Abstract
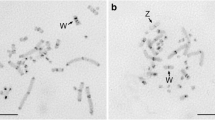
During the last years it became obvious that a lot of families of long-range repetitive DNA elements are located within the genomes of mammals. The principles underlying the evolution of such families, therefore, may have a greater impact than anticipated on the evolution of the mammalian genome as a whole. One of these families, called chAB4, is represented with about 50 copies within the human and the chimpanzee genomes and with only a few copies in the genomes of gorilla, orang-utan, and gibbon. Members of chAB4 are located on 10 different human chromosomes. FISH of chAB4-specific probes to chromosome preparations of the great apes showed that chAB4 is located, with only one exception, at orthologous places in the human and the chimpanzee genome. About half the copies in the human genome belong to two species-specific subfamilies that evolved after the divergence of the human and the chimpanzee lineages. The analysis of chAB4-specific PCR-products derived from DNA of rodent/human cell hybrids showed that members of the two human-specific subfamilies can be found on 9 of the 10 chAB4-carrying chromosomes. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the members of DNA sequence families can evolve as a unit despite their location at multiple sites on different chromosomes. The concerted evolution of the family members is a result of frequent exchanges of DNA sequences between copies located on different chromosomes. Interchromosomal exchanges apparently take place without greater alterations in chromosome structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A., Rainaldi G, Lobbiani A, Magnani I, Di Lernia R, Meneveri R, Siccardi AG, Ginelli E (1987) Chromosomal location by in situ hybridization of the human Sau3A family of DNA repeats. Hum Genet 75, 326–332
Assum G, Fink T, Klett C, Lengl B, Schanbacher M, Uhl S, Wöhr G (1991) A new multisequence family in human. Genomics 11, 397–409
Assum G, Fink T, Steinbeißer T, Fisel KJ (1993) Analysis of human extrachromosomal DNA-elements originating from different β-satellite subfamilies. Hum Genet 91, 489–495
Assum G, Gartmann C, Schempp W, Wöhr G (1994) Evolution of the chAB4 multisequence family in primates. Genomics 21, 34–41
Chance PF, Abbas N, Lensch MW, Pentao L, Roa BB, Patel PI, Lupski JR (1994) Two autosomal dominant neuropathies result from reciprocal DNA duplication/deletion of a region on chromosome 17. Hum Mol Genet 3, 223–228
Cooper KF, Fisher RB, Tyler-Smith C (1992) Structure of the pericentric long arm region of the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol 228, 421–432
Drwinga HL, Toji LH, Kim CH, Greene AE, Mulivor RA (1993) NIGMS human/rodent somatic cell hybrid mapping panels 1 and 2. Genomics 16, 311–314
Eichler EE, Lu F, Shen Y, Antonacci R, Jurecic V, Doggett NA, Moyzis RK, Baldini A, Gibbs RA, Nelson DL (1996) Duplication of a gene-rich cluster between 16p1 l.1 and Xq28: a novel pericentromeric-directed mechanism for paralogous genome evolution. Hum Mol Genet 5, 899–912
Eichler EE, Budarf ML, Rocchi M, Deaven LL, Doggett NA, Baldini A, Nelson DL, Mohrenweiser HW (1997) Interchromosomal duplications of the adrenoleukodystrophy locus: a phenomenon of pericentromeric plasticity. Hum Mol Genet 6, 991–1002
Eickenboom JCJ, Vink T, Briet E, Sixma JJ, Reitsma PH (1994) Multiple substitution in the von Willebrand factor gene that mimic the pseudogene sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91, 2221–2224
Frommer M, Paul C, Vincent PC (1988) Localisation of satellite DNA sequences on human chromosomes using bromodeoxyuridine-labeled probes. Chromosoma 97, 11–18
Grady DL, Ratliff RL, Robinson DL, McCanlies EC, Meyne J, Moyzis RK (1992) Highly conserved repetitive DNA sequences are present at human centromeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 1695–1699
Greig GM, Willard HE (1992) β satellite DNA: characterization and localization of two subfamilies from the distal and proximal short arms of the human acrocentric chromosomes. Genomics 12, 573–580
Groot PC, Mager WH, Henriquez NZ, Pronk JG, Arwert F, Planta RJ, Eriksson AW, Frants RR (1990) Evolution of the human α-amylase multigene family through unequal, homologous, and inter- and intrachromosomal crossovers. Genomics 8, 97–105
Hayashida H, Kuma K, Miyata T (1992) Interchromosomal gene conversion as a possible mechanism for explaining divergence patterns of ZFY-related genes. J Mol Evol 35, 181–183
Krystal M, D’Eustachio P, Ruddle FH, Arnheim N (1981) Human nucleolus organizers on non-homologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78, 5744–5748
Kurnit DM, Neve RL, Morton CC, Bruns GAD, Ma NSF, Cox DR, Klinger HP (1984) Recent evolution of DNA-sequence homology in the pericentromeric regions of human acrocentric chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38, 99–105
Maeda N, Smithies O (1986) The evolution of multigene families: Human haptoglobin genes. Annu Rev Genet 20, 81–108
Meyne J, Goodwin EH, Moyzis RK (1994) Chromosome localization and orientation of the simple sequence repeat of human satellite I DNA. Chromosoma 103, 99–103
Miyamoto MM, Slightom JL, Goodmann M (1987) Phylogenetic relations of human and African apes from DNA sequences in the ψ, η-globin region Science 238, 369–373
Patracchini P, Marchetti G, Aiello V, Croci G, Calzdari E, Bernardi F (1992) Characterization and mapping of the 5′ portion of von Willebrand factor pseudogene. Hum Genet 90, 297–298
Pentao L, Wise CA, Chinault AC, Patel PI, Lupski JR (1992) Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A tandem duplication appears to arise from recombination at repeat sequences flanking the 1.5 Mb monomer unit. Nature Genet 2, 292–300
Purandare SM, Huntsman Breidenbach H, Li Y, Zhu XL, Sawada S, Neil SM, Brothman A, White R, Cawthon R, Viskochil D (1995) Identification of neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) homologous loci by direct sequencing, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and PCR amplification of somatic cell hybrids. Genomics 30, 476–485
Régnier V, Meddeb M, Lecointre G, Richard F, Duverger A, Nguyen VC, Dutrillaux B, Bernheim A, Danglot G (1997) Emergence and scattering of multiple neurofibromatosis (NF1)-related sequences during hominoid evolution suggest a process of pericentromeric interchromosomal transposition. Hum Mol Genet 6, 9–16
Sakai KS, Ohta T, Minoshima S, Kudoh J, Wang Y, De Jona PJ, Shimizu N (1995) Human ribosomal RNA gene cluster: identification of the proximal end containing a novel tandem repeat sequence. Genomics 26, 521–526
Schempp W, Binkele A, Arnemann J, Gläser B, Ma K, Taylor K, Toder R, Wolfe J, Zeitler S, Chandley AC (1995) Comparative mapping of YRRM- and TSPY-related cosmids in man and hominoid apes. Chromosome Res 3, 227–234
Sibley CG, Ahlquist JE (1987) DNA hybridization evidence of hominoid phylogeny: results from an expanded data set. J Mol Evol 26, 99–121
Tagarro I, Fernández-Peralta AM, González-Aguilera JJ (1994) Chromosomal localization of human satellites 2 and 3 by a FISH method using oligonucleotides as probes. Hum Genet 93, 383–388
van Deutekom JCT, Lemmers RJLF, Grewal PK, Van Geel M, Romberg S, Dauwerse HG, Wright TJ, Padberg GW, Hofker MH, Hewitt JE, Frants RR (1996) Identification of the first gene (FRG1) from the FSHD region on human chromosome 4q35. Hum Mol Genet 5, 581–590
Waye JS, Willard HF (1989) Human β satellite DNA: genomic organization and sequence definition of a class of highly repetitive tandem DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86, 6250–6254
Weiner AM, Denison RA (1983) Either gene amplification or gene conversion may maintain the homogeneity of the multigene family encoding human U1 small nuclear RNA. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 47, 1141–1149
Wöhr G, Fink T, Assum G (1996) A palindromic structure in the pericentromeric region of various human chromosomes. Genome Res 6, 267–279
Worton RS, Sutherland J, Sylvester JE, Willard HF, Bodrug S, Dube L, Dutt C, Kean V, Ray PN, Schmickel R (1988) Human ribosomal RNA genes: orientation of the tandem array and conservation of the 5′ end. Science 239, 64–68
Yunis JJ, Prakash O (1982) The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science 215, 1525–1530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assum, G., Pasantes, J., Gläser, B. et al. Concerted evolution of members of the multisequence family chAB4 located on various nonhomologous chromosomes. Mammalian Genome 9, 58–63 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900680
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900680