Abstract
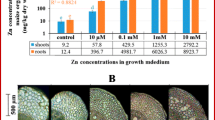
The effects of zinc (Zn) on seed germination and growth of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) were investigated. Under zinc stress, the seed germination rate did not show significant difference from that of the control. Hydroponics experiments indicated that Moso bamboo had a strong ability to accumulate Zn in the shoot and it reached its maximum value in the shoot at 100 μM Zn. The root Zn concentration ranged from 2,329.29 to 8,642.51 mg kg−1, with the root Zn concentration at 10 μM Zn being 58.23 times that of the control. The root morphology parameters slightly increased at the lower Zn treatments, while growth restriction was evident at higher Zn treatments. Root ultrastructural studies revealed that the cell structure, root tips, and organelles were significantly changed under Zn stress as compared to those of the control. Some abnormalities were evident in the cell walls, vacuoles, mitochondria, plasmalemma, tonoplast, and xylem parenchyma of root cells. While Moso bamboo seems a suitable candidate for phytoremediation, its metal remediation ability should be further explored in future investigations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anamika S, Eapen S, Fulekar MH (2009) Phytoremediation of cadmium, lead and zinc by Brassica juncea L. Czern and Coss. J Appl Biosci 13:726–736
Andrade SAL, Gratão PL, Schiavinato MA, Silveira AP, Azevedo RA, Mazzafera P (2009) Zn uptake, physiological response and stress attenuation in mycorrhizal jack bean growing in soil with increasing Zn concentrations. Chemosphere 75(10):1363–1370
Azzarello E, Pandolfi C, Giordano C, Rossi M, Mugnai S, Mancuso S (2012) Ultramorphological and physiological modifications induced by high zinc levels in Paulownia tomentosa. Environ Exp Bot 81:11–17
Chen H, Hong W, Lan B, Zheng YS, He DJ (1998) Study on biomass and productivity of Phyllostachys heterocycala cv. Pubescens forest in the north of Fujian. Sci Silvae Sin 34(S1):60–64 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen XG, Zhang XQ, Zhang YP, Booth T, He XH (2009) Changes of carbon stocks in bamboo stands in China during 100 years. Forest Ecol Manag 258(7):1489–1496
Cherif J, Derbel N, Nakkach M, Hv B, Jemal F, Lakhdar ZB (2010) Analysis of in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence spectra to monitor physiological state of tomato plants growing under zinc stress. J Photochem Photobiol B 101(3):332–339
Heumann HG (2002) Ultrastructural localization of zinc in zinc-tolerant Armeria maritima ssp. halleri by autometallography. J Plant Physiol 159(2):191–203
Hu PJ, Qiu RL, Senthilkumar P, Jiang D, Chen ZW, Tang YT, Liu FJ (2009) Tolerance, accumulation and distribution of zinc and cadmium in hyperaccumulator Potentilla griffithii. Environ Exp Bot 66(2):317–325
Islam E, Yang XE, Li TQ, Liu D, Jin XF, Meng FH (2007) Effect of Pb toxicity on root morphology, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 147(3):806–816
Jain R, Srivastava S, Solomon S, Shrivastava AK, Chandra A (2010) Impact of excess zinc on growth parameters, cell division, nutrient accumulation, photosynthetic pigments and oxidative stress of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Acta Physiol Plant 32(5):979–986
Jin XF, Yang XE, Islam E, Liu D, Mahmood Q, Li H, Li JY (2008) Ultrastructural changes, zinc hyperaccumulation and its relation with antioxidants in two ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. Plant Physiol Biochem 46(11):997–1006
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Corréal E, Zanuzzi A, Lutts S (2009) Variation in response to heavy metals during vegetative growth in Dorycnium pentaphyllum Scop. Plant Growth Regul 59(1):1–11
Li J, Huang ZY, Hu Y, Yang H (2013) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals by consuming shellfish collected from Xiamen, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(5):2937–2947
Lingua G, Franchin C, Todeschini V, Castiglione S, Biondi S, Burlando B, Parravicini V, Torrigiani P, Berta G (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi differentially affect the response to high zinc concentrations of two registered poplar clones. Environ Pollut 153(1):137–147
Lone MI, He ZL, Stoffella PJ, Yang XE (2008) Phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted soils and water: progresses and perspectives. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9(3):210–220
Michael PI, Krishnaswamy M (2011) The effect of zinc stress combined with high irradiance stress on membrane damage and antioxidative response in bean seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 74:171–177
Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants. Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 193–229
Rout GR, Das P (2003) Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism: I. Zinc. Agronomie 23(1):3–11
Shimokawa T, Ishida M, Yoshida S, Nojiri M (2009) Effects of growth stage on enzymatic saccharification and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of bamboo shoots for bioethanol production. Bioresour Technol 100(24):6651–6654
Singh OV, Labana S, Pandey G, Budhiraja R, Jain RK (2003) Phytoremediation: an overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61(5–6):405–412
Song XZ, Peng CH, Zhou GM, Jiang H, Wang WG, Xiang WH (2013) Climate warming-induced upward shift of Moso bamboo population on Tianmu Mountain, China. J Mt Sci Engl 10(3):363–369
Stoyanova Z, Doncheva S (2002) The effect of zinc supply and succinate treatment on plant growth and mineral uptake in pea plant. Braz J Plant Physiol 14(2):111–116
Tang YT, Qiu RL, Zeng XW, Ying RR, Yu FM, Zhou XY (2009) Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 66(1):126–134
Wang C, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Hou J, Zhang WJ, Li W, Lin ZP (2009) The effect of excess Zn on mineral nutrition and antioxidative response in rapeseed seedlings. Chemosphere 75(11):1468–1476
Watanabe ME (1997) Phytoremediation on the brink of commercialization. Environ Sci Technol 31(4):182A–186A
Xu Y, Wong MH, Yang JL, Ye ZQ, Jiang PK, Zheng SJ (2011) Dynamics of carbon accumulation during the fast growth period of bamboo plant. Bot Rev 77(3):287–295
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (31300520), Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation of China (LY12C16004), and Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (2014C33043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Chen, J., Mahmood, Q. et al. Effect of Zn toxicity on root morphology, ultrastructure, and the ability to accumulate Zn in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 13615–13624 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3271-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3271-3