Abstract
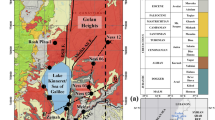
The historical Golden Horn Estuary (GHE), near the confluence of the Istanbul Strait (Bosphorus) and the Sea of Marmara in the European part of Istanbul, has been used as a natural harbor since 330 a.d. The sedimentary infill of the GHE is 15–46 m thick, deposited unconformably above the turbiditic sandstones of the Carboniferous Trakya Formation. Chronostratigraphic and paleontological analyses of the infill sequence indicate that the GHE was a fluvial channel prior to 13,500 cal. a (calibrated to calendar years) B.P. It subsequently became gradually influenced by marine waters, and was a brackish-water environment until 9,500 cal. a B.P. Normal marine salinities prevailed at ca. 9,500−5,600 cal. a B.P., with suboxic/dysoxic bottom-water conditions. The increase in salinity at 9,500 cal. a B.P. was most likely caused by Mediterranean water outflow into the Black Sea through the Istanbul Strait. The estuary was influenced by large fluvial inputs between 5,600 and 1,000 cal. a B.P., possibly during a distinct pluvial period, as shown by coarse siliciclastic sediments deposited on the flanks. It has become a highly polluted environment with marked anthropogenic inputs during the last millennium. The finding that the sediment infill sequence above the Carboniferous basement is not older than about 20 ka strongly suggests that the Golden Horn Estuary acquired its present-day morphology during the late glacial–Holocene period.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu AE, Hiscott RN, Kaminski MA, Mudie PJ, Gillespie H, Abrajano T, Yasar D (2002) Last glacial-Holocene paleoceanography of the black sea and Marmara sea: stable isotopic, foraminiferal and coccolith evidence. Mar Geol 190:119–149
Algan O, Gökasan E, Gazioglu C, Yücel ZY, Alpar B, Güneysu C, Kirci E, Demirel S, Sari E, Ongan D (2002) A high-resolution seismic study in sakarya delta and submarine canyon, southern black sea shelf. Cont Shelf Res 22:1511–1527
Alpar B, Yüce H, Türker A (2003) Water exchange in the golden horn. Turkish J Mar Sci 9:51–68
Bahr A, Arz H, Lamy F, Wefer G (2006) Late glacial to Holocene paleoenvironmental evolution of the black sea, reconstructed with stable oxygen isotope records obtained on ostracod shells. Earth Planet Sci Lett 241:863–875
Bahr A, Lamy F, Arz HW, Major CO, Kwiecien O, Wefer G (2008) Abrupt changes of temperature and water chemistry in the late pleistocene and early holocene black sea. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 9:1–16
Çagatay MN, Görür N, Algan O, Eastoe C, Tchapalyga A, Ongan D, Kuhn T, Kuscu I (2000) Late glacial-holocene palaeoceanography of the sea of Marmara: timing of connections with the Mediterranean and the black seas. Mar Geol 167:191–206
Çagatay MN, Görür N, Polonia A, Demirbağ E, Sakınç M, Cormier MH, Capotondi L, McHugh C, Emre Ö, Eriş K (2003) Sea-level changes and depositional environments in the Izmit Gulf, eastern Marmara Sea, during the late glacial-Holocene period. Mar Geol 202:159–173
Çagatay MN, Görür N, Flecker R, Sakınç M, Tünoglu C, Ellam R, Krijgsman W, Vincent S, Dikbas A (2006) Paratethyan-Mediterranean connectivity in the sea of Marmara region (NW Turkey) during the Messinian. Sed Geol 188/189:171–187
Cimerman F, Langer MR (1991) Mediterranean Foraminifera. Slovenska Akademija Znanosti in Umetnosti, Ljubljana
Cushman JA (1959) Foraminifera: their classification and economic use. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Ergin M (1990) A review of modern sedimentation in the Golden Horn Estuary (Sea of Marmara), Turkey. Boll Oceanol Teorica Applicata 8:135–151
Eriş KK, Ryan WBF, Çagatay MN, Sancar U, Lericolais G, Ménot G, Bard E (2007) The timing and evolution of the post-glacial transgression across the Sea of Marmara shelf south of Istanbul. Mar Geol 243:57–76
Görür N, Çagatay MN, Emre Ö, Alpar B, Sakınç M, Islamoglu Y, Algan O, Erkal T, Keçer M, Akkök R, Karlık G (2001) Is the abrupt drowning of the black sea shelf at 7150 yr a myth? Mar Geol 176:65–73
Kaminski MA, Aksu A, Box M, Hiscott RN, Filipescu S, Al-Salameen M (2002) Late glacial to Holocene benthic foraminifera in the Marmara sea: implications for black sea-mediterranean sea connections following the last deglaciation. Mar Geol 190:165–202
Kıratlı N, Ergin M (1996) Partitioning of heavy metals in surface black sea sediments. Appl Geochem 11:1–14
Lambeck K, Sivan D, Purcell A (2007) Timing of the last Mediterranean sea-black sea connection from isostatic models and regional sea level data. In: Yanko-Hombach V, Gilbert AS, Dolukhanov PM (eds) The Black Sea Flood question. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 797–808
Major CO, Goldstein SL, Ryan WBF, Lericolais G, Piotrowski AM, Hajdas I (2006) The co-evolution of Black Sea level and composition through the last deglaciation and its paleoclimatic significance. Quat Sci Rev 25:2031–2047
Meriç E, Sakınç M (1990) Foraminifera. In: Meriç E (ed) Late Quaternary (Holocene) bottom sediments of the southern Bosphorus and Golden Horn. Istanbul Technical University Publication, Istanbul, pp 13–41
Meriç E, Yanko V, Avşar N (1995) Foraminiferal fauna of the Quaternary sequence in the Gulf of Izmit (Hersek Burnu-Kaba Burun) (in Turkish). In: Meriç E (ed) Quaternary sequence in the Gulf of Izmit. Turkish Navy, Istanbul, pp 105–151
Meriç E, Kerey IE, Avşar N, Tugrul AB, Suner F, Sayar A (2003) New findings on the Holocene deposits in the Golden Horn (Istanbul) coastal area (Unkapani-Azapkapi) (in Turkish, with English Abstract). Hacettepe University, Institute of Earth Sciences, Ankara, pp 9–32
Meriç E, Görmüş M, Avşar N (2007) Holocene geologic history of the golden horn (Istanbul, NW Turkey) based on foraminiferal data. J Asian Earth Sci 30:353–363
Pickard GL (1975) Descriptive physical oceanography. Pergamon, Elmsford, NY
Polonia A, Gasperini L, Amorosi A, Bonatti E, Bortoluzzi G, Çagatay N, Capotondi L, Cormier MH, Gorur N, McHugh C, Seeber L (2004) Holocene slip rate of the North Anatolian fault beneath the Sea of Marmara. Earth Planet Sci Lett 227:411–426
Pritchard DW (1967) What is an estuary, physical viewpoint. Washington D.C., WA
Ryan WBF, Major C, Lericolais G, Goldstein SL (2003) Catastrophic flooding of the black sea. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 31:525–554
Sakınç M (2008) Benthic Foraminifera of Sea of Marmara: systematics and autoecology. Istanbul Technical University Publication, Istanbul
Sakınç M, Yaltırak C, Oktay FY (1999) Palaeogeographical evolution of the thrace neogene basin and the tethys-paratethys relations at northwestern Turkey (Thrace). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 153:17–40
Şamlı AC (1996) Benthic foraminifer fauna of holocene sediments in golden horn (Istanbul) (in Turkish, with english abstract). Tmmob Jeoloji Muhendisleri, Geol Bull Turkey 39:87–102
Sgarella F, Moncharmont-Zei M (1993) Benthic foraminifera of the gulf of Naples(Italy): systematics and autoecology. Modena Boll Soc Paleontol Ital 32:145–264
Siani G, Paterne M, Arnold M, Bard E, Metivier B, Tisnerat N, Bassinot F (2000) Radiocarbon reservoir ages in the Mediterranean sea and black sea. Radiocarbon 42:271–280
Stuiver M, Reimer PJ (1993) Extended 14C data base and revised CALIB 3.0 14C Age calibration program. Radiocarbon 35:215−230
Tolun L, Çagatay MN, Carrigan WJ (2002) Organic geochemistry and origin of late glacial-holocene sapropelic layers and associated sediments in Marmara Sea. Mar Geol 190:47–60
Tuncer G, Tuncel G, Balkas TI (2001) Evolution of metal pollution in the golden horn (Turkey) sediments between 1912 and 1987. Mar Pollut Bull 42:350–360
Wright R (1978) Neogene benthic foraminifers from DSDP leg 42A, Mediterranean Sea. University of California, Washington, DC, Initial Reports DSDP Project XLII part I:709–726
Yanko VV (1990) Stratigraphy and paleogeography of the marine pleistocene and holocene deposits of the southern seas of the USSR. Mem Soc Geol Ital 44:167–187
Yanko VV, Troitskaja TS (1987) Late quaternary foraminifera of the black sea (in Russian), vol. 694. Trudy Instituta Geologii i Geofisiki, Akademiya Nauk SSSR, Novosibirsk
Acknowledgements
We would to thank Mr. Murat Hızel of Anadolu Metro Construction Company for providing access to the drill hole material, and Dr. Levent Erel for his advice on archeological aspects of the study and his help during sampling. Ayyüz Sabuncu is thanked for identification of the ceramic pieces.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Irvalı, N., Çağatay, M.N. Late Pleistocene–Holocene history of the Golden Horn Estuary, Istanbul. Geo-Mar Lett 29, 151–160 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-008-0129-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-008-0129-z