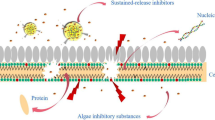
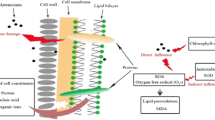
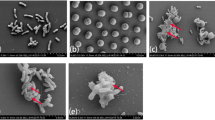
Abstract
To safely and effectively apply artemisinin sustained-release granules to control and prevent algal water-blooms, the effects of artemisinin and its sustained-release granules on freshwater alga (Scenedesmus obliquus (S. obliquus) and Microcystis aeruginosa (M. aeruginosa)), as well as the production and release of microcystins (MCs) were studied. The results showed that artemisinin sustained-release granules inhibited the growth of M. aeruginosa (above 95 % IR) and S. obliquus (about 90 % IR), with M. aeruginosa more sensitive. The artemisinin sustained-release granules had a longer inhibition effect on growth of pure algae and algal coexistence than direct artemisinin dosing. The artemisinin sustained-release granules could decrease the production and release of algal toxins due to the continued stress of artemisinin released from artemisinin sustained-release granules. There was no increase in the total amount of MC–LR in the algal cell culture medium.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babica P, Bláha L, Maršálek B (2006) Exploring the natural role of microcystins-a review of effects on photoautotrophic organisms. J Phycol 42:9–20
Boylan JD, Morris JE (2003) Limited effects of barley straw on algae and zooplankton in a Midwestern pond. Lake Reserv Manage 19:265–271
Chen JQ, Guo RX (2012) Access the toxic effect of the antibiotic cefradine and its UV light degradation products on two freshwater algae. J Hazar Mater 209:520–523
Chorus I (2001) Cyanotoxins: Occurrence, Causes, Consequences. In: Ingrid C. (ed) Heidelberg, Springer, p 357
Codd GA, Morrison LF, Metcalf JS (2005) Cyanobacterial toxins: risk management for health protection. Toxicol Appl Pharm 203:264–272
Daly RI, Ho L, Brookes JD (2007) Effect of chlorination on Microcystis aeruginosa cell integrity and subsequent microcystin release and degradation. Environ Sci Technol 41:4447–4453
de Figueiredo DR, Azeiteiro UM, Esteves SM (2004) Microcystin-producing blooms-a serious global public health issue. Ecotox and Environ Safety 59:151–163
Downing TG, Sember CS, Gehringer MM, Leukes W (2005) Medium N:P ratios and specific growth rate comodulate microcystin and protein content in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 and M. aeruginosa UV027. Microb Ecol 49:1–6
Fistarol GO, Legrand C, Granéli E (2003) Allelopathic effect of Prymnesium parvum on a natural community. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 255:115–125
Gross EM, Meyer H, Schilling G (1996) Release and ecological impact of algicidal hydrolysable polyphenols in Myriophyllum spicatum. Phytochemistry 41:133–138
Hilt S (2006) Allelopathic inhibition of epiphytes by submerged macrophytes. Aqua Bot 85:252–256
Hong Y, Hu HY, Xie X, Li FM (2008) Responses of enzymatic antioxidants and non-enzymatic antioxidants in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to the allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) isolated from reed (Phragmites communis). J Plant Physiol 165:1264–1273
ISO 8692 (2004)Water Quality – Fresh Water Algal Growth Inhibition Test With Scenedesmus subspicatus and Selenastrum capricornutum, Geneva, Switzerland
Jang MH, Ha K, Joo GJ, Takamura N (2003) Toxin production of cyanobacteria is increased by exposure to zooplankton. Freshwater Biol 48:1540–1550
Jones GJ, Orr PT (1994) Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a Microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res 28:871–876
Ke Z, Xie P, Guo L (2008) Controlling factors of spring–summer phytoplankton succession in Lake Taihu (Meiliang Bay, China). Hydrobiologia 607:41–49
Kearns KD, Hunter MD (2000) Green algal extracellular products regulate antialgal toxin production in a cyanobacterium. Environ Microbiol 2:291–297
Kong C, Wang P, Zhang C, Zhang M, Hu F (2006) Herbicidal potential of allelochemicals from Lantana camara against Eichhornia crassipes and the alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Weed Res 46:290–295
Men YJ, Hu HY (2007) Effects of allelochemical EMA from reed on the production and release of cyanotoxins in Microcystis aeruginosa. Environment Science 28:2058–2062 (in Chinese)
Mulderij G, Mau B, van Donk E, Gross EM (2007) Allelopathic activity of Stratiotes aloides on phytoplankton—towards identification of allelopathic substances. Hydrobiologia 584:89–100
Nakai S, Inoue Y, Hosomi M, Murakami A (2000) Myriophyllum spicatum-released allelopathic polyphenols inhibiting growth of blue-green algae Microcystis aeruginosa. Wat Res 34:3026–3032
Ni LX, Acharya K, Hao XY, Li SY (2012) Isolation and identification of an anti-algal compound from Artemisia annua and mechanisms of inhibitory effect on algae. Chemosphere 88:1051–1057
Ni LX, Acharya K, Ren GX, Li SY, Li YP, Li Y (2013) Preparation and characterization of anti-algal sustained-release granules and their inhibitory effects on algae. Chemosphere 91:608–615
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Robillot C, Vinh J, Puiseux-Dao S, Hennion MC (2000) Hepatotoxin production kinetics of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7820, as determined by HPLC-mass spectrometry and protein phosphatase bioassay. Environ Sci Technol 34:3372–3378
Sager L (2009) Measuring the trophic status of ponds: relationships between summer rate of periphytic net primary productivity and water physico–chemistry. Water Res 43:1667–1679
Song LR, Lei LM, He ZR, Liu YD (1999) Growth and toxin analysis in two toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystis viridis isolated from Dianchi Lake. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 23:402–408
Ueno Y, Nagata S, Tsutsumi T, Hasegawa A, Watanabe MF, Park H, Chen GC, Chen G, Yu SS (1996) Detection of microcystins, a blue-green algal hepatotoxin, in drinking water sampled in Haimen and Fusui, endemic areas of primary cancer in China, by highly sensitive immunoassay. Carcinogenesis 17:1317–1321
Umehara A, Tsutsumi H, Takahashi T (2012) Blooming of Microcystis aeruginosa in the reservoir of the reclaimed land and discharge of microcystins to Isahaya Bay (Japan). Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3257–3267
Vanormelingen P, Vyverman W, De Bock D, Van der Gucht K, De Meester L (2009) Local genetic adaptation to grazing pressure of the green alga Desmodesmus armatus in a strongly connected pond system. Limnol Oceanogr 54:503–511
Wang J, Zhu JY, Liu SP, Liu BY, Gao YN, Wu ZB (2011) Generation of reactive oxygen species in cyanobacteria and green algae induced by allelochemicals of submerged macrophytes. Chemosphere 85:977–982
Wiedner C, Visser PM, Fastner J, Metcalf JS, Codd GA, Mur LR (2003) Effects of light on the microcystin content of Microcystis Strain PCC7806. Appl Enviro Microb 69:1475–1481
Wu C, Chang XX, Dong HJ, Li DF, Liu JY (2008) Allelopathic inhibitory effect of Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. On Microcystis aeruginosa and its physiological mechanism. Acta Ecol Sin 28:2595–2603
Wu X, Wu H, Chen JR, Ye JY (2013) Effects of allelochemical extracted from water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes Linn.) on the growth, microcystin production and release of Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8192–8201
Xian QM, Chen HD, Liu HL, Zou HX, Yin DQ (2006) Isolation and identification of antialgal compounds from the leaves of Vallisneria spiralis L. by activity-guided fractionation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13:233–237
Xiao X, Chen YX, Liang XQ, Lou LP, Tang XJ (2010) Effects of Tibetan hulless barley on bloom-forming cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) measured by different physiological and morphologic parameters. Chemosphere 81:1118–1123
Yamamoto Y, Nakahara H (2005) Competitive dominance of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in nutrient-rich culture conditions with special reference to dissolved inorganic carbon uptake. Phycol Res 53:201–208
Zhang TT, He M, Wu AP, Nie LW (2009) Allelopathic effects of submerged macrophyte Chara vulgaris on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa. Allelopathy J 23:391–401
Zhu J, Liu B, Wang J, Gao Y, Wu Z (2010) Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat Toxicol 98:196–203
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported jointly by the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 51109061, 41373111, 51009049); the National Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51225901); the Research Fund for innovation team of Ministry of education (Grant No. IRT13061); the Jiangsu Water Resources Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 201371); and the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, L., Li, D., Hu, S. et al. Effects of artemisinin sustained-release granules on mixed alga growth and microcystins production and release. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 18637–18644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5438-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5438-y