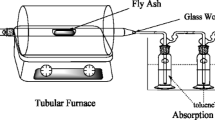
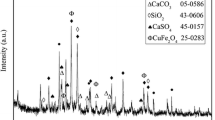
Abstract
In this study, simulated fly ash containing CuO/CuCl2 was heated at 350 °C in a flow of N2 and also in a nitrogen flow containing 10 vol% H2, to evaluate the influence of hydrogen adding on dioxin formation. The total polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/F) output derived from the CuO sample under N2 and 10 % H2 was 7.382 and 0.708 ng/g, respectively. As for CuCl2, it was 589 and 46.1 ng/g, respectively. The results show that the hydrogen adding has a good inhibition effect on PCDD/F formation; the inhibition rate was higher than 90 % for PCDD/Fs. HCl and NH3 were detected by Gasmet in the flue gas; the probable inhibition mechanism of hydrogen reaction was proposed, based on our measurements and others’ researches.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addink R PR, Olie K. (1993): Inhibition of PCDD/F formation during de novo synthesis on fly ash using N- and S-compounds. Organohalogen Compd 12:27–30
Addink R, Olie K (1995) Role of oxygen in formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans from carbon on fly ash. Environ Sci Technol 29:1586–90
Altarawneh M, Dlugogorski BZ, Kennedy EM, Mackie JC (2009) Mechanisms for formation, chlorination, dechlorination and destruction of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs). Prog Energ Combust 35:245–274
Buekens A, Stieglitz L, Hell K, Huang H, Segers P (2001) Dioxins from thermal and metallurgical processes: recent studies for the iron and steel industry. Chemosphere 42:729–735
Buser HR (1979) Formation of polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) and dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) from the pyrolysis of chlorobenzenes. Chemosphere 8:415–424
Cieplik MK, Epema OJ, Louw R (2002): Thermal hydrogenolysis of dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofuran. Eur J Org Chem 16:2792–2799
Gullett BK, Bruce KR, Beach LO (1990) The effect of metal-catalysts on the formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxin and polychlorinated dibenzofuran precursors. Chemosphere 20:1945–1952
Hagenmaier H, Kraft M, Brunner H, Haag R (1987) Catalytic effects of fly-ash from waste incineration facilities on the formation and decomposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ Sci Technol 21:1080–1084
Hajizadeh Y, Onwudili JA, Williams PT (2012) Effects of gaseous NH3 and SO2 on the concentration profiles of PCDD/F in flyash under post-combustion zone conditions. Waste Manag 32:1378–1386
Karasek FW, Dickson LC (1987) Model studies of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxin formation during municipal refuse incineration. Science 237:754–756
Luna A, Amekraz B, Morizur JP, Tortajada J, Mo O, Yanez M (2000) Reactions of urea with Cu + in the gas phase: an experimental and theoretical study. J Phys Chem A 104:3132–3141
Milligan MS, Altwicker ER (1995) Mechanistic aspects of the de-novo synthesis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and furans in fly-ash from experiments using isotopically labeled reagents. Environ Sci Technol 29:1353–1358
Olie K, Vermeulen PL, Hutzinger O (1977) Chlorodibenzo-p-dioxins and chlorodibenzofurans are trace components of fly ash and flue gas of some municipal incinerators in The Netherlands. Chemosphere 6:455–459
Rappe C, Marklund S, Buser HR, Bosshardt HP (1978) Formation of polychlorinated dibenzo-paea-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) by burning or heating chlorophenates. Chemosphere 7:269–281
Ruokojärvi PH, Halonen IA, Tuppurainen KA, Tarhanen J, Ruuskanen J (1998) Effect of gaseous inhibitors on PCDD/F formation. Environ Sci Technol 32:3099–3103
Ruokojarvi PH, Asikainen AH, Tuppurainen KA, Ruuskanen J (2004) Chemical inhibition of PCDD/F formation in incineration processes. Sci Total Environ 325:83–94
Stieglitz L, Zwick G, Beck J, Roth W, Vogg H (1989) On the de-novo synthesis of PCDD/PCDF on fly-ash of municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere 18:1219–1226
Takacs L, Moilanen GL (1991) Simultaneous control of PCDD/PCDF, HCl and NOx emissions from municipal solid-waste incinerators with ammonia injection. J Air Waste Manag 41:716–722
Takacs L, Mcqueen A, Moilanen GL (1993) Development of the ammonia injection technology (AIT) for the control of PCDD PCDF and acid gases from municipal solid-waste incinerators. J Air Waste Manag 43:889–897
Tuppurainen K, Aatamila M, Ruokojarvi P, Halonen I, Ruuskanen J (1999) Effect of liquid inhibitors on PCDD/F formation, prediction of particle-phase PCDD/F concentrations using PLS modelling with gas-phase chlorophenol concentrations as independent variables. Chemosphere 38:2205–2217
Vogg H, Stieglitz L (1986) Thermal-behavior of PCDD/PCDF in fly-ash from municipal incinerators. Chemosphere 15:1373–1378
Vogg H, Metzger M, Stieglitz L (1987) Recent findings on the formation and decomposition of PCDD/PCDF in municipal solid-waste incineration. Waste Manage Res 5:285–294
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Key Basic Research Development Program (No. 2011CB201500).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Leif Kronberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Li, X.D., Meng, W.J. et al. Reducing dioxin formation by adding hydrogen in simulated fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 13077–13082 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4335-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4335-8