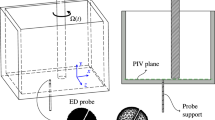
Abstract
Three-segment electrodiffusion probes embedded in a wall allow to determine simultaneously the three kinematic parameters of flow close to the probe surface: the flow directionθ, the wall shear rateq, and the normal velocity coefficientA,v z = −A z 2. A well-controlled three-dimensional flow, generated by a rotating disk, was used to demonstrate the capabilities of this new kind of electrodiffusion probes by comparing experimental results with the prediction based on the well-known hydrodynamical theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
normal flow coefficient, Eq. (1)
- A :
-
axis of the adjustment rod, Fig. 2
- c 0 :
-
concentration of depolarizer (mol/m3)
- D :
-
diffusivity of depolarizer (m2/s)
- E :
-
correction of total current on normal flow effect
- e x :
-
reference direction of the probe, Figs. 1 and 3
- F :
-
Faraday constant (F = 96,464 C/mol)
- F s :
-
normalized directional characteristic fors-th segment
- f sm ,g sm :
-
Fourier coefficients of directional characteristics, Eq. (4) and Table 3
- h m :
-
corrections of Fourier coefficients on normal flow effect, Eqs. (4) and (7)
- i s :
-
limiting diffusion current throughs-th segment (A)
- i tot (r):
-
total current through the probe in dependence on its eccentricity (A)
- K :
-
transport coefficient, Eqs. (3) and (5)
- n :
-
number of electrons involved in redox reaction
- O :
-
axis of the rotating disk, Fig. 2
- P :
-
centre of the probe, Fig. 2
- q :
-
magnitude of vectorial wall shear rate (s-1)
- q x ,q y :
-
components of vectorial wall shear rate
- Q :
-
ratio of the currents in an eccentric and the central position of the probe, Eq. (15)
- r :
-
radial coordinate, eccentricity of the probe
- r A :
-
eccentricity of the adjustment rod (r A =Ō Ā, Fig. 2)
- r, Φ, z :
-
polar coordinates on the rotating disk
- R :
-
effective radius of the probe (R = 0.337 mm)
- S :
-
macroscopic area of the probe (S = 0.357 mm2)
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates moving with the probe
- α :
-
adjustment angle, Figs. 2 and 3
- β :
-
angle included between local radius-vectorō ¯P of the probe and local direction of flow, Fig. 3
- θ :
-
angle included between reference directione x of the probe and local direction of flow, Fig. 3
- θ 0 :
-
theoretical prediction ofθ, Eq. (11)
- x 0 :
-
theoretical prediction ofx, Eq. (14)
- x exp x :
-
calculated from experimental data using Eq. (4)
- v :
-
kinematic viscosity (m2/s)
- σ :
-
angle implied between gradient ofq and direction of flow, Eq. (8)
- Ω :
-
angular speed of the rotating disk (rad/s)
References
Chin, D. T.; Litt, M. 1972: Mass transfer to point electrodes on the surface of a rotating disk. J. Electrochem. Soc. 119, 1338–1343
Hanratty, T. J.; Campbell, J. A. 1983: Measurement of wall shear stress. In: Fluid mechanics measurements (ed. Goldstein, R. J.). pp 559–615
Levich, V. G. 1962: Physicochemical hydrodynamics. New York: Prentice Hall
Menzel, Th.; Sobolik, V.; Wein, O.; Onken, U. 1987a: Segmentierte Elektrodiffusionssonden zur Messung des Wandschergeschwindigkeitsvektors. Chem.-Ing.-Tech. 59, 492–493
Menzel, Th.; Sobolik, V.; Onken, U.; Čermák, J. 1987b: Electrodiffusional probe for direction specific shear rate measurement. 9th Internat. Congress CHISA '87, Prague, Czechoslovakia
Mollet, L.; Dumargue, P.; Daguenet, M.; Bodiot, D. 1974: Calcul du flux limite de diffusion sur une microélectrode de section circulaire — équivalence avec une électrode de section rectangulaire. Vérification experimentale dans le cas du disque tournant en regime laminaire. Electrochim. Acta 19, 841–844
Nakoryakov, V. E.; Burdukov, A. P.; Kashinsky, O. N.; Geshev, P. I. 1986: Electrodiffusion method of investigation of turbulent flows. Novosibirsk: Institute of Thermophysics (in Russian)
Pauli, J.; Menzel, Th.; Onken U. 1989: Directional specific shear rate measurements in gas-liquid two-phase flow. Chem. Eng. Process, (in press)
Py, B.; Gosse, J. 1969: Sur la réalisation d'une sonde polarographique sensible à la direction de l'écoulement. C. R. Acad. Sci. 269, 401–405
Robertson, B.; Tribollet, B.; Deslouis, C. 1988: Measurement of diffusion coefficients by DC and EHD electrochemical methods. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 2279–2284
Schlichting, H. 1960: Boundary layer theory. New York: McGraw-Hill
Sobolik, V.; Mitschka, P.; Menzel, Th. 1986: Method of manufacture of segmented probe with circular cross-section. Czechoslovak Pat. AO 262 823
Wein, O.; Pokryvaylo, N. A. 1982: Convective diffusion to a rotating sphere electrode. Inzh. Phys. Zhurn. 43, 448–455 (in Russian)
Wein, O.; Sobolík, V. 1989: Segmented electrodiffusion probes simultaneous measurement of shear rate and normal flow component. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobolík, V., Wein, O., Gil, O. et al. Three-segment electrodiffusion probes for measuring velocity fields close to a wall. Experiments in Fluids 9, 43–48 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00575334
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00575334