Abstract
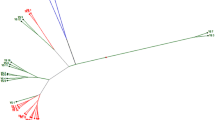
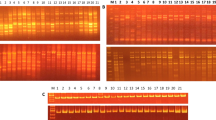
Brassica oleracea L. includes various types of important vegetables that show extremely diverse phenotypes. To elucidate the genetic diversity and relationships among commercial cultivars derived by different companies throughout the world, we characterized the diversity and genetic structure of 91 commercial B. oleracea cultivars belonging to six varietal groups, including cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kohlrabi, kale and kai-lan. We used 69 polymorphic microsatellite markers showing a total of 359 alleles with an average number of 5.20 alleles per locus. Polymorphism information content (PIC) values ranged from 0.06 to 0.73, with an average of 0.40. Among the six varietal groups, kohlrabi cultivars exhibited the highest heterozygosity level, whereas kale cultivars showed the lowest. Based on genetic similarity values, an UPGMA clustering dendrogram and a two-dimensional scale diagram (PCoA) were generated to analyze genetic diversity. The cultivars were clearly separated into six different clusters with a tendency to cluster into varietal groups. Model-based structure analysis revealed six genetic groups, in which cabbage cultivars were divided into two subgroups that were differentiated by their head shape, whereas cauliflower and kai-lan cultivars clustered together into a single group. Furthermore, we identified 18 SSR markers showing 27 unique alleles specific to only one cultivar that can be used to discriminate 22 cultivars from the others. Our phylogenetic and population structure analysis presents new insights into the genetic structure and relationships among 91 B. oleracea cultivars and provides valuable information for breeding of B. oleracea species. In addition, we demonstrate the utility of SSR markers as a powerful tool for discriminating between the cultivars. The SSR markers described herein will also be helpful for Distinctness, Uniformity and Stability (DUS) test of new cultivars.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GC, Flores-Vergara MA, Krasynanski S, Kumar S, Thompson WF (2006) A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nat Protoc 1:2320–2325
Belaj A, Satovic Z, Ismaili H, Panajoti D, Rallo L, Trujillo I (2003) RAPD genetic diversity of Albanian olive germplasm and its relationships with other Mediterranean countries. Euphytica 130:387–395
Bell CJ, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19:137–144
Burgess B, Mountford H, Hopkins CJ, Love C, Ling AE, Spangenberg GC, Edwards D, Batley J (2006) Identification and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers derived in silico from Brassica oleracea genome shotgun sequences. Mol Ecol Notes 6:1191–1194
Cheng X, Xu J, Xia S, Gu J, Yang Y, Fu J, Qian X, Zhang S, Wu J, Liu K (2009) Development and genetic mapping of microsatellite markers from genome survey sequences in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 118:1121–1131
Choi SR, Teakle GR, Plaha P, Kim JH, Allender CJ, Beynon E, Piao ZY, Soengas P, Han TH, King GJ, Barker GC, Hand P, Lydiate DJ, Batley J, Edwards D, Koo DH, Bang JW, Park BS, Lim YP (2007) The reference genetic linkage map for the multinational Brassica rapa genome sequencing project. Theor Appl Genet 115:777–792
Christensen S, Bothmer R, Poulsen G, Maggioni L, Phillip M, Andersen BA, Jørgensen RB (2010) AFLP analysis of genetic diversity in leafy kale (Brassica oleracea L. convar. acephala (DC.) Alef.) landraces, cultivars and wild populations in Europe. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:657–666
Chuang H-Y, Tsao S-J, Lin J-N, Chen K-S, Liou T-D, Chung M-C, Yang Y-W (2004) Genetic diversity andd relationship of non-heading Chinese cabbage in Taiwan. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin 45:331–337
Diederichsen A (2001) Cruciferae: Brassica. In: Hanelt P, Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research (eds) Mansfeld’s encyclopedia of agricultural and horticultural crops. Springer, Berlin, pp 1435–1446
Fahey J, Talalay P (1995) The role of crucifers in cancer chemoprotection. In: Gustine DL, Florens HE (eds) Phytochemicals and health. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockvill, pp 87–93
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Formisano G, Roig C, Esteras C, Ercolano MR, Nuez F, Monforte AJ, Picó MB (2012) Genetic diversity of Spanish Cucurbita pepo landraces: an unexploited resource for summer squash breeding. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59(6):1169–1184
Gepts P (1993) The use of molecular and biochemical markers in crop evolution studies. In: Hecht MK (ed) Evolutionary biology, vol 27. Plenum Press, New York, pp 51–94
Hasan M, Seyis F, Badani AG, Pons-Kühnemann J, Friedt W, Lühs W, Snowdon RJ (2005) Analysis of Genetic Diversity in the Brassica napus L. Gene Pool Using SSR Markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:793–802
Jain S, Jain RK, McCouch SR (2004) Genetic analysis of Indian aromatic and quality rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using panels of fluorescently-labeled microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:965–977
Jarne P, Lagoda PJL (1996) Microsatellites, from molecules to populations and back. Trends in Ecol Evol 11:424–429
Kang J, Fang Z, Wang X, Xu D, Liu Y, Yang L, Zhuang M, Zhang Y (2011) Genetic diversity and relationships among cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) landraces in China revealed by AFLP markers. Afr J Biotechnol 32:5940
Kianian SF, Quiros CF (1992) Trait inheritance, fertility and genomic relationships of some n = 9 Brassica species. Genet Resour Crop Evol 39:165–175
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: integrated analysis environment for genetic marker data. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Louarn S, Torp AM, Holme IB, Andersen SB, Jensen BD (2007) Database derived microsatellite markers (SSRs) for cultivar differentiation in Brassica oleracea. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1717–1725
Lowe AJ, Moule C, Trick M, Edwards KJ (2004) Efficient large-scale development of microsatellites for marker and mapping applications in Brassica crop species. Theor Applied Genet 108:1103–1112
Lu X, Liu L, Gong Y, Zhao L, Song X, Zhu X (2009) Cultivar identification and genetic diversity analysis of broccoli and its related species with RAPD and ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 122:645–648
Lukens LN, Quijada PA, Udall J, Pires JC, Schranz ME, Osborn TC (2004) Genome redundancy and plasticity within ancient and recent Brassica crop species. Biol J Linn Soc 82:665–674
Marquez-Lema A, Velasco L, Perez-Vich B (2010) Transferability, amplification quality and genome specifity of microsatellites in Brassica carinata and related species. J Appl Genet 51:123–131
Moxon ER, Wills C (1999) DNA microsatellites: agents of evolution? Sci Am 280:94–99
Nienhuis J, Sills G (1992) The potential of hybrid varieties in self-pollinated vegetables. In: Dattee Y, Dumas C, Gallais A (eds) Reproductive biology and plant breeding. Springer, Berlin, pp 387–396
Paterson AH, Lan T-h, Amasino R, Osborn TC, Quiros C (2001) Brassica genomics: a complement to, and early beneficiary of, the Arabidopsis sequence. Genome Biology 2:1011.1011–1011.1014
Piquemal J, Cinquin E, Couton F, Rondeau C, Seignoret E, Doucet I, Perret D, Villeger M-J, Vincourt P, Blanchard P (2005) Construction of an oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) genetic map with SSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 111:1514–1523
Plieske J, Struss D (2001) Microsatellite markers for genome analysis in Brassica. I. development in Brassica napus and abundance in Brassicaceae species. Theor Appl Genet 102:689–694
Powel W, Machray GC, Povan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1:215–222
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Purugganan MD, Boyles AL, Suddith JI (2000) Variation and Selection at the CAULIFLOWER Floral Homeotic Gene Accompanying the Evolution of Domesticated Brassica oleracea. Genetics 155:855–862
Quiros CF, Farnham MW (2011) The genetics of Brassica oleracea. In: Schmidt R, Bancroft I (eds) Genetics and genomics of the Brassicaceae. Springer Science+Business Media, Berlin, pp 261–289
Riaz A, Li G, Quresh Z, Swati MS, Quiroz CF (2001) Genetic diversity of oilseed rape inbred lines based on SRAP and its relation to hybrid perfomance. Plant Breeding 120:411–415
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-PC, numerical taxonomy system for the PC, ExeterSoftware, Ver. 2.1. Applied Biostatistics Inc, Setauket
Santos JBd, Nienhuis J, Skroch P, Tivang J, Slocum MK (1994) Comparison of RAPD and RFLP genetic markers in determining genetic similarity among Brassica oleracea L. genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 87:909–915
Shengwu H, Ovesna J, Kucera L, Vyvadilova M (2003) Evaluation of genetic diversity of Brassica napus germplasm from China and Europe assessed by RAPD markers. Plant Soil Environ 49:106–113
Smith LB, King GJ (2000) The distribution of BoCAL-a alleles in Brassica oleracea ia consistent with a genetic model for curd development and domestication of the cauliflower. Mol Breed 6:603–613
Smith OS, Smith JSC, Bowen SL, Tenborg RA, Wall SJ (1990) Similarities among a group of elite maize inbreds as measured by pedigree, F1 grain yield, grain yield, heterosis, and RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 80:833–840
Song KM, Osborn TC, William PH (1988) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) 2. Preliminary analysis of subspecies within B. rapa (syn. campestris) and B. oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 76:593–600
Song K, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1990) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) 3. Genome relationships in Brassica and related genera and the origin of B. oleracea and B. rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Genet 79:497–506
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Kage T, Hirai M (2002) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 104:1092–1098
Syed NH, Chen ZJ (2005) Molecular marker genotypes, heterozygosity and genetic interactions explain heterosis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Heredity 94(3):295–304
Tonguc M, Griffiths PD (2004) Genetic relationship of Brassica vegetables determined using database derived simple sequence repeats. Euphytica 137:193–201
van Hintum TJ, van de Wiel CC, Visser DL, van Treuren R, Vosman B (2007) The distribution of genetic diversity in a Brassica oleracea gene bank collection related to the effects on diversity of regeneration, as measured with AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 114:777–786
Zhang Q, Zhou ZQ, Yang GP, Xu CG, Liu KD, Maroof MAS (1996) Molecular markers heterozygosity and hybrid performance in indica and japonica rice. Theor Appl Genet 93:1218–1224
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program (No. 309008-05) for Agriculture and Forestry, Ministry of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Republic of Korea. Nur Kholilatul Izzah is supported by the Islamic Development Bank (IDB), Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Izzah, N.K., Lee, J., Perumal, S. et al. Microsatellite-based analysis of genetic diversity in 91 commercial Brassica oleracea L. cultivars belonging to six varietal groups. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60, 1967–1986 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-013-9966-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-013-9966-3