Abstract
As an important chemokine receptor, the role of CX3CR1 has been studied extensively on the migration of lymphocytes including T and B cells. Although CX3CR1+ B cells have immune suppressor properties, little is known about its role on the regulation of BCR signaling and B cell differentiation as well as the underlying molecular mechanism. We have used CX3CR1 KO mice to study the effect of CX3CR1 deficiency on BCR signaling and B cell differentiation. Interestingly, we found that proximal BCR signaling, such as the activation of CD19, BTK and SHIP was reduced in CX3CR1 KO B cells upon antigenic stimulation. However, the activation of mTORC signaling was enhanced. Mechanistically, we found that the reduced BCR signaling in CX3CR1 KO B cells was due to reduced BCR clustering, which is caused by the enhanced actin accumulation by the plasma membrane via increased activation of WASP. This caused an increased differentiation of MZ B cells in CX3CR1 KO mice and an enhanced generation of plasma cells (PC) and antibodies. Our study shows that CX3CR1 regulates BCR signaling via actin remodeling and affects B cell differentiation and the humoral immune response.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 May 2020
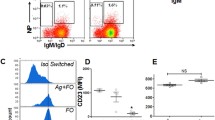
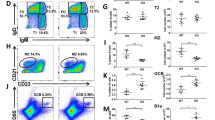
In the original published version of the article, the red squares in the figures which indicated the corrections.
References
Combadiere C, Ahuja SK, Murphy PM (1995) Cloning, chromosomal localization, and RNA expression of a human beta chemokine receptor-like gene. DNA Cell Biol 14:673–680
Combadiere C, Salzwedel K, Smith ED, Tiffany HL, Berger EA, Murphy PM (1998) Identification of CX3CR1. A chemotactic receptor for the human CX3C chemokine fractalkine and a fusion coreceptor for HIV-1. J Biol Chem 273:23799–23804
Imai T, Hieshima K, Haskell C, Baba M, Nagira M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Nomiyama H, Schall TJ, Yoshie O (1997) Identification and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1, which mediates both leukocyte migration and adhesion. Cell 91:521–530
Landsman L, Bar-On L, Zernecke A, Kim KW, Krauthgamer R, Shagdarsuren E, Lira SA, Weissman IL, Weber C, Jung S (2009) CX3CR1 is required for monocyte homeostasis and atherogenesis by promoting cell survival. Blood 113:963–972
Wu Z (2014) CX3CR1(+) B cells show immune suppressor properties. J Biol Chem 289:22630–22635
Zhivaki D, Lemoine S, Lim A, Morva A, Vidalain PO, Schandene L, Casartelli N, Rameix-Welti MA, Herve PL, Deriaud E, Beitz B, Ripaux-Lefevre M, Miatello J, Lemercier B, Lorin V, Descamps D, Fix J, Eleouet JF, Riffault S, Schwartz O, Porcheray F, Mascart F, Mouquet H, Zhang X, Tissieres P, Lo-Man R (2017) Respiratory syncytial virus infects regulatory B cells in human neonates via chemokine receptor CX3CR1 and promotes lung disease severity. Immunity 46:301–314
Ferretti E, Bertolotto M, Deaglio S, Tripodo C, Ribatti D, Audrito V, Blengio F, Matis S, Zupo S, Rossi D, Ottonello L, Gaidano G, Malavasi F, Pistoia V, Corcione A (2011) A novel role of the CX3CR1/CX3CL1 system in the cross-talk between chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and tumor microenvironment. Leukemia 25:1268–1277
Mionnet C, Buatois V, Kanda A, Milcent V, Fleury S, Lair D, Langelot M, Lacoeuille Y, Hessel E, Coffman R, Magnan A, Dombrowicz D, Glaichenhaus N, Julia V (2010) CX3CR1 is required for airway inflammation by promoting T helper cell survival and maintenance in inflamed lung. Nat Med 16:1305–1312
Ren H, Zhao T, Sun J, Wang X, Liu J, Gao S, Yu M, Hao J (2013) The CX3CL1/CX3CR1 reprograms glucose metabolism through HIF-1 pathway in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Cell Biochem 114:2603–2611
Liu JF, Tsao YT, Hou CH (2017) Fractalkine/CX3CL1 induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1-dependent tumor metastasis through the CX3CR1/PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway in human osteosarcoma. Oncotarget 8:54136–54148
Lee SJ, Namkoong S, Kim YM, Kim CK, Lee H, Ha KS, Chung HT, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2006) Fractalkine stimulates angiogenesis by activating the Raf-1/MEK/ERK- and PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent signal pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H2836–2846
Fumarola C, La Monica S, Alfieri RR, Borra E, Guidotti GG (2005) Cell size reduction induced by inhibition of the mTOR/S6K-signaling pathway protects Jurkat cells from apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 12:1344–1357
Lang CH, Frost RA (2005) Endotoxin disrupts the leucine-signaling pathway involving phosphorylation of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and S6K1 in skeletal muscle. J Cell Physiol 203:144–155
Fiano V, Ghimenti C, Imarisio S, Silengo L, Schiffer D (2004) PAkt, cyclin D1 and p27/Kip.1 in glioblastomas with and without EGFR amplification and PTEN mutation. Anticancer Res 24:2643–2647
Otero DC, Anzelon AN, Rickert RC (2003) CD19 function in early and late B cell development: I. Maintenance of follicular and marginal zone B cells requires CD19-dependent survival signals. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 170:73–83
Thomas MD, Srivastava B, Allman D (2006) Regulation of peripheral B cell maturation. Cell Immunol 239:92–102
Pillai S, Cariappa A (2009) The follicular versus marginal zone B lymphocyte cell fate decision. Nat Rev Immunol 9:767–777
De S, Barnes BJ (2014) B cell transcription factors: potential new therapeutic targets for SLE. Clin Immunol (Orlando, Fla.) 152:140–151
Cariappa A, Tang M, Parng C, Nebelitskiy E, Carroll M, Georgopoulos K, Pillai S (2001) The follicular versus marginal zone B lymphocyte cell fate decision is regulated by Aiolos, Btk, and CD21. Immunity 14:603–615
Liu W, Meckel T, Tolar P, Sohn HW, Pierce SK (2010) Intrinsic properties of immunoglobulin IgG1 isotype-switched B cell receptors promote microclustering and the initiation of signaling. Immunity 32:778–789
Tolar P, Hanna J, Krueger PD, Pierce SK (2009) The constant region of the membrane immunoglobulin mediates B cell-receptor clustering and signaling in response to membrane antigens. Immunity 30:44–55
Tolar P, Sohn HW, Pierce SK (2005) The initiation of antigen-induced B cell antigen receptor signaling viewed in living cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nat Immunol 6:1168–1176
Mattila PK, Feest C, Depoil D, Treanor B, Montaner B, Otipoby KL, Carter R, Justement LB, Bruckbauer A, Batista FD (2013) The actin and tetraspanin networks organize receptor nanoclusters to regulate B cell receptor-mediated signaling. Immunity 38:461–474
Treanor B, Depoil D, Gonzalez-Granja A, Barral P, Weber M, Dushek O, Bruckbauer A, Batista FD (2010) The membrane skeleton controls diffusion dynamics and signaling through the B cell receptor. Immunity 32:187–199
Liu C, Bai X, Wu J, Sharma S, Upadhyaya A, Dahlberg CI, Westerberg LS, Snapper SB, Zhao X, Song W (2013) N-wasp is essential for the negative regulation of B cell receptor signaling. PLoS Biol 11:e1001704
Hao S, August A (2005) Actin depolymerization transduces the strength of B-cell receptor stimulation. Mol Biol Cell 16:2275–2284
Seeley-Fallen MK, Liu LJ, Shapiro MR, Onabajo OO, Palaniyandi S, Zhu X, Tan TH, Upadhyaya A, Song W (2014) Actin-binding protein 1 links B-cell antigen receptors to negative signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9881–9886
Sharma S, Orlowski G, Song W (2009) Btk regulates B cell receptor-mediated antigen processing and presentation by controlling actin cytoskeleton dynamics in B cells. J Immunol (Baltimore Md. : 1950) 182:329–339
Huang L, Zhang Y, Xu C, Gu X, Niu L, Wang J, Sun X, Bai X, Xuan X, Li Q, Shi C, Yu B, Miller H, Yang G, Westerberg LS, Liu W, Song W, Zhao X, Liu C (2017) Rictor positively regulates B cell receptor signaling by modulating actin reorganization via ezrin. PLoS Biol 15:e2001750
Pore D, Huang E, Dejanovic D, Parameswaran N, Cheung MB, Gupta N (2018) Cutting edge: deletion of Ezrin in B cells of lyn-deficient mice downregulates lupus pathology. J Immunol 201:1353–1358
Pore D, Matsui K, Parameswaran N, Gupta N (2016) Cutting edge: Ezrin regulates inflammation by limiting B cell IL-10 production. J Immunol 196:558–562
Treanor B, Depoil D, Bruckbauer A, Batista FD (2011) Dynamic cortical actin remodeling by ERM proteins controls BCR microcluster organization and integrity. J Exp Med 208:1055–1068
Parameswaran N, Enyindah-Asonye G, Bagheri N, Shah NB, Gupta N (2013) Spatial coupling of JNK activation to the B cell antigen receptor by tyrosine-phosphorylated ezrin. J Immunol 190:2017–2026
Pore D, Gupta N (2015) The ezrin-radixin-moesin family of proteins in the regulation of B-cell immune response. Crit Rev Immunol 35:15–31
Dichmann S, Herouy Y, Purlis D, Rheinen H, Gebicke-Harter P, Norgauer J (2001) Fractalkine induces chemotaxis and actin polymerization in human dendritic cells. Inflamm Res 50:529–533
Ha N, Pham DH, Shahsafaei A, Naruse C, Asano M, Thai TH (2014) HP-1gamma controls high-affinity antibody response to T-dependent antigens. Front Immunol 5:271
Domeier PP, Schell SL, Rahman ZS (2017) Spontaneous germinal centers and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 50:4–18
Liu C, Miller H, Hui KL, Grooman B, Bolland S, Upadhyaya A, Song W (2011) A balance of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and SHIP activation regulates B cell receptor cluster formation by controlling actin remodelling. J Immunol (Baltimore Md.: 1950) 187:230–239
Smith TG, Robbins PA, Ratcliffe PJ (2008) The human side of hypoxia-inducible factor. Br J Haematol 141:325–334
Wilkins SE, Abboud MI, Hancock RL, Schofield CJ (2016) Targeting Protein-Protein Interactions in the HIF System. ChemMedChem 11:773–786
Rozen-Zvi B, Hayashida T, Hubchak SC, Hanna C, Platanias LC, Schnaper HW (2013) TGF-beta/Smad3 activates mammalian target of rapamycin complex-1 to promote collagen production by increasing HIF-1alpha expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F485–494
Shulby SA, Dolloff NG, Stearns ME, Meucci O, Fatatis A (2004) CX3CR1-fractalkine expression regulates cellular mechanisms involved in adhesion, migration, and survival of human prostate cancer cells. Can Res 64:4693–4698
Gaudin F, Nasreddine S, Donnadieu AC, Emilie D, Combadiere C, Prevot S, Machelon V, Balabanian K (2011) Identification of the chemokine CX3CL1 as a new regulator of malignant cell proliferation in epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 6:e21546
Saitoh Y, Koizumi K, Sakurai H, Minami T, Saiki I (2007) RANKL-induced down-regulation of CX3CR1 via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway suppresses Fractalkine/CX3CL1-induced cellular responses in RAW264.7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 364:417–422
El-Shazly AE, Doloriert HC, Bisig B, Lefebvre PP, Delvenne P, Jacobs N (2013) Novel cooperation between CX3CL1 and CCL26 inducing NK cell chemotaxis via CX3CR1: a possible mechanism for NK cell infiltration of the allergic nasal tissue. Clin Exp Allergy 43:322–331
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81861138002, 81722002 and 31970839) and the start-up funding from Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NL and PJ drafted the initial manuscript. CL designed the research, reviewed and revised the manuscript. AC performed the TRIFm experiments, XL and NL performed Seahorse experiments. NL and YJ performed the confocal experiments. NL, YJ, LY, PJ, DK, JL, JC, QC carried out the flow cytometry assay, ELISA, and Western blotting. NL analyzed the data and generated figures. JJ, HM, LW, CW, QG assisted with the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Jiang, P., Chen, A. et al. CX3CR1 positively regulates BCR signaling coupled with cell metabolism via negatively controlling actin remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 4379–4395 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03416-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03416-7