Sumary
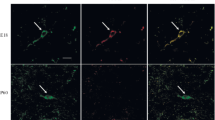
1. We investigate here for the first time in primate brain the combinatorial expression of the three major functionally relevant proteins for catecholaminergic neurotransmission tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), aromatic acid acid decarboxylase (AADC), and the brain-specific isoform of the vesicular monoamine transporter, VMAT2, using highly specific antibodies and immunofluorescence with confocal microscopy to visualize combinatorial expression of these proteins.
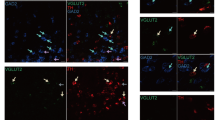
2. In addition to classical TH, AADC, and VMAT2-copositive catecholaminergic neurons, two unique kinds of TH-positive neurons were identified based on co-expression of AADC and VMAT2.
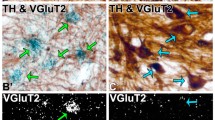
3. TH and AADC co-positive, but VMAT2-negative neurons, are termed “nonexocytotic catecholaminergic TH neurons.” These were found in striatum, olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, area postrema, nucleus tractus solitarius, and in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.
4. TH-positive neurons expressing neither AADC nor VMAT2 are termed “dopaergic TH neurons.” We identified these neurons in supraoptic, paraventricular and periventricular hypothalamic nuclei, thalamic paraventicular nucleus, habenula, parabrachial nucleus, cerebral cortex and spinal cord. We were unable to identify any dopaergic (TH-positive, AADC-negative) neurons that expressed VMAT2, suggesting that regulatory mechanisms exist for shutting off VMAT2 expression in neurons that fail to biosynthesize its substrates.
5. In several cases, the corresponding TH phenotypes were identified in the adult rat, suggesting that this rodent is an appropriate experimental model for further investigation of these TH-positive neuronal cell groups in the adult central nervous system. Thus, no examples of TH and VMAT2 co-positive neurons lacking AADC expression were found in rodent adult nervous system.
6. In conclusion, the adult mammalian nervous system contains in addition to classical catecholaminergic neurons, cells that can synthesize dopamine, but cannot transport and store it in synaptic vesicles, and neurons that can synthesize only L-dopa and lack VMAT2 expression. The presence of these additional populations of TH-positive neurons in the adult primate CNS has implications for functional catecholamine neurotransmission, its derangement in disease and drug abuse, and its rescue by gene therapeutic maneuvers in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andresen, M. C., Doyle, M. W., Jin, Y. H., and Bailey, T. W. (2001). Cellular mechanisms of baroreceptor integration at the nucleus tractus solitarius. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 940:132–141.
Anlauf, M., Schäfer, M. K.-H., Eiden, L. E., and Weihe, E. (2003). Chemical coding of the human gastrointestinal nervous system: Cholinergic, VIPergic and catecholaminergic phenotypes. J. Comp. Neurol. 459:90–111.
Asmus, S. E., Parsons, S., and Landis, S. C. (2000). Developmental changes in the transmitter properties of sympathetic neurons that innervate the periosteum. J. Neurosci. 20:1495–1504.
Axelrod, J. (1986). Doing research in the Intramural Program of the National Institutes of Health. Perspect. Biol. Med. 29:S131–S137.
Balan, I. S., Ugrumov, M. V., Calas, A., Mailly, P., Kreiger, M., and Thibault, J. (2000). Tyrosine hydroxylase-expressing and/or aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-expressing neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus of perinatal rats: differentiation and sexual dimorphism. J. Comp. Neurol. 425:167–176.
Betarbet, R., Turner, R., Chockkan, V., DeLong, M. R., Allers, K. A., Walters, J., Levey, A. I., and Greenamyre, J. T. (1997). Dopaminergic neurons intrinsic to the primate striatum. J. Neurosci. 17:6761–6768.
Carlsson, A. (2001). A paradigm shift in brain research. Science 294:1021–1024.
Cases, O., Lebrand, C., Giros, B., Vitalis, T., De Maeyer, E., Caron, M. G., Price, D. J., Gaspar, P., and Seif, I. (1998). Plasma membrane transporters of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine mediate serotonin accumulation in atypical locations in the developing brain of monoamine oxidase. A knock-outs. J. Neurosci. 18:6914–6927.
Cochard, P., Goldstein, M., and Black, I. B. (1978). Ontogenetic appearance and disappearance of tyrosine hydroxylase and catecholamines in the rat embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75:2986–2990.
Del Tredici, K., Rub, U., De Vos, R. A., Bohl, J. R., and Braak, H. (2002). Where does parkinson disease pathology begin in the brain? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 61:413–426.
Erickson, J. D., Schäfer, M. K.-H., Bonner, T. I., Eiden, L. E., and Weihe, E. (1996). Distinct pharmacological properties and distribution in neurons and endocrine cells of two isoforms of the human vesicular monoamine transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:5166–5171.
Ershov, P. V., Ugrumov, M. V., Calas, A., Krieger, M., and Thibault, J. (2002a). Differentiation of tyrosine hydroxylase-synthesizing and/or aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-synthesizing neurons in the rat mediobasal hypothalamus: Quantitative double-immunofluorescence study. J. Comp. Neurol. 446:114–22.
Ershov, P. V., Ugrumov, M. V., Calas, A., Krieger, M., and Thibault, J. (2005). Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons triggers an expression of individual enzymes of dopamine synthesis in non-dopaminergic neurons of the arcuate nucleus in adult rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 30:27–33.
Ershov, P. V., Ugrumov, M. V., Calas, A., Makarenko, I. G., Krieger, M., and Thibault, J. (2002b). Neurons possessing enzymes of dopamine synthesis in the mediobasal hypothalamus of rats. Topographic relations and axonal projections to the median eminence in ontogenesis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 24:95–107.
Fon, E. A., Pothos, E. N., Sun, B.-C., Killeen, N., Sulzer, D., and Edwards, R. H. (1997). Vesicular transport regulates monoamine storage and release but is not essential for amphetamine action. Neuron 19:1271–1283.
Gaspar, P., Berger, B., Febvret, A., Vigny, A., Krieger-Poulet, M., and Borri-Volta Horni, C. (1987). Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the human cerebral cortex: a novel catechol aminergic group? Neurosci. Lett. 80:257–262.
Guillemot, F., Lo, L.-C., Hohnson, J. E., Auerbach, A., Anderson, D. J., and Joyner, A. L. (1993). Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is required for the early development of olfactory and autonomic neurons. Cell 75:463–476.
Habecker, B. A., Klein, M. G., Sundgren, N. C., Li, W., and Woodward, W. R. (2002). Developmental regulation of neurotransmitter phenotype through tetrahydrobiopterin. J. Neurosci. 22:9445–9452.
Halasz, N., Ljungdahl, A., Hokfelt, T., Johansson, O., Goldstein, M., Park, D., and Biberfeld, P. (1977). Transmitter histochemistry of the rat olfactory bulb. I. Immunohistochemical localization of monoamine synthesizing enzymes. Support for intrabulbar, periglomerular dopamine neurons. Brain Res. 126:455–474.
Hansson, S., Mezey, E., and Hoffman, B. J. (1998a). Ontogeny of vesicular monoamine transporter mRNAs VMAT1 and VMAT2. II. Expression in neural crest derivatives and their target sites in the rat. Dev. Brain Res. 110:159–174.
Hansson, S. R., Hoffman, B. J., and Mezey, E. (1998b). Ontogeny of vesicular monoamine transporter mRNAs VMAT1 and VMAT2. I. The developing rat central nervous system. Dev. Brain Res. 110:135–158.
Hirayama, K., and Kapatos, G. (1998). Nigrostriatal dopamine neurons express low levels of GTP cyclohydrolase I protein. J. Neurochem. 70:164–170.
Hirsch, M.-R., Tiveron, M.-C., Guillemot, F., Brunet, J.-F., and Goridis, C. (1998). Control of noradrenergic differentiation and Phox2a expression by MASH1 in the central and peripheral nervous system. Development 125:599–608.
Hoffman, B. J., Palkovits, M., Pacak, K., Hansson, S. R., and Mezey, E. (1998). Regulation of dopamine transporter mRNA levels in the central nervous system. Adv. Pharmacol. 42:202–206.
Huang, M. H., Bahl, J. J., Wu, Y., Hu, F., Larson, D. F., Roeske, W. R., and Ewy, G. A. (2005). Neuroendocrine properties of intrinsic cardiac adrenergic cells in fetal rat heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288:H497–H503.
Ikemoto, K., Nagatsu, I., Kitahama, K., Jouvet, A., Nishimura, A., Nishi, K., Maeda, T., and Arai, R. (1998a). A dopamine-synthesizing cell group demonstrated in the human basal forebrain by dual labeling immunohistochemical technique of tyrosine hydroxlase and aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase. Neurosci. Lett. 243:129–132.
Ikemoto, K., Nagatsu, I., Nishimura, A., Nishi, K., and Arai, R. (1998b). Do all of human midbrain tyrosine hydroxylase neurons synthesize dopamine? Brain Res. 805:255–258.
Jonakait, G. M., Markey, K. A., Goldstein, M., Dreyfus, C. F., and Black, I. B. (1985). Selective expression of high-affinity uptake of catecholamines by transiently catecholaminergic cells of the rat embryo: studies in vivo and in vitro. Dev. Biol. 108:6–17.
Kariya, S., Takahaski, N., Hirano., M., and Ueno, S. (2005). Increased vulnerability to L-Dopa toxicity in dopaminergic neurons from VMAT2 heterozygote Knockout mice. J. Mol. Neurosci. 27:277–279.
Kitahama, K., Ikemoto, K., Jouvet, A., Nagatsu, I., Geffard, M., Okamura, H., and Pearson, J. (1998). Dopamine synthesizing enzymes in paraventricular hypothalamic neurons of the human and monkey (Macaca fuscata). Neurosci. Lett. 243:1–4.
Kitahama, K., Sakamoto, N., Jouvet, A., Nagatsu, I., and Pearson, J. (1996). Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons in the human brainstem. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 10:137–146.
Komori, K., Fujii, T., and Nagatsu, I. (1991). Do some tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the human ventrolateral arcuate nucleus and globus pallidus produce only L-dopa? Neurosci. Lett. 133:203–206.
Landis, S. C., Jackson, P. C., Fredieu, J. R., and Thibault, J. (1987). Catecholaminergic properties of cholinergic neurons and synapses in adult rat ciliary ganglion. J. Neurosci. 7:3574–3587.
Landis, S. C., Siegel, R. E., and Schwab, M. (1988). Evidence for neurotransmitter plasticity in vivo. II. Immunocytochemical studies of rat sweat gland innervation during development. Dev. Biol. 126:129–140.
Lebrand, C., Cases, O., Adelbrecht, C., Doye, A., Alvarez, C., El Mestikawy, S., Seif, I., and Gaspar, P. (1996). Transient uptake and storage of serotonin in developing thalamic neurons. Neuron 17:823–835.
Lebrand, C., Cases, O., Wehrlé, R., Blakely, R. D., Edwards, R. H., and Gaspar, P. (1998). Transient developmental expression of monoamine transporters in the rodent forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 401:506–524.
Liang, N. Y., and Rutledge, C. O. (1982). Evidence for carrier-mediated efflux of dopamine from corpus striatum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:2479–2484.
Mack, G. W., Shannon, L. M., and Nadel, E. R. (1986). Influence of beta-adrenergic blockade on the control of sweating in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 61:1701–1705.
Misu, Y., Goshima, Y., and Miyamae, T. (2002). Is DOPA a neurotransmitter? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 23:262–268.
Misu, Y., Kitahama, K., and Goshima, Y. (2003). l-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine as a neurotransmitter candidate in the central nervous system. Pharmacol. Ther. 97:117–137.
Palfi, S., Leventhal, L., Chu, Y., Ma, S. Y., Emborg, M., Bakay, R., Deglon, N., Hantraye, P., Aebischer, P., and Kordower, J. H. (2002). Lentivirally delivered glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases the number of striatal dopaminergic neurons in primate models of nigrostriatal degeneration. J. Neurosci. 22:4942–4954.
Rao, M. S., Jaszczak, E., and Landis, S. C. (1994). Innervation of footpads of normal and mutant mice lacking sweat glands. J. Comp. Neurol. 346:613–625.
Saavedra, J. M., Brownstein, M., Palkovits, M., Kizer, S., and Axelrod, J. (1974). Tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase: distribution in the individual rat hypothalamic nuclei. J. Neurochem. 23:869–871.
Sanchez-Gonzalez, M. A., Garcia-Cabezas, M. A., Rico, B., and Cavada, C. (2005). The primate thalamus is a key target for brain dopamine. J. Neurosci. 25:6076–6083.
Saper, C. B., and Sawchenko, P. E. (2003). Magic peptides, magic antibodies: guidelines for appropriate controls for immunohistochemistry. J. Comp. Neurol. 465:161–163.
Schütz, B., Schäfer, M. K.-H., Eiden, L. E., and Weihe, E. (1998a). Ontogeny of vesicular amine transporter expression in the rat: new perspectives on aminergic neuronal and neuroendocrine differentiation. Adv. Pharmacol. 42:903–908.
Schütz, B., Schäfer, M. K.-H., Eiden, L. E., and Weihe, E. (1998b). Vesicular amine transporter expression and isoform selection in developing brain, peripheral nervous system and gut. Dev. Brain Res. 106:181–204.
Ugrumov, M., Melnikova, V., Ershov, P., Balan, I., and Calas, A. (2002). Tyrosine hydroxylase- and/or aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-expressing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus: ontogenesis and functional significance. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:533–548.
Ugrumov, M. V. (1997). Hypothalamic monoaminergic systems in ontogenesis: Development and functional significance. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 41:809–816.
Ugrumov, M. V., Melnikova, V. I., Lavrentyeva, A. V., Kudrin, V. S., and Rayevsky, K. S. (2004). Dopamine synthesis by non-dopaminergic neurons expressing individual complementary enzymes of the dopamine synthetic pathway in the arcuate nucleus of fetal rats. Neuroscience 124:629–635.
Weihe, E., Anlauf, M., Schäfer, M.-K. H., Hartschuh, W., and Eiden, L. E. (1998). VMAT2 is the transporter mediating sequestration of monoamines in rat and human platelets, mast cells, and cutaneous dendritic cells. (abstract). Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. Nov. 7–12: No. 301.1.
Weihe, E., and Eiden, L. E. (2000). Chemical neuroanatomy of the vesicular amine transporters. FASEB J. 14:2435–2449.
Weihe, E., Schäfer, M. K.-H., Erickson, J. D., and Eiden, L. E. (1994). Localization of vesicular monoamine transporter isoforms (VMAT1 and VMAT2) to endocrine cells and neurons in rat. J. Mol. Neurosci. 5:149–164.
Weihe, E., Schutz, B., Hartschuh, W., Anlauf, M., Schafer, M. K., and Eiden, L. E. (2005). Co-expression of cholinergic and noradrenergic phenotypes in human and non-human autonomic nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 492:370–379.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Petra Lattermann, Elke Rodenberg-Frank, Romy Weber and Marion Zibuschka, for technical assistance and Uw Schneider and Heidemarie Schneiter for preparing digital images. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Volkswagen-Stiftung to EW and LEE, and by the National Institute of Mental Health Intramural Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weihe, E., Depboylu, C., Schütz, B. et al. Three Types of Tyrosine Hydroxylase-Positive CNS Neurons Distinguished by Dopa Decarboxylase and VMAT2 Co-Expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 657–676 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9053-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9053-9