Abstract
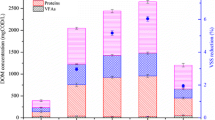
Anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge (WAS) for recycling valuable volatile fatty acids (VFAs) is economically valuable. However, the fermentation of protein is the rate-limiting step of VFA production with WAS as a substrate. In this study, the effect of redox mediators (RMs, i.e., riboflavin and lawsone) on the enhanced production of VFAs from WAS was investigated. The results indicate that both RMs can promote protein-dependent fermentation, increasing maximum VFA accumulation by 43.9% and 42.5% respectively. In cultures supplemented with riboflavin and lawsone, VFA production was highly correlated with protease activities, but not with α-glucosidase activities. This implies that RMs affected the redox reaction of amino acids degradation, resulting in an increased release of ammonia. Sequencing results showed that RMs significantly increased the abundance of bacteria related to VFA fermentation and protein/amino acid degradation at the levels of phylum, class, order, family, and even genus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1998) Standard methods for analysis of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Alexandria
Ariesyady HD, Ito T, Okabe S (2007) Functional bacterial and archaeal community structures of major trophic groups in a full-scale anaerobic sludge digester. Water Res 41:1554–1568
Baeta BEL, Aquino SFD, Silva SDQ, Rabelo CA (2012) Anaerobic degradation of azo dye Drimaren blue HFRL in UASB reactor in the presence of yeast extract a source of carbon and redox mediator. Biodegradation 23:199–208
Bermúdez-Penabad N, Kennes C, Veiga MC (2017) Anaerobic digestion of tuna waste for the production of volatile fatty acids. Waste Manag 68:96–102
Brutinel ED, Gralnick JA (2012) Shuttling happens: soluble flavin mediators of extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:41–48
Cervantes FJ, Van Der Velde S, Lettinga G, Field JA (2000) Competition between methanogenesis and quinone respiration for ecologically important substrates in anaerobic consortia. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 34:161–171
Chen Y, Jiang S, Yuan H, Zhou Q, Gu G (2007) Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res 41:683–689
Chen H, Yan SH, Ye ZL, Meng HJ, Zhu YG (2012) Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1454–1463
Chen Y, Luo J, Yan Y, Feng L (2013) Enhanced production of short-chain fatty acid by co-fermentation of waste activated sludge and kitchen waste under alkaline conditions and its application to microbial fuel cells. Appl Energy 102:1197–1204
Dai R, Chen X, Ma C, Xiang X, Li G (2016) Insoluble/immobilized redox mediators for catalyzing anaerobic bio-reduction of contaminants. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 15:379–409
de Bruin W, Kritzinger Q, Bornman R, Korsten L (2019) Occurrence, fate and toxic effects of the industrial endocrine disrupter, nonylphenol, on plants-a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 181:419–427
de Vladar HP (2012) Amino acid fermentation at the origin of the genetic code. Biol Direct 7:6
Duan X, Wang X, Xie J, Feng L, Yan Y, Zhou Q (2016) Effect of nonylphenol on volatile fatty acids accumulation during anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Res 105:209–217
Feng Y, Zhang Y, Quan X, Chen S (2014) Enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge digestion by the addition of zero valent iron. Water Res 52:242–250
Gonzalez A, Hendriks A, van Lier J, de Kreuk M (2018) Pre-treatments to enhance the biodegradability of waste activated sludge: elucidating the rate limiting step. Biotechnol Adv 36:1434–1469
Gulhane M, Pandit P, Khardenavis A, Singh D, Purohit H (2017) Study of microbial community plasticity for anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste in anaerobic baffled reactor. Renew Energy 101:59–66
Hu J, Xu Q, Li X, Wang D, Zhong Y, Zhao J, Zhang D, Yang Q, Zeng G (2018a) Sulfamethazine (SMZ) affects fermentative short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Sci Total Environ 639:1471–1479
Hu J, Zhao J, Wang D, Li X, Zhang D, Xu Q, Peng L, Yang Q, Zeng G (2018b) Effect of diclofenac on the production of volatile fatty acids from anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 254:7–15
Hu K, Xu L, Chen W, Jia SQ, Wang W, Han F (2018c) Degradation of organics extracted from dewatered sludge by alkaline pretreatment in microbial electrolysis cell. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:8715–8724
Huang X, Mu T, Shen C, Lu L, Liu J (2016a) Effects of bio-surfactants combined with alkaline conditions on volatile fatty acid production and microbial community in the anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 114:24–30
Huang J, Zhou R, Chen J, Han W, Chen Y, Wen Y, Tang J (2016b) Volatile fatty acids produced by co-fermentation of waste activated sludge and henna plant biomass. Bioresour Technol 211:80–86
Li N, He J, Yan H, Chen S, Dai X (2017) Pathways in bacterial and archaeal communities dictated by ammonium stress in a high solid anaerobic digester with dewatered sludge. Bioresour Technol 241:95–102
Li J, Hao X, van Loosdrecht MC, Luo Y, Cao D (2019) Effect of humic acids on batch anaerobic digestion of excess sludge. Water Res 155:431–443
Liu K, Chen Y, Xiao N, Zheng X, Li M (2015) Effect of humic acids with different characteristics on fermentative short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Environ Sci Technol 49:4929–4936
Luo J, Feng L, Zhang W, Li X, Chen H, Wang D, Chen Y (2014) Improved production of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge driven by carbohydrate addition in continuous-flow reactors: influence of SRT and temperature. Appl Energy 113:51–58
Masuda M, Freguia S, Wang YF, Tsujimura S, Kano K (2010) Flavins contained in yeast extract are exploited for anodic electron transfer by Lactococcus lactis. Bioelectrochemistry 78:173–175
Pei D, Xiao C, Hu Q, Tang J (2016) Electrokinetic gathering and removal of heavy metals from sewage sludge by ethylenediamine chelation. Procedia Environ Sci 31:725–734
Ramsay IR, Pullammanappallil PC (2001) Protein degradation during anaerobic wastewater treatment: derivation of stoichiometry. Biodegradation 12:247–256
Rao Y, Wan J, Liu Y, Angelidaki I, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Luo G (2018) A novel process for volatile fatty acids production from syngas by integrating with mesophilic alkaline fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Res 139:372–380
Shao M, Guo L, She Z, Gao M, Zhao Y, Sun M, Guo Y (2019) Enhancing denitrification efficiency for nitrogen removal using waste sludge alkaline fermentation liquid as external carbon source. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4633–4644
Shen D, Yin J, Yu X, Wang M, Long Y, Shentu J, Chen T (2017) Acidogenic fermentation characteristics of different types of protein-rich substrates in food waste to produce volatile fatty acids. Bioresour Technol 227:125–132
van der Zee FP, Cervantes FJ (2009) Impact and application of electron shuttles on the redox (bio) transformation of contaminants: a review. Biotechnol Adv 27:256–277
van der Zee FP, Bisschops IA, Lettinga G, Field JA (2003) Activated carbon as an electron acceptor and redox mediator during the anaerobic biotransformation of azo dyes. Environ Sci Technol 37:402–408
Wang C, Liu Y, Jin S, Chen H, Xu X, Wang Z, Xing B, Zhu L (2019) Responsiveness extracellular electron transfer (EET) enhancement of anaerobic digestion system during start-up and starvation recovery stages via magnetite addition. Bioresour Technol 272:162–170
Watanabe K, Manefield M, Lee M, Kouzuma A (2009) Electron shuttles in biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:633–641
Xie J, Chen Y, Duan X, Feng L, Yan Y, Wang F, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Zhou Q (2019) Activated carbon promotes short-chain fatty acids production from algae during anaerobic fermentation. Sci Total Environ 658:1131–1138
Xiong JQ, Govindwar S, Kurade MB, Paeng KJ, Roh HS, Khan MA, Jeon BH (2019) Toxicity of sulfamethazine and sulfamethoxazole and their removal by a green microalga, Scenedesmus obliquus. Chemosphere 218:551–558
Yang X, Du M, Lee DJ, Wan C, Zheng L, Wan F (2012) Improved volatile fatty acids production from proteins of sewage sludge with anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) under anaerobic condition. Bioresour Technol 103:494–497
Yang G, Zhang P, Zhang G, Wang Y, Yang A (2015) Degradation properties of protein and carbohydrate during sludge anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 192:126–130
Ye T, Li X, Zhang T, Su Y, Zhang W, Li J, Gan Y, Zhang A, Liu Y, Xue G (2018) Copper(II) addition to accelerate lactic acid production from co-fermentation of food waste and waste activated sludge: understanding of the corresponding metabolisms, microbial community and predictive functional profiling. Waste Manag 76:414–422
Yin J, Yu X, Zhang Y, Shen D, Wang M, Long Y, Chen T (2016) Enhancement of acidogenic fermentation for volatile fatty acid production from food waste: effect of redox potential and inoculum. Bioresour Technol 216:996–1003
Yin Q, Yang S, Wang Z, Xing L, Wu G (2018) Clarifying electron transfer and metagenomic analysis of microbial community in the methane production process with the addition of ferroferric oxide. Chem Eng J 333:216–225
Yu X, Yin J, Shen D, Shentu J, Long Y, Chen T (2018) Improvement of acidogenic fermentation for volatile fatty acid production from protein-rich substrate in food waste. Waste Manag 74:177–184
Zhang Z, Li H, Zhu J, Liu W, Xin X (2011) Improvement strategy on enhanced biological phosphorus removal for municipal wastewater treatment plants: full-scale operating parameters, sludge activities, and microbial features. Bioresour Technol 102:4646–4653
Zhang D, Jiang H, Chang J, Sun J, Tu W, Wang H (2019) Effect of thermal hydrolysis pretreatment on volatile fatty acids production in sludge acidification and subsequent polyhydroxyalkanoates production. Bioresour Technol 279:92–100
Zhao J, Li Y, Chen X, Li Y (2018) Effects of carbon sources on sludge performance and microbial community for 4-chlorophenol wastewater treatment in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour Technol 255:22–28
Zhou A, Du J, Varrone C, Wang Y, Wang A, Liu W (2014) VFAs bioproduction from waste activated sludge by coupling pretreatments with Agaricus bisporus substrates conditioning. Process Biochem 49:283–289
Zhu Y, Wu M, Gao N, Chu W, Zhao L, Wang Q (2019) Enhanced dissimilatory perchlorate reduction in the presence of humic acids or 2,6-anthraquinone disulfonate as quinone redox mediators. Chem Eng J 357:75–83
Funding
This research was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M642349) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51408171), Jingang Huang received partial financial support from the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Details about pH, ORP, ammonia concentrations, and important bacteria can be found in the Supplementary Materials.
ESM 1
(DOC 405 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Chen, S., Wu, W. et al. Insights into redox mediator supplementation on enhanced volatile fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 27052–27062 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05927-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05927-z