Abstract
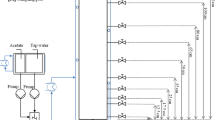
Aquifer thermal energy storage may result in increases in the groundwater temperature up to 70 °C and more. This may lead to geochemical and microbiological alterations in the aquifer. To study the temperature effects on the indigenous microbial community composition, sediment column experiments at four different temperatures were carried out and the effluents were characterized geochemically and microbiologically. After an equilibrium phase at groundwater temperature of 10 °C for 136 days, one column was kept at 10 °C as a reference and the others were heated to 25, 40 and 70 °C. Genetic fingerprinting and quantitative PCR revealed a change in the bacterial community composition and abundance due to the temperature increase. While at 25 °C only slight changes in geochemical composition and gene copy numbers for bacteria were observed, increasing concentrations of total organic carbon in the 40 °C column were followed by a strong increase in bacterial abundance. Thermophilic bacteria became dominant at 70 °C. Temporary sulfate reduction took place at 40 and 70 °C and this correlated with an increased abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB). Furthermore, a coexistence of SRB and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) at all temperatures indicated an interaction of these physiological groups in the sediments. The results show that increased temperatures led to significant shifts in the microbial community composition due to the altered availability of electron donors and acceptors. The interplay of SRB and SOB in sedimentary biofilms facilitated closed sulfur cycling and diminished harmful sulfur species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Amann RI, Stromley J, Devereux R et al (1992) Molecular and microscopic identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in multispecies biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:614–623
Balkwill DL, Ghiorse WC (1985) Characterization of subsurface bacteria associated with two shallow aquifers in Oklahoma. Appl Environ Microbiol 50(3):580–588
Bauer S, Beyer C, Dethlefsen F, Dietrich P, Duttmann R, Ebert M, Feeser V, Goerke U, Koeber R, Kolditz O, Rabbel W, Schanz T, Schaefer D, Wuerdemann H, Dahmke A (2013) Impacts of the use of the geological subsurface for energy storage: an investigation concept. Environ Earth Sci 70:3935–3943
Bauer S, Pfeiffer T, Boockmeyer A, Dahmke A, Beyer C (2015) Quantifying induced effects of subsurface renewable energy storage. Energy Procedia 76:633–641
Baumgartner LK, Reid RP, Dupraz C, Decho AW, Buckley DH, Spear JR, Przekop KM, Visscher PT (2006) Sulfate reducing bacteria in microbial mats: changing paradigms, new discoveries. Sediment Geol 185:131–145
Beckwith CR, Edwards MJ, Lawes M, Shi L, Butt JN, Richardson DJ, Clarke TA (2015) Characterization of MtoD from Sideroxydans lithotrophicus: a cytochrome c electron shuttle used in lithoautotrophic growth. Front Microbiol 28(6):332
Blum P, Campillo G, Münch W, Kölbel T (2010) CO2 savings of ground source heat pump systems: a regional analysis. Renew Energy 35:122–127
Bonte M, Stuyfzand PJ, Hulsmann A, Van Beelen P (2011a) Underground thermal energy storage: environmental risks and policy developments in the Netherlands and the EU. Ecol Soc 16(1):22
Bonte M, Stuyfzand PJ, Van Den Berg G (2011b) The effects of aquifer thermal energy storage on groundwater quality and the consequences for drinking water production: a case study from the Netherlands. Water Sci Technol 63:1922–1931
Bonte M, Breukelen BVAN, Stuyfzand P (2013a) Environmental impacts of aquifer thermal energy storage investigated by field and laboratory experiments. J Water Clim Chang 4(2):77–89
Bonte M, van Breukelen BM, Stuyfzand PJ (2013) Temperature-induced impacts on groundwater quality and arsenic mobility in anoxic aquifer sediments used for both drinking water and shallow geothermal energy production. Water Res 47:5088–5100
Bonte M, Stuyfzand PJ, Breukelen BMV (2014) Reactive transport modeling of thermal column experiments to investigate the impacts of aquifer thermal energy storage on groundwater quality. Environ Sci Technol 48:12099–12107
Brielmann H, Griebler C, Schmidt SI et al (2009) Effects of thermal energy discharge on shallow groundwater ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68:273–286
Brielmann H, Lueders T, Schreglmann K, Ferraro F, Avramov M, Hammerl V, Blum P, Bayer P, Griebler C (2011) Oberflächennahe Geothermie und ihre potenziellen Auswirkungen auf Grundwasserökosysteme. Grundwasser 16:77–91
Brons HJ (1992) Biogeochemical aspects of aquifer thermal energy storage. PhD Thesis, Wageningen University
Brons HJ, Griffioen J, Appelo CAJ, Zehnder AJB (1991) (Bio)geochemical reactions in aquifer material from a thermal energy storage site. Water Res 25(6):729–736
Daumas S, Cord-Ruwisch R, Garcia JL (1988) Desulfotomaculum geothermicum sp. nov., a thermophilic, fatty acid-degrading, sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated with H2 from geothermal ground water. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 54(2):165–178
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Einsiedl F, Pilloni G, Ruth-Anneser B, Lueders T, Griebler C (2015) Spatial distributions of sulphur species and sulphate-reducing bacteria provide insights into sulphur redox cycling and biodegradation hot-spots in a hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 156:207–221
Griebler C, Lueders T (2009) Microbial biodiversity in groundwater ecosystems. Freshw Biol 54(4):649–677
Griffioen J, Appelo CAJ (1993) Nature and extent of carbonate precipitation during aquifer thermal energy storage. Appl Geochem 8:161–176
Grimont F, Grimont PAD (2006) The genus Serratia. In: The prokaryotes. A handbook on the biology of bacteria, Chapter 3.3.11, 6:219–244. doi:10.1007/0-387-30746-x_11
Hähnlein S, Bayer P, Ferguson G, Blum P (2013) Sustainability and policy for the thermal use of shallow geothermal energy. Energy Policy 59:914–925
Hallbeck L, Pedersen K (2014) The family Gallionellaceae. In: The prokaryotes, pp 853–858. ISBN: 978-3-642-30196-4
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):1–9
Handley KM, VerBerkmoes NC, Steefel CI, Williams KH, Sharon I, Miller CS, Frischkorn KR, Chourey K, Thomas BC, Shah MB, Long PE, Hettich RL, Banfield JF (2013) Biostimulation induces syntrophic interactions that impact C, S and N cycling in a sediment microbial community. ISME J 7(4):800–816
Hedrich S, Schlömann M, Johnson DB (2011) The iron-oxidizing proteobacteria. Microbiology 157(6):1551–1564
Herrmann M, Rusznyák A, Akob DM, Schulze I, Opitz S, Totsche KU, Küsel K (2015) Large fractions of CO2-fixing microorganisms in pristine limestone aquifers appear to be involved in the oxidation of reduced sulfur and nitrogen compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(7):2384–2394
Holm TR, Eisenreich SJ, Rosenberg HL, Holm NP (1987) Groundwater geochemistry of short-term aquifer thermal energy storage test cycles. Water Resour Res 23:1005–1019
Hubert C, Loy A, Nickel M et al (2009) A constant flux of diverse thermophilic bacteria into the cold Arctic seabed. Science 325(5947):1541–1544
Irgens RL, Gosink JJ, Staley JT (1996) Polaromonas vacuolata gen. nov., sp. nov., a psychrophilic, marine, gas vacuolate bacterium from Antarctica. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46(3):822–826
Jesußek A, Grandel S, Dahmke A (2013a) Impacts of subsurface heat storage on aquifer hydrogeochemistry. Environ Earth Sci 69:1999–2012
Jesußek A, Köber R, Grandel S, Dahmke A (2013b) Aquifer heat storage: sulphate reduction with acetate at increased temperatures. Environ Earth Sci 69:1763–1771
Kabuth A, Dahmke A, Beyer C, Bilke L, Dethlefsen F, Dietrich P, Duttmann R, Ebert M, Feeser V, Görke UJ, Köber R, Rabbel W, Schanz T, Schäfer D, Würdemann H, Bauer S (2017) Energy storage in the geological subsurface: dimensioning, risk analysis and spatial planning: the ANGUS + project. Environ Earth Sci 76:23
Kaksonen AH, Spring S, Schumann P, Kroppenstedt RM, Puhakka JA (2007) Desulfurispora thermophila gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, spore-forming sulfate-reducer isolated from a sulfidogenic fluidized-bed reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(5):1089–1094
Kalmbach S, Manz W, Wecke J, Szewzyk U (1999) Aquabacterium gen. nov., with description of Aquabacterium citratiphilum sp. nov., Aquabacterium parvum sp. nov. and Aquabacterium commune sp. nov., three in situ dominant bacterial species from the Berlin drinking water system. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49(2):769–777
Lerm S, Alawi M, Miethling-Graff R, Wolfgramm M, Rauppach K, Seibt A, Würdemann H (2011) Influence of microbial processes on the operation of a cold store in a shallow aquifer: impact on well injectivity and filter lifetime. Grundwasser 16:93–104
Lerm S, Westphal A, Miethling-Graff R, Alawi M, Seibt A, Wolfgramm M, Würdemann H (2013) Thermal effects on microbial composition and microbiologically induced corrosion and mineral precipitation affecting operation of a geothermal plant in a deep saline aquifer. Extremophiles 17:311–327
Losey NA, Stevenson BS, Busse HJ, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Rijpstra WI, Rudd S, Lawson PA (2013) Thermoanaerobaculum aquaticum gen. nov., sp. nov., the first cultivated member of Acidobacteria subdivision 23, isolated from a hot spring. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(11):4149–4157
Lu S, Ryu SH, Chung BS, Chung YR, Park W, Jeon CO (2007) Simplicispira limi sp. nov., isolated from activated sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(1):31–34
Lueders K, Firmbach L, Ebert M, Dahmke A, Dietrich P, Koeber R (2016) Gas phase formation during thermal energy storage in near surface aquifers—experimental and modelling results. Environ Earth Sci 75:1404
Margesin R, Spröer C, Zhang DC, Busse HJ (2012) Polaromonas glacialis sp. nov. and Polaromonas cryoconiti sp. nov., isolated from alpine glacier cryoconite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62(11):2662–2668
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nadkarni MA, Martin FE, Jacques NA, Hunter N (2002) Determination of bacterial load by real-time PCR using a broad-range (universal) probe and primers set. Microbiology 148:257–266
Okabe S, Ito T, Sugita K, Satoh H (2005) Succession of internal sulfur cycles and sulfur-oxidizing bacterial communities in microaerophilic wastewater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(5):2520–2529
Pavel AB, Vasile CI (2012) PyElph—a software tool for gel images analysis and phylogenetics. BMC Bioinform 13:13–19
Saito T, Hamamoto S, Ueki T, Ohkubo S, Moldrup P, Kawamoto K, Komatsu T (2016) Temperature change affected groundwater quality in a confined marine aquifer during long-term heating and cooling. Water Res 94:120–127
Saner D, Juraske R, Kübert M, Blum P, Hellweg S, Bayer P (2010) Is it only CO2 that matters? A life cycle perspective on shallow geothermal systems. Renew Sust Energ Rev 14(7):1798–1813
Satoh H, Odagiri M, Ito T, Okabe S (2009) Microbial community structures and in situ sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing activities in biofilms developed on mortar specimens in a corroded sewer system. Water Res 43(18):4729–4739
Sercu B, Boon N, Vander Beken S, Verstraete W, Van Langenhove H (2007) Performance and microbial analysis of defined and non-defined inocula for the removal of dimethyl sulfide in a biotrickling filter. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:661–672
Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. K Dan Vidensk Selsk 5(4):1–34
Wagner M, Roger AJ, Flax JL, Brusseau GA, Stahl DA (1998) Phylogeny of dissimilatory sulfite reductases supports an early origin of sulfate respiration. J Bacteriol 180:2975–2982
Westphal A, Lerm S, Miethling-Graff R, Seibt A, Wolfgramm M, Würdemann H (2016) Effects of plant downtime on the microbial community composition in the highly saline brine of a geothermal plant in the North German Basin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(7):3277–3290
Westphal A, Jesußek A, Kleyböcker A, Lienen T, Köber R, Würdemann H (2017) Aquifer heat storage: abundance and diversity of the microbial community with acetate at increased temperatures. Environ Earth Sci 76:66
Willems A, Busse J, Goor M, Pot B, Falsen E, Jantzen E, Hoste B, Gillis M, Kersters K, Auling G, De Ley J (1989) Hydrogenophaga, a new genus of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria that includes Hydrogenophaga flava comb. nov. (Formerly Pseudomonas flava), Hydrogenophaga palleronii (Formerly Pseudomonas palleronii), Hydrogenophaga pseudoflava (Formerly Pseudomonas pseudoflava and “Pseudomonas carboxydoflava”), and Hydrogenophaga taeniospiralis (Formerly Pseudomonas taeniospiralis). Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:319–333
Wilms R, Sass H, Köpke B, Cypionka H, Engelen B (2007) Methane and sulfate profiles within the subsurface of a tidal flat are reflected by the distribution of sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic archaea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:611–621
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Federal Ministry of Education and Research for funding the “ANGUS+” (FKZ: 03EK3022D) project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on ‘Subsurface Energy Storage’, guest edited by Sebastian Bauer, Andreas Dahmke, and Olaf Kolditz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lienen, T., Lüders, K., Halm, H. et al. Effects of thermal energy storage on shallow aerobic aquifer systems: temporary increase in abundance and activity of sulfate-reducing and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Earth Sci 76, 261 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6575-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6575-z