Abstract
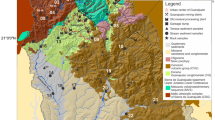
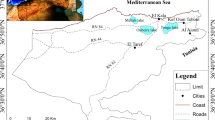
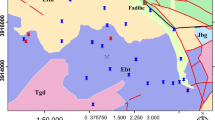
To date, there have been few detailed studies regarding the impact of mining and metallogenic activities on solid fractions in the Azzaba mercurial district (northeast Algeria) despite its importance and global similarity with large Hg mines. To assess the degree, distribution, and sources of pollution, a physical inventory of apparent pollution was developed, and several samples of mining waste, process waste, sediment, and soil were collected on regional and local scales to determine the concentration of Hg and other metals according to their existing mineralogical association. Several physico-chemical parameters that are known to influence the pollution distribution are realized. The extremely high concentrations of all metals exceed all norms and predominantly characterize the metallurgic and mining areas; the metal concentrations significantly decrease at significant low distances from these sources. The geo-accumulation index, which is the most realistic assessment method, demonstrates that soils and sediments near waste dumps and abandoned Hg mines are extremely polluted by all analyzed metals. The pollution by these metals decreases significantly with distance, which indicates a limited dispersion. The results of a clustering analysis and an integrated pollution index suggest that waste dumps, which are composed of calcine and condensation wastes, are the main source of pollution. Correlations and principal component analysis reveal the important role of hosting carbonate rocks in limiting pollution and differentiating calcine wastes from condensation waste, which has an extremely high Hg concentration (˃1 %).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, P. W. (2002). Soils: their implications to human health. Science of the Total Environment, 291(1–3), 1–32. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01102-0.
Afnor, NF P 94–048 Détermination de la teneur en carbonate, Saint-Denis : AFNOR, 1996.
Alligui, F. (2011). Geochemical natural and artificial dispersion of mercury in Azzaba—Skikda Province—and its impact on environment. Algiers: Department of Geology. University of science and technology Houari Boumediene.
Alligui, F., & Boutaleb, A. (2010). Impact of mercury mine activities on water resources at Azzaba—north-east of Algeria. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 6(4), 395–401. doi:10.3844/ajessp.2010.395.401.
Alligui, F., & Boutaleb, A. (2013). Origin and speciation of selected trace elements in groundwater: a case study of Azzaba District in northeast of Algeria. Journal of Environmentalentomology, 2(6), 134–139.
Allison, F. E. (1973). Soil organic matter and its role in crop production. New York: Elsevier.
Arenas-Lago, D., Andrade, M. L., Lago-Vila, M., Rodríguez-Seijo, A., & Vega, F. A. (2014). Sequential extraction of heavy metals in soils from a copper mine: distribution in geochemical fractions. Geoderma, 230–231, 108–118. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.04.011.
Bako, S. P., Ezealor, A. U., & Tanimu, Y. (2014). Heavy metal deposition in soils and plants impacted by anthropogenic modification of two sites in the Sudan Savanna of North Western Nigeria. Environmental Risk Assessment of Soil Contamination, 24, 697–721.
Banat, K. M., Howari, F. M., & Al-Hamad, A. A. (2005). Heavy metals in urban soils of Central Jordan: should we worry about their environmental risks? Environmental Research, 97(3), 258–273. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2004.07.002.
Ben Salem, Z., Capelli, N., Laffray, X., Elise, G., Ayadi, H., & Aleya, L. (2014). Seasonal variation of heavy metals in water, sediment and roach tissues in a landfill draining system pond (Etueffont, France). Ecological Engineering, 69, 25–37. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.03.072.
Benderradji, M. E. H. (1999). Quelques indices d’appreciation de la pollution mercurifere dans le milieu eco-geographique de la depressionde Azzaba-Nord Est Algerien. Observatorio Medioambiental, 2, 191–215.
Benhamza, M. (2007). Geophysical contribution to hydrogeological study of northnumidic mercurial zone (Azzaba)—determination of pollution degree. Annaba: University of Annaba.
Benhamza, M., Kherici, N., Picard-Bonnaud, F., & Nezzal, A. (2008). Qualité des eaux souterraines de la zone mercurielle nord numidique (azzaba), nord est Algérie. Evalution de la contamination de la population par le mercure inorganique. Bulletin du Service Géologique National, 19(2), 135–149.
Biester, H., Gosar, M., & Müller, G. (1999). Mercury speciation in tailings of the Idrija mercury mine. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 65(3), 195–204. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(99)00027-8.
Biester, H., Müller, G., & Schöler, H. F. (2002). Binding and mobility of mercury in soils contaminated by emissions from chlor-alkali plants. Science of the Total Environment, 284(1–3), 191–203. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00885-3.
Bikmeev, R. (1970). Geochemical study report. E.R.E. M. Algeria: unpublished E.R.E.M. Report.
Bouarroudj, M. T. (1986). Metallogenic study of the nord-numidicmercurious belt (Azzaba District, North-East Algeria) control and perspectives researches. Ph.D. Thesis, Pierre and Marie Curie University.
Boyd, S. E. (2002). Guidelines for the conduct of benthic studies at aggregate dredging sites. Lowestoft, Department for Transport, Local Government and the Regions. CEFAS, 1–117.
Burgos, P., Madejón, E., Pérez-de-Mora, A., & Cabrera, F. (2006). Spatial variability of the chemical characteristics of a trace-element-contaminated soil before and after remediation. Geoderma, 130(1–2), 157–175. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.01.016.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60(4), 542–551. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.072.
Cohen, J., Cohen, P., West, S. G., & Aiken, L. S. (2003). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences (3rd ed.). Mahwah: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
Esmaeili, A., Moore, F., Keshavarzi, B., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Kermani, M. (2014). A geochemical survey of heavy metals in agricultural and background soils of the Isfahan industrial zone, Iran. Catena, 121, 88–98. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2014.05.003.
Fagbot, E. O., & Olanipekun, E. O. (2010). Evaluation of the status of heavy metal pollution of sediment of Agbabu bitumen deposit area, Nigeria. European Journal of Scientific Research, 41(3), 373–382.
Fernández-Martínez, R., Loredo, J., Ordóñez, A., & Rucandio, M. I. (2006). Physicochemical characterization and mercury speciation of particle-size soil fractions from an abandoned mining area in Mieres, Asturias (Spain). Environmental Pollution, 142(2), 217–226. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.034.
Fernández-Martínez, R., Larios, R., Gomez-Pinilla, I., Gomez-Mancebo, B., Lopez-Andrés, S., Loredo, J., Ordonez, A., & Rucandio, I. (2015). Mercury accumulation and speciation in plants and soils from abandoned cinnabar mines. Geoderma, 253–254, 30–38. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.04.005.
Garcia-Ordiales, E., Loredo, J., Esbrí, J. M., Lominchar, M. A., Millan, R., & Higueras, P. (2014). Stream bottom sediments as a means to assess metal contamination in the historic mining district of Almadén (Spain). International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 28(6), 357–376. doi:10.1080/17480930.2014.967917.
Garcia-Ordiales, E., Esbri, J. M., Covelli, S., Lopez-Berdonces, M. A., Higueras, P. L., & Loredo, J. (2015). Heavy metal contamination in sediments of an artificial reservoir impacted by long-term mining activity in the Almadén mercury district (Spain). Environmental Science and Pollution Research. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4770-6.
García-Sánchez, A., Murciego, A., Álvarez-Ayuso, E., Regina, I. S., & Rodríguez-González, M. A. (2009). Mercury in soils and plants in an abandoned cinnabar mining area (SW Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 1319–1324.
Gemici, Ü., Tarcan, G., Melis Somay, A., & Akar, T. (2009). Factors controlling the element distribution in farming soils and water around the abandoned Halıköy mercury mine (Beydağ, Turkey). Applied Geochemistry, 24(10), 1908–1917. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.07.004.
Global Alliance on Health and Pollution (GAHP). Summary guidance on soil screening levels (1). Version 1, December 2013. http://www.gahp.net/new/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/GUIDANCE-ON-SCREENING-LEVELS-Version-1-Dec-2013.pdf.
Golia, E. E., Dimirkou, A., & Floras, S. A. (2015). Spatial monitoring of arsenic and heavy metals in the Almyros area, Central Greece. Statistical approach for assessing the sources of contamination. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(7), 399. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4624-1.
Gosar, M. (2008). Mercury in river sediments, floodplains and plants growing thereon in drainage area of Idrija Mine, Slovenia. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 17(2), 227–236. doi:10.1007/BF02839798.
Gosar, M., & Teršič, T. (2012). Environmental geochemistry studies in the area of Idrija mercury mine, Slovenia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34(Suppl. 1), 27–41. doi:10.1007/s10653-011-9410-6.
Gosar, M., & Tersic, T. (2015). Contaminated sediment loads from ancient mercury ore roasting sites, Idrija area, Slovenia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 149, 97–105. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.11.012.
Gray, J., E., Adams, M. J., Crock, J. G., & Theodorakos, P. M. (1999). Geochemical data for environmental studies of mercury mines in Nevada. U.S. Geological Survey. Open-File Report, 99–576.
Gray, J. E., Gent, C. A., & Snee, L. W. (2000). The southwestern Alaska mercury belt and its relationship to the circum-pacific metallogenic mercury province. Polarforschung, 68, 187–196.
Gray, J. E., Crock, J. G., & Fey, D. L. (2002). Environmental geochemistry of abandoned mercury mines in West-Central Nevada, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 17(8), 1069–1079. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00004-5.
Gray, J. E., Hines, M. E., Higueras, P. L., Adatto, I., & Lasorsa, B. K. (2004). Mercury speciation and microbial transformations in mine wastes, stream sediments, and surface waters at the Almaden mining district, Spain. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(16), 4285–4292. doi:10.1021/es040359d.
Greve, M. H., & Madsen, H. B. (1999). Soil mapping in Denmark, European Soil Bureau-report No. 6. http://eusoils.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ESDB_Archive/eusoils_docs/esb_rr/n06_soilresources_of_europe/PDF/DENM05.pdf.
Hartsock, N. J., Mueller, T. G., Thomas, G. W., Barnhisel, R. I., & Wells, K. L. (2000). Soil electrical conductivity variability, in Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference of Precision Agriculture.
Hellal, L., & Djouada, S. (1994). Contribution to geological study of mercuro-polymetallic deposits of mining district of Azzaba (Ismail, Guenicha, Mrasma). Skikda: University of Constantine.
Higueras, P., Oyarzun, R., Biester, H., Lillo, J., & Lorenzo, S. (2003). A first insight into mercury distribution and speciation in soils from the Almaden mining district, Spain. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 80(1), 95–104. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00185-7.
Higueras, P., Oyarzun, R., Lillo, J., Sánchez-Hernández, J. C., Molina, J. A., Esbrí, J. M., et al. (2006). The Almadén district (Spain): anatomy of one of the world’s largest Hg-contaminated sites. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 112–124. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.04.042.
Higueras, P., Amoros, J.A., Esbrí, J.M., Garcia-Navarro, F.J., Pérez de los Reyes, C., Moreno, G. (2012). Time and space variations in mercury and other trace element contents in olive tree leaves from the Almaden Hg-mining district. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 123, 143–151. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.04.012
Hu, X., Du, Y., Feng, J., Fang, S., Gao, X., & Xu, S. (2013). Spatial and seasonal variations of heavy metals in wetland soils of the tidal flats in the Yangtze estuary, China: environmental implications. Pedosphere, 23(4), 511–522. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(13)60044-2.
Huang, P., Patel, M., Santagata, M.C., & Bobet, A. (2009). Classification of organic soils. Publication FHWA/IN/JTRP-2008/02. Joint Transportation Research Program, Indiana Department of Transportation and Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, 2009. doi:10.5703/1288284314328.
Kabata-Pendias, A & Pendias, H. (2001). Trace Elements in Soils and Plants. Third Edition. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Kahoul, M., Alioua, A., Derbal, N., & Ayad, W. (2014). Behavior of soil micromycetes regarding the mercury pollution in the area of Azzaba (Algeria). Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 5(5), 1470–1476.
Kaur, M., & Kaur, U. (2013). Comparison between K-mean and hierarchical algorithm using query redirection. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 3(7), 1454–1459.
Kermani, S., Boutiba, M., Boutaleb, A., & Fagel, N. (2016). Distribution of heavy and clay minerals in coastal sediment of Jijel, east of Algeria: indicators of sediment sources and transport and deposition environments. Arabian Journal of Geoscience, 9, 1–18. doi:10.1007/s12517-015-2155-2.
Lamari, S., & Younsi, C. (1988). Geology and mineralization of Hg (Pb,Zn) Mrasma deposit and Pb – Hg of grayer in north Numidian chain (Azzaba, Algeria). Algiers: Department of Geology. University of science and technology Houari Boumediene.
Lee, H., Kabir, I. M., Kwon, P. S., Kim, J. M., Kim, J. G., et al. (2009). Contamination assessment of abandoned mines by integrated pollution index in the Han River watershed. Open Environmental Pollution and Toxicology Journal, 1(1), 27–33. doi:10.2174/1876397900901010027.
Li, P., Feng, X., Shang, L., Qiu, G., Meng, B., Liang, P., et al. (2008). Mercury pollution from artisanal mercury mining in Tongren, Guizhou, China. Applied Geochemistry, 23(8), 2055–2064. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.04.020.
Li, P., Feng, X., Qiu, G., Shang, L., & Wang, S. (2012). Mercury pollution in Wuchuan mercury mining area. Guizhou: Southwestern China: the impacts from large scale and artisanal mercury mining. Environment International, 42, 59–66.
Lin, Y., Larssen, T., Vogt, R. D., & Feng, X. (2010). Identification of fractions of mercury in water, soil and sediment from a typical Hg mining area in Wanshan, Guizhou Province, China. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 60–68.
Loppi, S. (2001). Environmental distribution of mercury and other trace elements in the geothermal area of Bagnore (Mt. Amiata, Italy). Chemosphere, 45(6–7), 991–995. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00028-5.
Loredo, J., Pereira, A., & Ordóñez, A. (2003). Untreated abandoned mercury mining works in a scenic area of Asturias (Spain). Environment International, 29, 481–491. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00007-2.
Loredo, J., Ordóñez, A., & Álvarez, R. (2006). Environmental impact of toxic metals and metalloids from the Muñón Cimero mercury-mining area (Asturias, Spain). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 136(3), 455–467. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.048.
Loska, K., Wiechuła, D., Barska, B., Cebula, E., & Chojnecka, E. (2003). Assessment of arsenic enrichment of cultivated soils in Southern Poland. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 12(2), 187–192.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31. doi:10.1007/s002440010075.
McLean, E. O. (1982). Soil pH and lime requirements. In A. L. Page, H. R. Miller, & R. D. Keeney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis part II—chemical and microbiological properties. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Inc. Soil Science of America, Inc.
Megueddem, M., Belmahi, H., Azzouz, M., & Reggabi, M. (2004). Quantitative determination of blood mercury in professionally exposed subjects. Revue Française Des laboartoires, 363, 41–46.
Millan, R., Schmid, T., Sierra, M. J., Carrasco-Gil, S., Villadoniga, M., Rico, C., Ledesma, D. M. S., & Puente, F. J. D. (2011). Spatial variation of biological and pedological properties in an area affected by a metallurgical mercury plant: Almadenejos (Spain). Applied Geochemistry, 26, 174–181. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.11.016.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geological Journal, 2, 108–118.
Navarro, A., Cardellach, E., & Corbella, M. (2009). Mercury mobility in mine waste from Hg-mining areas in Almería, Andalusia (Se Spain). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 101(3), 236–246. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.08.004.
Nwadinigwe, C. A., Udo, G. J., & Nwadinigwe, A. O. (2014). Seasonal variations of heavy metals concentrations in sediment samples around major tributaries in Ibeno coastal area, Niger Delta, Nigeria. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research, 3(11), 254–265.
Oluyemi, E. A., Feuyit, G., Oyekunle, J. A. O., & Ogunfowokan, A. O. (2008). Seasonal variations in heavy metal concentrations in soil and some selected crops at a landfill in Nigeria. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2(5), 089–096.
Ordóñez, A., Álvarez, R., & Loredo, J. (2014). Soil pollution related to the mercury mining legacy at Asturias (Northern Spain). International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 28(6), 389–396. doi:10.1080/17480930.2014.967920.
Pérez-Sirvent, C., Martínez-Sánchez, M. J., García-Lorenzo, M. L., Molina, J., & Tudela, M. L. (2009). Geochemical background levels of zinc, cadmium and mercury in anthropically influenced soils located in a semi-arid zone (SE, Spain). Geoderma, 148(3–4), 307–317. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.10.017.
Preacher, K. J., & MacCallum, R. C. (2002). Exploratory factor analysis in behavior genetics research: factor recovery with small sample sizes. Behavior Genetics, 32(2), 153–161.
Qingjie, G., Jun, D., Yunchuan, X., Qingfei, W., & Liqiang, Y. (2008). Calculating pollution indices by heavy metals in ecological geochemistry assessment and a case study in parks of Beijing. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 19(3), 230–241. doi:10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60042-4.
Qiu, G., Feng, X., Wang, S., & Shang, L. (2005). Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou province, southwestern China. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 627–638.
Rafiei, B., Khodaei, A. S., Khodabakhsh, S., Hashemi, M., & Nejad, M. B. (2010). Contamination assessment of lead, zinc, copper, cadmium, arsenic and antimony in Ahangaran Mine soils, Malayer, west of Iran. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 19(5), 573–586. doi:10.1080/15320383.2010.499921.
Rahman, S. H., Khanam, D., Adyel, T. M., Islam, M. S., Ahsan, M. A., & Akbor, M. A. (2012). Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil around Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ), Bangladesh: implication of seasonal variation and indices. Applied Sciences, 2(4), 584–601. doi:10.3390/app2030584.
Rakotomalala, R. (2005). TANAGRA: free software for teaching and research. In Actes de EGC’2005, RNTI-E-3, 2, 697–702.
Rawat, M., Ramanathan, A., & Subramanian, V. (2009). Quantification and distribution of heavy metals from small-scale industrial areas of Kanpur City, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(2–3), 1145–1149. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.115.
Redoil, Resisting environmental destruction on indigenous lands (2007). Mining and toxic metals, a case study of the proposed Donlin Creek mine. http://www.akaction.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Mining_and_Toxic_Metals.pdf.
Reimann, C., & Caritat, P. (1998). Chemical elements in the environment. Berlin: Springer Verlag.
Reis, A. T., Rodrigues, S. M., Davidson, C. M., Pereira, E., & Duarte, A. C. (2010). Extractability and mobility of mercury from agricultural soils surrounding industrial and mining contaminated areas (Portugal). Chemosphere, 81(11), 1369–1377. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.030.
Rimondi, V., Gray, J. E., Costagliola, P., Vaselli, O., & Lattanzi, P. (2012). Concentration, distribution, and translocation of mercury and methylmercury in mine-waste, sediment, soil, water, and fish collected near the Abbadia San Salvatore mercury mine, Monte Amiata district, Italy. Science of the Total Environment, 414, 318–327. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.065.
Shotyk, W., Chen, B., & Krachler, M. (2005). Lithogenic, oceanic and anthropogenic sources of atmospheric Sb to a maritime blanket bog, Myrarnar, Faroe Islands. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 7(12), 1148–1154. doi:10.1039/b509928p.
Singh, S., Raju, N. J., & Nazneen, S. (2015). Environmental risk of heavy metal pollution and contamination sources using multivariate analysis in the soils of Varanasi environs, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(6), 345. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4577-4.
Soper, D.S. (2016). p-value calculator for correlation coefficients [software]. Available from http://www.danielsoper.com/statcalc.
Soro, G., Metongo, B. S., Soro, N., Ahoussi, E. K., Kouamé, F. K., Zade, S. G. P., et al. (2009). Métaux lourds (Cu, Cr, Mn et Zn) dans les sédiments de surface d’une lagune tropicale africaine: cas de la lagune Ebrie (Côte d’Ivoire). International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 3(6), 1408–1427.
Swarnalatha, K., Letha, J., Ayoob, S., & Nair, A. G. (2015). Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of a tropical lake. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(6), 322. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4558-7.
Teršič, T., Gosar, M., & Biester, H. (2011). Environmental impact of ancient small-scale mercury ore processing at Pšenkon soil (Idrija area, Slovenia). Applied Geochemistry, 26(11), 1867–1876. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.010.
Teršič, T., Biester, H., & Gosar, M. (2014). Leaching of mercury from soils at extremely contaminated historical roasting sites (Idrija area, Slovenia). Geoderma, 226–227, 213–222. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.02.006.
Tomiyasu, T., Matsuyama, A., Imura, R., Kodamatani, H., Miyamoto, J., Kono, Y., et al. (2012). The distribution of total and methylmercury concentrations in soils near the Idrija mercury mine, Slovenia, and the dependence of the mercury concentrations on the chemical composition and organic carbon levels of the soil. Environmental Earth Science, 65(4), 1309–1322. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1379-z.
United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) (2010). Technical and economic criteria for processing mercury–containing tailings. Final report USEPA. Human health medium specific screening levels. Braunschweig: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.unep.org/chemicalsandwaste/Portals/9/Mercury/Documents/PartneshipsAreas/Technical%20and%20economic%20criteria-2010.pdf.
USEPA. (2008) Human health medium specific screening levels. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Vidal, J., Pérez-Sirvent, C., Martínez-Sánchez, M. J., & Navarro, M. C. (2004). Origin and behaviour of heavy metals in agricultural calcaric fluvisols in semiarid conditions. Geoderma, 121(3–4), 257–270. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.12.001.
Wei, B., & Yang, L. (2010). A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchemical Journal, 94(2), 99–107. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2009.09.014.
Wei, Z., Wang, D., Zhou, H., & Qi, Z. (2011). Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution with principal component analysis and geoaccumulation index. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 10, 1946–1952.
Yahaya, M., Mohammad, S., & Abdullahi, B. (2009). Seasonal variations of heavy metals concentration in abattoir dumping site soil in Nigeria. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 13(4), 9–13. doi:10.4314/jasem.v13i4.55387.
Zhang, H., Chen, J., Zhu, L., Yang, G., & Li, D. (2014). Anthropogenic mercury enrichment factors and contributions in soils of Guangdong Province, South China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144, 312–319. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seklaoui, M., Boutaleb, A., Benali, H. et al. Environmental assessment of mining industry solid pollution in the mercurial district of Azzaba, northeast Algeria. Environ Monit Assess 188, 621 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5619-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5619-2