Abstract
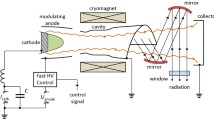
Gyrotrons are the most powerful terahertz sources and have potential applications in many areas. A terahertz gyrotron oscillator with a pulsed solenoid producing up to an 8 T magnetic field has been designed, constructed and tested. In a 7.96 T magnetic field, 3 kW output power radiations at 0.22 THz frequency have been generated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel P H. Terahertz technology. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech, 2002, 50: 910–920
Mueller E R. Terahertz radiation: Applications and sources. The Industrial Phys, 2003, 27–29
Liu S. New advance in terahertz technology. Chin Basic Sci, 2006, 8(1): 7–13
Hong K D, Brand G F, Idehara T. A 150-600 GHz step-tunable gyrotron. J Appl Phys, 1993, 74(8): 5250–5258
Chu K R. The electron cycltron maser. Rev Modern Phys, 2004, 76(2): 489–540
Piosczyk B, Braz O, Dammertz G. A 1.5-MW, 140-GHz, TE28, 16-coaxial cavity gyrotron. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 1997, 25(3): 460–469
Piosczyk B, Dammertz G, Dumbrajs O. A 2-MW, 170-GHz coaxial cavity gyrotron. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2004, 32(2): 413–417
Idehara T, Tsuchiya H, Watanabe O. The first experiment of a THz gyrotron with a pulse magent. Int J Infrared Millim Wave, 2006, 27(3): 319–331
Saito T, Nakano T, Hoshizuki H. Performance test of CW 300GHz Gyrotron FU CW I. Int J Infrared Millim Wave, 2007, 28: 1063–1078
Saito T, Idehara T, Mitsudo T. Oscillation characteristics of CW 300 GHz gyrotron FU CW I. In: Proceeding of 31st International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves and 14th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics. Beijing, 2006
Bandurkin I V, Bratman V L, Fedotov A E. Orotrons and gyrodevices at terahertz waves. ICOPS, 2006. 465
Hornstein M K, Bajaj V S, Griffin R G. Continuous-wave operation of a 460-GHz second harmonic gyrotron oscillator. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci, 2006, 34(3): 524–533
Hornstein M K, Bajaj V S, Griffin R G. Second harmonic operation at 460 GHz and broadband continuous frequency tuning of a gyrotron oscillator. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(5): 798–807
Bajaj V S, Farrar C, Hornstein M K. Dynamic nuclear polarization at 9 Tesla using a novel 250 GHz gyrotron microwave source. J Mag Res, 2002, 160(2): 85–90
Liu S G. Relativistic Electronics. Bejing: Science Press, 1986. 324–351
Goplen B, Ludeking L, Smithe L. User-configurable MAGIC for electromagnetic PIC calculations. Comp Phys Commun, 1995, 87: 54–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the State Key Development Program of Basic Research of China (Grant No. 2007CB310400) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 1067611)
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Liu, S., Li, X. et al. Design and demonstration of a 0.22 THz gyrotron oscillator. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54, 1495–1499 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0172-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0172-9