Abstract
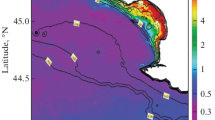
The monthly mean suspended sediment concentration in the upper layer of the East China Seas was derived from the retrieval of the monthly binned SeaWiFS Level 3 data during 1998 to 2006. The seasonal variation and spatial distribution of the suspended sediment concentration in the study area were investigated. It was found that the suspended sediment distribution presents apparent spatial characteristics and seasonal variations, which are mainly affected by the resuspension and transportation of the suspended sediment in the study area. The concentration of suspended sediment is high inshore and low offshore, and river mouths are generally high concentration areas. The suspended sediment covers a much wider area in winter than in summer, and for the same site the concentration is generally higher in winter. In the Yellow and East China Seas the suspended sediment spreads farther to the open sea in winter than in summer, and May and October are the transitional periods of the extension. Winds, waves, currents, thermocline, halocline, pycnocline as well as bottom sediment feature and distribution in the study area are important influencing factors for the distribution pattern. If the 10 mg L-1 contour line is taken as an indicator, it appears that the transportation of suspended sediment can hardly reach 124°00′E in summer or 126°00′E in winter, which is due to the obstruction of the Taiwan Warm Current and the Kuroshio Current in the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, P. K., and S. Z. Yan, 1996. Suspended sediments front and its impacts on the material transport of the Changjiang River. J. East Chin. Norm. Univ. (Natl. Sci.), 1: 85–94.
Deng, M., and Y. Li, 2003. Use of SeaWiFS imagery to detect three-dimensional distribution of suspended sediment. Intl. J. Remote Sens., 24(3): 519–534.
Fan, K. L., 1979. On upwelling off the Peng-hu Islands. Acta Oceanographica Taiwanica, 9: 50–57.
Guan, B. X., 2002. The Flow Opposing the Wind in Winter near the Southeastern Chinese Coast. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao, 1–267 (in Chinese).
Guo, Z. G., Z. S. Yang, D. Q. Zhang, D. J. Fan, and L. Kun, 2002. Seasonal distribution of suspended matter in the northern East China Sea and barrier effect of current circulation on its transport. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 24(5): 71–80.
Jiang, W. S., and W. X. Sun, 2001. 3D suspended particulate matter transportation model in the Bohai Sea II. Simulation results. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 32(1): 94–100.
Jiang, W. S., J. Su, H. Yang, Y. J. Zhang, H. Jiang, Q. W. Wang, et al., 2002. The relationship between SPM concentratin and hydrodynamic condition in the Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 24(suppl): 212–217.
Li, G. X., Z. G. Yang, and Y. Liu, 2005. Study on the Formation of the Seafloor Sediment Environment in the East China Seas. Science Press, Beijing, 1–65 (in Chinese).
Li, S. H., and C. X. Yun, 2006. Coastal current systems and the movement and expansion of suspended sediment from Changjiang River Estuary. Mar. Sci. Bull., 8(1): 22–33.
Li, S. H., J. W. Tang, and C. X. Yun, 2002. A study on the quantitative remote sensing model for the sediment concentration in estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 24(2): 51–58.
Liu, F., H. J. Huang, and A. Gao, 2006. Distribution of suspended matter on the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea and effect of ocean current on its distribution. Mar. Sci., 30(1): 68–72.
Pan, D. L., T. M. Mao, S. J. Li, and H. Q. Huang, 2001. Study on detection of coastal water environment of China by ocean color remote sensing. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 20(1): 51–63.
Qin, Y. S., and F. Li, 1982. Study on the suspended matter of the sea water of the Bohai Gulf. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 4(2): 191–200.
Qin, Y. S., F. Li, S. M. Xu, J. Milliman, and R. Limeburner, 1989. Suspended matter in the South Yellow Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 20(2): 101–112.
Sun, X. G., M. Fang, and W. Huang, 2000. Spatial and temporal variations in suspended particulate matter transport on the Yellow and East China Sea shelf. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 31(6): 581–587.
Tang, Y. X., 1996. Distributional features and seasonal variations of temperature fronts in the East China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 27(4): 436–444.
Tu, J. Z., 1996. Variation and distribution of thermocline layers in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Mar. Sci. Bull., 11(4): 27–32.
Wang, Y. G., and Y. E. Bao, 1996. Mechanisms controlling the transport and dispersion of suspended sediments from the Liaohe Estuary. J. Oceanogr. Huanghai Bohai Seas, 14(1): 33–40.
Whitehouse, R., R. Soulsby, W. Roberts, and H. Mitchener, 2000. Dynamics of Estuarine Muds. Thomas Telford Publishing, Thomas Telford Ltd., London, 1–210.
Wu, Y. S., and Z. Y. Wang, 2002. Effect of the Bohai Sea dynamics on sediment transport discharged from the Yellow River. J. Oceanogr. Huanghai Bohai Seas, 20(2): 22–30.
Yang, Z. S., Z. G. Guo, Z. X. Wang, J. P. Xu, and W. B. Gao, 1992. Basic pattern of transport of suspended matter from the Yellow Sea and East China Sea to the eastern deep seas. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 14(2): 81–90.
Zhao, B. R., and D. M. Cao, 1998. Dynamic analysis and numerical modeling of forming mechanisms of winter circulations in the Bohai Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin., 29(1): 86–95.
Zheng, T. M., Y. Y. Zhao, F. Li, Y. S. Qin, and J. D. Milliman, 1990. Suspended matter in summer of South Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin., 12(6): 749–757.
Zhou, X. B., and W. X. Sun, 2006. Numerical simulation of Lagrangian circulation in the East China Sea II. Simulation of the circulations. Period. Ocean Univ. Chin., 36(1): 7–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Jiang, W. Study on the seasonal variation of the suspended sediment distribution and transportation in the East China Seas based on SeaWiFS data. J. Ocean Univ. China 7, 385–392 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0385-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-008-0385-6