 441–446 (2014)
Jiang, Linan, Mikkelsen, J., Koo, J.-M., Huber, D., Yao, Shuhuai, Zhang, Lian, Zhou, Peng, Maveety, J.G., Prasher, R., Santiago, J.G., Kenny, T.W., Goodson, K.E.: Closed-loop electroosmotic microchannel cooling system for VLSI circuits. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 25, 347–355 (2002)
Linde, N., Binley, A., Tryggvason, A., Pedersen, L.B., Revil, A.: Improved hydrogeophysical characterization using joint inversion of cross-hole electrical resistance and ground-penetrating radar traveltime data. Water Resour. Res. 42, W04410 (2006)
Lockhart, N., Hart, G.: Electro-osmotic dewatering of fine suspensions: the efficacy of current interruptions. Dry. Technol. 6, 415–423 (1988)
Luong, D.T., Sprik, R.: Streaming potential and electroosmosis measurements to characterize porous materials. ISRN Geophys. 496352, 1–8 (2013)
Lyklema, J.: Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science. Academic Press, New York (1995)
Mandelbrot, B.B.: The Fractal Geometry of Nature. W.H. Freeman, New York (1982)
Mohiuddin Mala, G., Li, D.-D., Werner, C., Jacobasch, H.-J., Ning, Y.: Flow characteristics of water through a microchannel between two parallel plates with electrokinetic effects. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 18, 489–496 (1997)
Nourbehecht, B.: Irreversible thermodynamic effects in inhomogeneous media and their applications in certain geoelectric problems. PhD thesis, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (1963)
Ohshima, H., Kondo, T.: Electrokinetic flow between two parallel plates with surface charge layers: electro-osmosis and streaming potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 135, 443–448 (1990)
Olivares, W., Croxton, T.L., McQuarrie, D.A.: Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J. Phys. Chem. 84, 867–869 (1980)
Ottosen, L., Rörig-Dalgaard, I.: Drying brick masonry by electro-osmosis. In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Masonry Conference. British Masonry Society (2006)
Paillat, T., Moreau, E., Grimaud, P.O., Touchard, G.: Electrokinetic phenomena in porous media applied to soil decontamination. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 7, 693–704 (2000)
Pascal, J., Oyanader, M., Arce, P.: Effect of capillary geometry on predicting electroosmotic volumetric flowrates in porous or fibrous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 378, 241–250 (2012)
Pengra, D., Li, S.X., Wong, P.: Determination of rock properties by low frequency ac electrokinetics. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 29485–29508 (1999)
Pride, S.: Governing equations for the coupled electromagnetics and acoustics of porous media. Phys. Rev. B 50, 15678–15696 (1994)
Pride, S.R., Morgan, F.D.: Electrokinetic dissipation induced by seismic waves. Geophysics 56, 914–925 (1991)
Quincke, G.: Ueber die fortführung materieller theilchen durch strömende elektricität. Ann. Phys. 189, 513–598 (1861)
Reddy, K.R., Parupudi, U.S., Devulapalli, S.N., Xu, C.Y.: Effects of soil composition on the removal of chromium by electrokinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 55, 135–158 (1997)
Reuss, F.: Sur un nouvel effet de l’électricité galvanique. Mémoires de la Societé Imperiale de Naturalistes de Moscou 2, 327–336 (1809)
Revil, A., Cathles III, L.M., Manhardt, P.D.: Permeability of shaly sands. Water Resour. Res. 3, 651–662 (1999)
Revil, A., Leroy, P.: Constitutive equations for ionic transport in porous shales. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 109, B03208 (2004)
Revil, A., Linde, N.: Chemico-electromechanical coupling in microporous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 302, 682–694 (2006)
Revil, A., Linde, N., Cerepi, A., Jougnot, D., Matthäi, S., Finsterle, S.: Electrokinetic coupling in unsaturated porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 313, 315–327 (2007)
Rice, C., Whitehead, R.: Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J. Phys. Chem. 69, 4017–4024 (1965)
Sen, P.N., Goode, P.A.: Influence of temperature on electrical conductivity on shaly sands. Geophysics 57, 89–96 (1992)
Singhal, V., Garimella, S.V., Raman, A.: Microscale pumping technologies for microchannel cooling systems. Birck NCN Publ. 57, 191–221 (2004)
Smoluchowski, M.: Contribution à la théorie de l’endosmose électrique et de quelques phénomènes corrélatifs. Bulletin de l’Académie des Sciences de Cracovie 8, 182–200 (1902)
Soldi, M., Guarracino, L., Jougnot, D.: An analytical effective excess charge density model to predict the streaming potential generated by unsaturated flow. Geophys. J. Int. 216, 380–394 (2019)
Thanh, L., Jougnot, D., Do, P., Ca, N., Hien, N.: A physically based model for the streaming potential coupling coefficient in partially saturated porous media. Water 12, 1588 (2020)
Thanh, L., Sprik, R.: Zeta potential measurement using streaming potential in porous media. VNU J. Sci. Math. Phys. 31, 56–65 (2015)
Thanh, L.D., Jougnot, D., Van Do, P., Van Nghia, A.: A physically based model for the electrical conductivity of water-saturated porous media. Geophys. J. Int. 219, 866–876 (2019)
Thanh, L.D., Van Do, P., Van Nghia, N., Ca, N.X.: A fractal model for streaming potential coefficient in porous media. Geophys. Prospect. 66, 753–766 (2018)
Tsai, N.-C., Sue, C.-Y.: Review of mems-based drug delivery and dosing systems. Sens. Actuators A 134, 555–564 (2007)
Vennela, N., Bhattacharjee, S., De, S.: Sherwood number in porous microtube due to combined pressure and electroosmotically driven flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 66, 6515–6524 (2011)
Vinogradov, J., Jaafar, M.Z., Jackson, M.D.: Measurement of streaming potential coupling coefficient in sandstones saturated with natural and artificial brines at high salinity. J. Geophys. Res. 115 (2010)
Wang, J., Hu, H., Guan, W.: The evaluation of rock permeability with streaming current measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 206, 1563–1573 (2016)
Wang, J., Hu, H., Guan, W., Li, H.: Electrokinetic experimental study on saturated rock samples: zeta potential and surface conductance. Geophys. J. Int. 201, 869–877 (2015)
Wang, X., Cheng, C., Wang, S., Liu, S.: Electroosmotic pumps and their applications in microfluidic systems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 6, 145–162 (2009)
Wise, D.L., Trantolo, D.J.: Remediation of Hazardous Waste Contaminated Soils. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1994)
Wu, R.C., Papadopoulos, K.D.: Electroosmotic flow through porous media: cylindrical and annular models. Colloids Surf. A 161, 469–476 (2000)
Wyllie, M.R.J., Rose, W.: Some theoretical considerations related to the quantitative evaluation of the physical characteristics of reservoir rock from electrical log data. Society of Petroleum Engineers (1950)
Yao, S., Santiago, J.G.: Porous glass electroosmotic pumps: theory. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 268, 133–142 (2003)
Yu, B., Cheng, P.: A fractal permeability model for bi-dispersed porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 45, 2983–2993 (2002)
Yu, B., Lee, L.J., Cao, H.: Fractal characters of pore microstructures of textile fabrics. Fractals 09, 155–163 (2001)
Zeng, S., Chen, C.H., Mikkelsen, J.C., Santiago, J.G.: Fabrication and characterization of electroosmotic micropumps. Sens. Actuators B 79, 107–114 (2001)
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under Grant Number 103.99-2019.316. Additionally, D. Jougnot and A. Mendieta strongly thank the financial support of ANR EXCITING (Grant ANR-17-CE06-0012) for the PhD thesis funding of A. Mendieta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thanh, L.D., Jougnot, D., Van Do, P. et al. Electroosmotic Coupling in Porous Media, a New Model Based on a Fractal Upscaling Procedure. Transp Porous Med 134, 249–274 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01444-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01444-7