Abstract
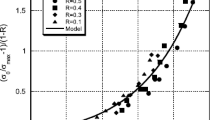
The effect of axial residual stress on the properties of continuous fibre composites is calculated. It is emphasized that composite strength should be considered as a more complex phenomenon than usually done so by merely considering ultimate strength. It is shown that the information contained in σ(ε)-curves if plotted in a more suitable form as hysteresis and set versus total strain, taking into account residual stress, may be a useful means for characterizing the composite and for detecting deviations from perfect structure. Conclusions are derived as to how composite performance may be improved. The results are substantiated by metallic composite data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Hill, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 12 (1964) 213.
A. L. Cunningham and J. A. Alexander, 12th National SAMPE Symposium Anaheim, California (1967).
I. M. Pavlow and A. P. Artamonov, Second International Symposium on Composite Metallic Materials, Bratislava (1975).
A. A. Baker, J. Mater. Sci. 3 (1968) 412.
A. Varschavsky, ibid 7 (1972) 159.
A. Kelly and H. Lilholt, Phil. Mag. 20 (1969) 311.
W. F. Stuhrke, ASTM Special Technical Publication No. 438 (1968) 108.
R. E. Lee and S. J. Harris, J. Mater. Sci. 9 (1974) 359.
P. Neumann and P. Haasen, Phil. Mag. 23 (1971) 285.
K. Tanaka and T. Mori, ibid 23 (1971) 737.
H. Lilholt, in “The Microstructure and Design of Alloys” 36I (1973) p. 237.
D. R. Clarke, in “The Microstructure and Design of Alloys” 36II (1973) p. 1.
K. K. Chawla and M. Metzger, J. Mater. Sci. 7 (1972) 34.
J. R. Hancock and J. C. Grosskreutz, ASTM STP No. 438 (1968) 134.
M. R. Pinnel and A. Lawley, Met. Trans. 1 (1970) 1337.
M. R. Pinnel, D. R. Hay and A. Lawley, ASTM STP No. 438 (1968) 95.
R. L. Mehan, ASTM STP No. 438 (1968) 29.
V. S. Ivanova, I. M. Kop'ev, F. M. Elkin, Yu. E. Busalov, V. I. Beljaev and V. B. Kasperovich, “Aluminievye i magnievye splavy armirovannye voloknami” (izdatel'stvo “Nauka”, Moscow, 1974) pp. 105, 110–120.
N. J. Parrat, Chem. Eng. Prog. 62 (1966) 61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, H.J. The effect of axial residual stress on the mechanical behaviour of composites. J Mater Sci 12, 797–809 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548173
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00548173