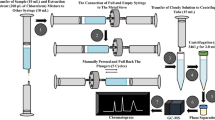
Abstract
In the last years, several scientific studies have shown that carbamazepine (CBZ) is one of the most frequently detected pharmaceutical in aquatic environment. However, little data is available on its detection and its transformation products (TPs) in marine water. The use of polar organic chemical integrative sampling (POCIS) passive samplers as a semi-quantitative and qualitative tool for screening of pharmaceuticals and TPs in seawater has been studied. Furthermore, the uptake rates of the target compounds were also determined under laboratory experiments to characterize the levels accumulated in devices. The results confirmed the presence of residues of anticonvulsant CBZ as well as some of its main metabolites, over a 1-year monitoring campaign carried out in French coast on the Mediterranean Sea. The work reports for the first time the presence of two TPs (10,11-dihydro-10,11-trans-dihydroxycarbamazepine (TRANS) and 10-hydroxy-10,11-dihydrocarbamazepine (10OH)) in marine water. The results contribute in assessing the environmental and human health risk of pharmaceuticals on coastal areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez DA, Petty JD, Huckins JN, Jones-Lepp TL, Getting DT, Goddard JP, Manahan SE (2004) Development of a passive, in situ, integrative sampler for hydrophilic organic contaminants in aquatic environments. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1640–1648
Bartelt-Hunt SL, Snow DD, Damon T, Shockley J, Hoagland K (2009) The occurrence of illicit and therapeutic pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluent and surface water in Nebraska. Environ Pollut 157:786–791
Commission Decision 2002/657/EC (2002) Off J Eur Communities L221:8
European parliament legislative resolution of 16 December 2008 on the proposal for a directive of the European parliament and of the council on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy and amending Directive 2008/105/CE [COM (2007)0765-C6-0468/2007-2007/0279(COD)]
European parliament legislative resolution of 22 May 2007 on the proposal for a directive of the European parliament and of the council on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy and amending Directive 2000/60/EC [COM(2006)0397-C6-0243/2006-2006/0129(COD)]
Greenwood R, Mills GA, Vrana B (2009) Potential applications of passive sampling for monitoring non-polar industrial pollutants in the aqueous environment in the support of REACH. J Chromatogr A 1216:631–639
Gros M, Petrovic M, Barceló D (2009) Tracing pharmaceutical residues of different therapeutic classes in environmental waters by using liquid chromatography/quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry and automated library searching. Anal Chem 81:898–912
ISO/IEC/EN 17025 Guidelines. General requirements for the competence of calibration and testing laboratories
Leclercq M, Mathieu O, Gomez E, Casellas C, Fenet H, Hillaire-Buys D (2009) Presence and fate of carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and seven of their metabolites at wastewater treatment plants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:408–415
Li H, Helm PA, Metcalfe CD (2010) Sampling in the great lakes for pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and endocrine-disrupting substances using the passive polar organic chemical integrative sampler. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:751–762
Loos R, Locoro G, Contini S (2010) Occurrence of polar organic contaminants in the dissolved water phase of the Danube River and its major tributaries using SPE-LC-MS2 analysis. Water Res 44:2325–2335
Macleod SL, McClure EL, Wong CS (2007) Laboratory calibration and field deployment of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler for pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater and surface water. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2517–2529
Martínez Bueno MJ, Hernando MD, Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR (2009) Application of passive sampling devices for screening of micro-pollutants in marine aquaculture using LCMSMS. Talanta 77:1518–1527
Martínez Bueno MJ, Gómez MJ, Herrera S, Hernando MD, Agüera A, Fernández-Alba AR (2012) Occurrence and persistence of organic emerging contaminants and priority pollutants in five sewage treatment plants of Spain: two years pilot survey monitoring. Environ Pollut 164:267–273
Martínez Bueno MJ, Boillot C, Fenet H, Chiron S, Casellas C, Gómez E (2013) Fast and easy extraction combined with high resolution-mass spectrometry for residue analysis of two anticonvulsants and their transformation products in marine mussels. J Chromatogr A 1305:27–34
Metcalfe CD, Miao XS, Koenig BG, Struger J (2003) Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower great lakes, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2881–2889
Morin N, Miège C, Randon J, Coquery M (2012) Chemical calibration, performance, validation and applications of the polar organic chemical integrative sampler (POCIS) in aquatic environments. Trends Anal Chem 36:144–175
Munaron D, Tapie N, Budzinski H, Andral B, Gonzalez JL (2012) Pharmaceuticals, alkylphenols and pesticides in Mediterranean coastal waters: results from a pilot survey using passive samplers. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 114:82–92
Nödler K, Licha T, Bester K, Sauter M (2010) Development of a multi-residue analytical method, based on liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, for the simultaneous determination of 46 micro-contaminants in aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A 1217:6511–6521
Pinhancos R, Maass S, Ramanathan DM (2011) High-resolution mass spectrometry method for the detection, characterization and quantitation of pharmaceuticals in water. J Mass Spectrom 46:1175–1181
Ternes TA (2001) In pharmaceuticals and metabolites as contaminants of the aquatic environment. In pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: scientific and regulatory issues. In: Daughton CG, Jones-Lepp TL (eds) ACS symposium series 791. American Chemical Society, Washingon, DC
Togola A, Budzinski H (2007) Development of polar organic integrative samplers for analysis of pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems. Anal Chem 79:6734–6741
Wille K, Claessens M, Rappé K, Monteyne E, Janssen CR, De Brabander HF, Vanhaeck L (2011) Rapid quantification of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in passive samplers using ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:9162–9173
Zhang Z, Hibberd A, Zhou JL (2008) Analysis of emerging contaminants in sewage effluent and river water: comparison between spot and passive sampling. Anal Chim Acta 607:37–44
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful for the financial support given by the Sanofi and the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche (Project PEPSEA). This work was conducted within the Chair Emerging Pollutants (Veolia-Hydrosciences). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the staff of the Ifremer LER-LR laboratory for assistance with POCIS collection. M.J. Martínez Bueno wishes to thank the University of Montpellier for the post-doc grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hongwen Sun
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez Bueno, M.J., Herrera, S., Munaron, D. et al. POCIS passive samplers as a monitoring tool for pharmaceutical residues and their transformation products in marine environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5019–5029 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3796-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3796-5