Abstract
The authors describe three fluorescein-conjugated peptides generated by cell-phage display for use as a diagnostic probes for fluorescent detection and imaging of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium. The authors also designed a polyvalent-directed peptide polymer synthesized with poly-D-lysine and bifunctional succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate with an affinity and sensitivity that is higher by more than an order of magnitude compared to single peptides due to multiple binding site interactions. In order to establish a diagnostic system for food poisoning, imaging analysis was performed using fluorescence microscopy. The limit of detection of the diagnostic system based on polyvalent directed peptide interaction is 102 colony-forming units per mL for Salmonella.

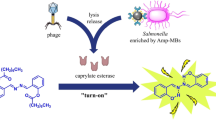
Schematic of a fluorescent method for detection and imaging of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium by using a fluorescein labeled polyvalent-directed peptide polymer (PDPP) with a high affinity and sensitivity as a diagnostic probe. The system uses a microplate reader and was applied to the detection of food poisoning.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Velge P, Cloeckaert A, Barrow P (2005) Emergence of salmonella epidemics: the problems related to salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis and multiple antibiotic resistance in other major serotypes. Vet Res 36:267–288
Duan N, Wu S, Chen X, Huang Y, Xia Y, Ma X, Wang Z (2013) Selection and characterization of aptamers against salmonella typhimurium using whole-bacterium systemic evolution of ligands by exponential entichment (SELEX). J Agric Food Chem 61:3229–3234
Coburn B, Grassl GA, Finlay BB (2007) Salmonella, the host and disease: a brief review. Cell Biol 85:112–118
Bajpai VK, Baek KH, Kang SC (2012) Control of salmonella in foods by using essential oils: a review. Food Res Int 45:722–734
Lee DY, Lee E, Min JE, Kim SH, Oh HB, Park MS (2011) Epidemic by salmonella I 4,[5],12:i:- and characteristics of isolates in korea. Infect Chemother 43:186–190
Tindall BJ, Grimont PA, Garrity GM, Euzeby JP (2005) Nomenclature and taxonomy of the genus salmonella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:521–524
Abubakar I, Irvine L, Aldus CF, Wyatt GM, Fordham R, Schelenz S, Shepstone L, Howe A, Peck M, Hunter PR (2007) A systematic review of the clinical, public health and cost-effectiveness of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection and identification of bacterial intestinal pathogens in faeces and food. Health Technol Assess 11:1–216
González-Escalona N, Brown EW, Zhang G (2012) Development and evaluation of a multiplex real-time pcr (qpcr) assay targeting ttrRSBCA locus and invA gene for accurate detection of salmonella spp. in fresh produce and eggs. Food Res Int 48:202–208
Holt PS, Gast RK, Greene CR (1995) Rapid detection of salmonella enteritidis in pooled liquid egg samples using a magnetic bead-ELISA system. J Food Prot 58:967–972
Kuang H, Wang W, Xu L, Ma W, Liu L, Wang L, Xu C (2013) Monoclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin a. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:1598–1608
Dong Y, Xu Y, Yong W, Chu X, Wang D (2014) Aptamer and its potential applications for food safety. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 54:1548–1561
Singh AK, Senapati D, Wang S, Griffin J, Neely A, Candice P, Naylor KM, Varisli B, Kalluri JR, Ray PC (2009) Gold nanorod based selective identification of Escherichia coli bacteria using two-photon Rayleigh scattering spectroscopy. ACS Nano 3:1906–1912
Yang L, Li Y (2006) Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli o157:h7 and salmonella typhimurium using quantum dots as fluorescence labels. Analyst 131:394–401
Gao J, Li L, Ho PL, Mak GC, Gu H, Xu B (2006) Combining fluorescent probes and biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for rapid detection of bacteria in human blood. Adv Mater 18:3145–3148
Gu L, Elkin T, Jiang X, Li H, Lin Y, Qu L, Tzeng TR, Joseph R, Sun YP (2005) Single-walled carbon nanotubes displaying multivalent ligands for capturing pathogens. Chem Commun 7:874–876
Lee KM, Runyon M, Herrman TJ, Phillips R, Hsieh (2015) Review of salmonella detection and identification methods: aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. J Food Control 47:264–276
Wu J, Zhu Y, Xue F, Mei Z, Yao L, Wang X, Zheng L, Liu J, Liu G, Peng C, Chen W (2014) Recent trends in SELEX technique and its application to food safety monitoring. Microchim Acta 181:479–491
Guo Y, Wang Y, Liu S, Yu J, Wang H, Liu X, Huang J (2017) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of E. coli and S. typhimurium based on target recycling amplification using self-assembled hairpin probes on a gold electrode. Microchimi Acta. Doi: 10.1007/s00604-016-2017-y
Seker UOS, Demir HV (2011) Material binding peptides for nanotechnology. Molecules 16:1426–1451
Ploss M, Facey SJ, Bruhn C, Zemel L, Hofmann K, Stark RW, Albert B, Hauer B (2014) Selection of peptides binding to metallic borides by screening M13 phage display libraries. BMC Biotechnol 14:12
Wolcke J, Weinhold E (2001) A dna-binding peptide from a phage display library. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 20:1239–1241
Kim J, Park HY, Choi KJ, Jung H, Han SH, Lee JS, Park JS, Yoon MY (2006) Screening of peptides bound to anthrax protective antigen by phage display. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:1784–1790
Even-Desrumeaux K, Chames P (2012) Phage display and selections on cells. Methods Mol Biol 907:225–235
Carmona SJ, Sartor PA, Leguizamon MS, Campetella OE, Aguero F (2012) Diagnostic peptide discovery: prioritization of pathogen diagnostic markers using multiple features. PLoS One 7:e50748
Kolovskaya OS, Savitskaya AG, Zamay TN, Reshetneva IT, Zamay GS, Erkaev EN, Wang X, Wehbe M, Salmina AB, Perianova OV, Zubkova OA, Spivak EA, Mezko VS, Glazyrin YE, Titova NM, Berezovski MV, Zamay AS (2013) Development of bacteriostatic dna aptamer for salmonella. J Med Chem 56:1564–1572
Liu K, Yan X, Mao B, Wang S, Deng L (2016) Aptamer-based detection of salmonella enteritidis using double signal amplification by klenow fragment and dual fluorescence. Microchim Acta 183:643–649
Park HY, Gedi V, Kim J, Park HC, Han SH, Yoon MY (2011) Ultrasensitive diagnosis for an anthrax-protective antigen based on a polyvalent directed peptide polymer coupled to zinc oxide nanorods. Adv Mater 23:5425–5429
Singh A, Arutyunov D, Szymanski CM, Evoy S (2012) Bacteriophage based probes for pathogen detection. Analyst 137:3405–3421
Gray BP, Brown KC (2014) Combinatorial peptide libraries: mining for cell-binding peptides. Chem Rev 114:1020–1081
Varner CT, Rosen T, Martin JT, Kane RS (2015) Recent advance in engineering polyvalent biological interactions. Biomacromolecules 16:43–55
Fischer D, Li Y, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J, Kissel T (2003) In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 24:1121–1131
Delibato E, Fiore A, Anniballi F, Auricchio B, Filetici E, Orefice L, Losio MN, Medici DD (2011) Comparison between two standardized cultural methods and 24 hour duplex sybr green real-time pcr assay for salmonella detection in meat samples. New Microbiol 34:299–306
Liu GF, Wang JY, Xu LW, Ding X, Zhou SN (2010) Sensitive and rapid detection of vibrio corallilyticus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification targeted to the alpha subunit gen of rna polymerase. Lett Appl Microbiol 51:301–307
Shanmugasamy M, Velayutham T, Rajeswar J (2011) Inv a gene specific pcr for detection of salmonella from broilers. Veterinary World 4:562–564
Schmidt R, Koberl M, Mostafa A, Ramadan EM, Monschein M, Jensen KB, Bauer R, Berg G (2014) Effects of bacterial inoculants on the indigenous microbiome and secondary metabolites of chamomile plants. Front Microbiol 5:1–11. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00064
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ907052) funded by the Rural Development Administration and a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. 201500000001213).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 8822 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SC., Kim, MS., Yoo, KC. et al. Sensitive fluorescent imaging of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium using a polyvalent directed peptide polymer. Microchim Acta 184, 2611–2620 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2240-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2240-1