Abstract
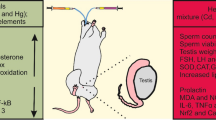
Mercury (Hg) is a heavy metal toxicant, causing several adverse reactions to animals and humans including reproductive dysfunction. The potential protective role of Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract (ZSCLE) against testicular impairments associated with mercury chloride (HgCl2) exposure in rats was investigated in the current study. Four experimental groups were employed as follows (n = 7): group I served as control, group II was gavaged with ZSCLE (300 mg/kg), group III was administered with HgCl2 (0.4 mg/kg), and group IV was preadministered with ZSCLE 1 h before HgCl2. All groups were treated daily for 28 days. The exposure to HgCl2 caused a marked increase in Hg concentration in the testicular tissue, which was accompanied with a decrease in testis index. A reproductive impairment was recorded following HgCl2 exposure as verified through the decrease in levels of testosterone, luteinizing, and follicle-stimulating hormones. HgCl2 was found to enhance the development of oxidative damage in the testicular tissue as presented by the imbalance between pro-oxidants and antioxidant molecules. In addition, excessive release of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β was recorded in response to HgCl2 intoxication. Furthermore, a disturbance in the apoptotic proteins in favor of the pro-apoptotic proteins was also observed following HgCl2 intoxication. However, ZSCLE administration along with HgCl2 abolished significantly the molecular, biochemical, and histopathological alterations induced by HgCl2 intoxication. Our findings suggest that ZSCLE could be used to mitigate reproductive dysfunction associated with HgCl2 exposure.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- FSH:
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- Hg:
-
Mercury
- HgCl2 :
-
Mercury chloride
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- LH:
-
Luteinizing hormone
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- ZSCLE:
-
Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract
References
Abarikwu SO, Benjamin S, Ebah SG, Obilor G, Agbam G (2017) Oral administration of Moringa oleifera oil but not coconut oil prevents mercury-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Andrologia:49. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12597
Abdelfattah MS, Elmallah MIY, Ebrahim HY, Almeer RS, Eltanany RMA, Abdel Moneim AE (2019) Prodigiosins from a marine sponge-associated actinomycete attenuate HCl/ethanol-induced gastric lesion via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. PLoS One 14:e0216737
Ads DE, Rajendrasozhan S, Hassan S, Sharawy S, Humaidi J (2018) Phytochemical screening of different organic crude extracts from the stem bark of Ziziphus spina-christi (L.). 29. https://doi.org/10.4066/biomedicalresearch.29-17-1668
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Albasher G, Albrahim T, Alsultan N, Alfaraj S, Alharthi MS, Kassab RB, Abdel Moneim AE (2019) Red beetroot extract mitigates chlorpyrifos-induced reprotoxicity associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07009-6
Al Omairi NE, Radwan OK, Alzahrani YA, Kassab RB (2018) Neuroprotective efficiency of Mangifera indica leaves extract on cadmium-induced cortical damage in rats. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0222-6
Alabi OA, Esan BE, Sorungbe AA (2017) Genetic, Reproductive and hematological toxicity induced in mice exposed to leachates from petrol, diesel and kerosene dispensing sites. J Health Pollut 7:58–70. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-7.16.58
Al-Brakati AY, Kassab RB, Lokman MS, Elmahallawy EK, Amin HK, Abdel Moneim AE (2019) Role of thymoquinone and ebselen in the prevention of sodium arsenite-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 38:482–493. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327118818246
Almeer RS, El-Khadragy MF, Abdelhabib S, Abdel Moneim AE (2018a) Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract ameliorates schistosomiasis liver granuloma, fibrosis, and oxidative stress through downregulation of fibrinogenic signaling in mice. PLoS One 13:e0204923. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204923
Almeer RS, Mahmoud SM, Amin HK, Abdel Moneim AE (2018b) Ziziphus spina-christi fruit extract suppresses oxidative stress and p38 MAPK expression in ulcerative colitis in rats via induction of Nrf2 and HO-1 expression. Food Chem Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.03.002
Almeer RS et al (2018c) Royal jelly abrogates cadmium-induced oxidative challenge in mouse testes: involvement of the Nrf2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123979
Baxter DC, Frech W (1989) Determination of mercury by atomic absorption spectrometry using a platinum-lined graphite furnace for in situ preconcentration. Anal Chim Acta 225:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)84605-X
Bhatia A, Mishra T (2010) Hypoglycemic activity of Ziziphus mauritiana aqueous ethanol seed extract in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Pharm Biol 48:604–610. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880200903218935
Boujbiha MA, Hamden K, Guermazi F, Bouslama A, Omezzine A, Kammoun A, El Feki A (2009) Testicular toxicity in mercuric chloride treated rats: association with oxidative stress. Reprod Toxicol 28:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2009.03.011
Boujbiha MA et al (2012) Hematotoxicity and genotoxicity of mercuric chloride following subchronic exposure through drinking water in male rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 148:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9342-8
Darbandi M, Darbandi S, Agarwal A, Sengupta P, Durairajanayagam D, Henkel R, Sadeghi MR (2018) Reactive oxygen species and male reproductive hormones. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-018-0406-2
De Vega L, Fernandez RP, Mateo MC, Bustamante JB, Herrero AM, Munguira EB (2002) Glutathione determination and a study of the activity of glutathione-peroxidase, glutathione-transferase, and glutathione-reductase in renal transplants. Ren Fail 24:421–432
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Diab MM, Othman MS, Aref AM, Abdel Moneim AE (2014) The potential protective role of Physalis peruviana L. fruit in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 74:98–106
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel Moneim AE (2018a) Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract pretreatment inhibits liver and spleen injury in a mouse model of sepsis via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0439-8
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Moneim AEA (2018b) Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract pretreatment inhibits liver and spleen injury in a mouse model of sepsis via anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0439-8
Dkhil MA, Kassab RB, Al-Quraishy S, Abdel-Daim MM, Zrieq R, Abdel Moneim AE (2018c) Ziziphus spina-christi (L.) leaf extract alleviates myocardial and renal dysfunction associated with sepsis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 102:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.032
El-Desoky GE, Bashandy SA, Alhazza IM, Al-Othman ZA, Aboul-Soud MA, Yusuf K (2013) Improvement of mercuric chloride-induced testis injuries and sperm quality deteriorations by Spirulina platensis in rats. PLoS One 8:e59177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059177
El-Din MS, Taha AM, Sayed AA, Salem AM (2019) Ziziphus spina-christi leaves methanolic extract alleviates diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Biochem Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2018-0318
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Ferrer-Sueta G, Radi R (2009) Chemical biology of peroxynitrite: kinetics, diffusion, and radicals. ACS Chem Biol 4:161–177. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb800279q
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Hansen JM, Zhang H, Jones DP (2006) Differential oxidation of thioredoxin-1, thioredoxin-2, and glutathione by metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 40:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.09.023
Hazelhoff MH, Bulacio RP, Chevalier A, Torres AM (2018) Renal expression of organic anion transporters is modified after mercuric chloride exposure: gender-related differences. Toxicol Lett 295:390–396
Hong EH, Song JH, Kang KB, Sung SH, Ko HJ, Yang H (2015) Anti-influenza activity of Betulinic acid from Zizyphus jujuba on influenza a/PR/8 virus. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 23:345–349. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2015.019
Hussain S, Atkinson A, Thompson SJ, Khan AT (1999) Accumulation of mercury and its effect on antioxidant enzymes in brain, liver, and kidneys of mice. J Environ Sci Health B 34:645–660. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601239909373219
Jiang X et al (2018) Lactobacillus brevis 23017 relieves mercury toxicity in the colon by modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation through the interplay of MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling cascades. Front Microbiol 9:2425. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02425
Kadioglu O et al (2016) Evaluating ancient Egyptian prescriptions today: anti-inflammatory activity of Ziziphus spina-christi. Phytomedicine 23:293–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.01.004
Kalender S, Uzun FG, Demir F, Uzunhisarcıklı M, Aslanturk A (2013) Mercuric chloride-induced testicular toxicity in rats and the protective role of sodium selenite and vitamin E. Food Chem Toxicol 55:456–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.01.024
Li A et al (2018) Hepatorenal protective effects of medicinal herbs in An-Gong-Niu-Huang Wan (AGNH) against cinnabar- and realgar-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory damage in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 119:445–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.054
Liu B et al (2018) Protective effects of dietary luteolin against mercuric chloride-induced lung injury in mice: involvement of AKT/Nrf2 and NF-kappaB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol 113:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.02.003
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mailloux RJ (2018) Mitochondrial antioxidants and the maintenance of cellular hydrogen peroxide levels. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2018:7857251. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7857251
Martinez CS et al (2014) 60-Day chronic exposure to low concentrations of HgCl2 impairs sperm quality: hormonal imbalance and oxidative stress as potential routes for reproductive dysfunction in rats. PLoS One 9:e111202. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111202
Martinez CS et al (2017) Reproductive dysfunction after mercury exposure at low levels: evidence for a role of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) 1 and GPx4 in male rats. Reprod Fertil Dev 29:1803–1812. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD16310
Mathur S, Hoskins C (2017) Drug development: lessons from nature. Biomed Rep 6:612–614. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2017.909
Mohammadi S, Movahedin M, Mowla S (2008) Antioxidant effects of selenium on sperm parameters and testicular structure in young and aged mice. J Reprod Infert 9:229–238
Moneim AE (2015) Mercury-induced neurotoxicity and neuroprotective effects of berberine. Neural Regen Res 10:881–882. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.158336
Naik SR, Bhagat S, Shah PD, Tare AA, Ingawale D, Wadekar RR (2013) Evaluation of anti-allergic and anti-anaphylactic activity of ethanolic extract of Zizyphus jujuba fruits in rodents. Rev Bras 23:811–818. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2013000500014
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Opferman JT, Kothari A (2018) Anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members in development. Cell Death Differ 25:37–45
Orr SE, Bridges CC (2017) Chronic kidney disease and exposure to nephrotoxic metals. Int J Mol Sci 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051039
Othman MS, Safwat G, Aboulkhair M, Abdel Moneim AE (2014) The potential effect of berberine in mercury-induced hepatorenal toxicity in albino rats. Food Chem Toxicol 69:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.012
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Perron NR, Brumaghim JL (2009) A review of the antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenol compounds related to iron binding. Cell Biochem Biophys 53:75–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9043-x
Shahat AA, Pieters L, Apers S, Nazeif NM, Abdel-Azim NS, Berghe DV, Vlietinck AJ (2001) Chemical and biological investigations on Zizyphus spina-christi L. Phytother Res 15:593–597
Tan X et al (2018) Dietary luteolin protects against HgCl2-induced renal injury via activation of Nrf2-mediated signaling in rat. J Inorg Biochem 179:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.11.010
Teixeira FB, de Oliveira ACA, Leão LKR, Fagundes NCF, Fernandes RM, Fernandes LMP, da Silva MCF, Amado LL, Sagica FES, de Oliveira EHC, Crespo-Lopez ME, Maia CSF, Lima RR (2018) Exposure to inorganic mercury causes oxidative stress, cell death, and functional deficits in the motor cortex. Front Mol Neurosci 11:125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00125
Unoki T, Akiyama M, Kumagai Y, Goncalves FM, Farina M, da Rocha JBT, Aschner M (2018) Molecular pathways associated with methylmercury-induced Nrf2 modulation. Front Genet 9:373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00373
Venkatesan RS, Sadiq AM (2017) Effect of morin-5′-sulfonic acid sodium salt on the expression of apoptosis related proteins caspase 3, Bax and Bcl 2 due to the mercury induced oxidative stress in albino rats. Biomed Pharmacother 85:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.090
Yin M et al (2019) Oleuropein suppresses oxidative, inflammatory, and apoptotic responses following glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Life Sci 232:116634
Yousef AS, Fahad AA, Abdel Moneim AE, Metwally DM, El-Khadragy MF, Kassab RB (2019) The neuroprotective role of coenzyme Q10 against lead acetate-induced neurotoxicity is mediated by antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activities. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16162895
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Research Supporting Project number: RSP-2019/96, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for supporting the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeer, R.S., Albasher, G., Kassab, R.B. et al. Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract attenuates mercury chloride-induced testicular dysfunction in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 3401–3412 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07237-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07237-w