Abstract
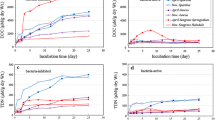
Diurnal variation of dissolved oxygen (DO), organic and inorganic carbon (DOC, DIC), nitrogen (DON, DIN), and phosphorus (DOP, DIP) flux across the sediment–water interface was assessed in fish farm impacted and pristine seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadows in the Aegean Sea (Greece). DIC consumption decreased by 52% and DO production decreased by 60% in the light, suggesting reduced photosynthetic performance of the plant community under the fish cages probably due to organic matter loading. In light there was 4 and 15 times higher release of dissolved inorganic and organic matter, respectively, compared to dark incubations under the cages, indicating that fish farming impact is more intense during daytime. DO was taken up, while DIC was released in the dark in both stations, representing a direct measure of mineralization. Dissolved inorganic matter flux (as the sum of DIN and DIP fluxes) was positively related to DIC flux, rendering mineralization as the main driver of nutrient flux under the cages. On average, the impacted meadow released DIN and DIP both in light and dark, while efflux of dissolved organic matter (as the sum of DOC, DON, and DOP fluxes) increased by 132% in the light and by 21% in the dark, implying that the degrading seagrass meadow is a source of dissolved matter to the surrounding water. Shoot density and leaf production were negatively correlated with both diel DIN and DIP fluxes, showing that meadow regression is accompanied by DIN and DIP release from the sediment. Hence, nutrient efflux can adequately illustrate meadow deterioration and, therefore, can be used as indicator of P. oceanica community health.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolaki, E. T., N. Marba, M. Holmer & I. Karakassis, 2009a. Fish farming enhances biomass and nutrient loss in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 81: 390–400.
Apostolaki, E. T., N. Marba, M. Holmer & I. Karakassis, 2009b. Fish farming impact on decomposition of Posidonia oceanica litter. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 369: 58–64.
Apostolaki, E. T., M. Holmer, N. Marba & I. Karakassis, 2010. Metabolic imbalance in coastal vegetated (Posidonia oceanica) and unvegetated benthic ecosystems. Ecosystems. doi:10.1007/s10021-010-9330-9.
Barron, C. & C. M. Duarte, 2009. Dissolved organic matter release in a Posidonia oceanica meadow. Marine Ecology Progress Series 374: 75–84.
Barron, C., C. M. Duarte, M. Frankignoulle & A. V. Borges, 2006. Organic carbon metabolism and carbonate dynamics in a Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadow. Estuaries and Coasts 29: 417–426.
Blaabjerg, V., K. N. Mouritsen & K. Finster, 1998. Diel cycles of sulphate reduction rates in sediments of a Zostera marina bed (Denmark). Aquatic Microbial Ecology 15: 97–102.
Borg, J. A., A. A. Rowden, M. J. Attrill, P. J. Schembri & M. B. Jones, 2006. Wanted dead or alive: high diversity of macroinvertebrates associated with living and ‘dead’ Posidonia oceanica matte. Marine Biology 149: 667–677.
Borowitzka, M. A., P. S. Lavery & M. van Keulen, 2006. Epiphytes of seagrasses. In Larkum, A. W. D., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds.), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, The Netherlands: 441–461.
Brylinsky, M., 1977. Release of dissolved organic matter by some marine macrophytes. Marine Biology 39: 213–220.
Burkholder, J. M., D. A. Tomasko & B. W. Touchette, 2007. Seagrasses and eutrophication. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 46–72.
Calleja, M. L., C. Barron, J. A. Hale, T. K. Frazer & C. M. Duarte, 2006. Light regulation of benthic sulfate reduction rates mediated by seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) metabolism. Estuaries and Coasts 29: 1255–1264.
Cebrian, J., C. M. Duarte, N. Marba & S. Enriquez, 1997. Magnitute and fate of the production of four co-occuring Western Mediterranean seagrass species. Marine Ecology Progress Series 155: 29–44.
Christensen, P. B., S. Rysgaard, N. P. Sloth, T. Dalsgaard & S. Schwaerter, 2000. Sediment mineralization, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in an estuarine fjord with sea cage trout farms. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21: 73–84.
Dalsgaard, T., 2003. Benthic primary production and nutrient cycling in sediments with benthic microalgae and transient accumulation of macroalgae. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 2138–2150.
Diaz-Almela, E., N. Marba, E. Alvarez, R. Santiago, M. Holmer, A. Grau, R. Danovaro, M. Argyrou, I. Karakassis & C. M. Duarte, 2008. Benthic input rates predict seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) fish farm-induced decline. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 1332–1342.
Duarte, C. M., 2002. The future of seagrass meadows. Environmental Conservation 29: 192–206.
Duarte, C. M., W. C. Dennison, R. J. W. Orth & T. J. B. Carruthers, 2008. The charisma of coastal ecosystems: addressing the imbalance. Estuaries and Coasts: J CERF 31: 233–238.
Eyre, B. D. & A. J. P. Ferguson, 2002. Comparison of carbon production and decomposition, benthic nutrient fluxes and denitrification in seagrass, phytoplankton, benthic microalgae- and macroalgae-dominated warm-temperate Australian lagoons. Marine Ecology Progress Series 229: 43–59.
Frankovich, T. A. & J. W. Fourqurean, 1997. Seagrass epiphyte loads along a nutrient availability gradient, Florida Bay, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series 159: 37–50.
Frederiksen, M., M. Holmer, E. Diaz-Almela, N. Marba & C. M. Duarte, 2007. Sulfide invasion in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica at Mediterranean fish farms: assessment using stable sulfur isotopes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 345: 93–104.
Goodman, J. L., K. A. Moore & W. C. Dennison, 1995. Photosynthetic responses of eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) to light and sediment sulfide in a shallow barrier island lagoon. Aquatic Botany 50: 37–47.
Hall, P. O. J. & R. C. Aller, 1992. Rapid, small-volume, flow injection analysis for ΣCO2 and NH4 + in marine and freshwaters. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 1113–1119.
Hansen, J. W., B. Thamdrup & B. B. Jorgensen, 2000. Anoxic incubation of sediment in gas-tight plastic bags: a method for biogeochemical process studies. Marine Ecology Progress Series 208: 273–282.
Hemminga, M. A. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Seagrass Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK: 298 pp.
Holmer, M. & M. Frederiksen, 2007. Stimulation of sulfate reduction rates in Mediterranean fish farm sediments inhabited by the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Biogeochemistry 85: 169–184.
Holmer, M., F. O. Anderesen, N. Holmboe, E. Kristensen & N. Thongtham, 2001. Spatial and temporal variability in benthic processes along a mangrove-seagrass transect near the Bangrong mangrove, Thailand. Wetlands Ecology and Management 9: 141–158.
Holmer, M., N. Marba, J. Terrados, C. M. Duarte & M. D. Fortes, 2002. Impacts of milkfish (Chanos chanos) aquaculture on carbon and nutrient fluxes in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44: 685–696.
Holmer, M., C. M. Duarte & N. Marba, 2003. Sulfur cycling and seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) status in carbonate sediments. Biogeochemistry 66: 223–239.
Holmer, M., M. Argyrou, T. Dalsgaard, R. Danovaro, E. Diaz-Almela, C. M. Duarte, M. Frederiksen, A. Grau, I. Karakassis, N. Marba, S. Mirto, M. Perez, A. Pusceddu & M. Tsapakis, 2008. Effects of fish farm waste on Posidonia oceanica meadows: synthesis and provision of monitoring and management tools. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 1618–1629.
Ibarra-Obando, S. E., S. V. Smith, M. Poumian-Tapia, V. Camacho-Ibar, J. D. Carriquiry & M. Montes-Hugo, 2004. Benthic metabolism in San Quintin Bay, Baja California, Mexico. Marine Ecology Progress Series 283: 99–112.
Ivancic, I. & D. Deggobis, 1984. An optimal manual procedure for ammonia analysis in natural waters by the indophenol blue method. Water Research 18: 1143–1147.
Karakassis, I., M. Tsapakis, E. Hatziyanni & P. Pitta, 2001. Diel variation of nutrient and chlorophyll in sea bass and sea bream cages in the Mediterranean. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 10: 278–283.
Lopez y Royo, C., G. Casazza, C. Pergent-Martini & G. Pergent, 2010. A biotic index using the seagrass Posidonia oceanica (BiPo), to evaluate ecological status of coastal waters. Ecological Indicators 10: 380–389.
Marba, N., R. Santiago, E. Diaz-Almela, E. Alvarez & C. M. Duarte, 2006. Seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) vertical growth as an early indicator of fish-farm-derived stress. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 67: 475–483.
Mateo, M. A., J.-L. Sanchez-Lizaso & J. Romero, 2003. Posidonia oceanica “banquettes”: a preliminary assessment of the relevance for meadow carbon and nutrients budget. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 56: 85–90.
Mazzella, L., M. B. Scipione & M. C. Buia, 1989. Spatio-temporal distribution of algal and animal communities in a Posidonia oceanica meadow. Marine Ecology – Publicazioni della Stazione Zoologica di Napoli 10: 107–129.
McRoy, C. P. & J. J. Goering, 1974. Nutrient transfer between the seagrass Zostera marina and its epiphytes. Nature 248: 173–174.
Montefalcone, M., 2009. Ecosystem health assessment using the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica: a review. Ecological Indicators 9: 595–604.
Papageorgiou, N., I. Kalantzi & I. Karakassis, 2010. Effects of fish farming on different sediment types of the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Environmental Research. doi:10.1010/j.marenvres.2009.12.007.
Penhale, P. A. & W. O. J. Smith, 1977. Excretion of dissolved organic carbon by eelgrass (Zostera marina) and its epiphytes. Limnology and Oceanography 22: 400–407.
Penhale, P. A. & G. W. Thayer, 1980. Uptake and transfer of carbon and phosphorus by eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) and its epiphytes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 42: 113–123.
Perez, M., T. Garcia, O. Invers & J. M. Ruiz, 2008. Physiological responses of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica as indicators of fish farm impact. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 869–879.
Pergent-Martini, C., V. Leoni, V. Pasqualini, G. D. Adrizzone, E. Balestri, R. Bedini, A. Belluscio, T. Belsher, J. Borg, C. F. Boudouresque, S. Boumaza, J. M. Bouquegneau, M. C. Buia, S. Calvo, J. Cebrian, E. Charbonnel, F. Cinelli, A. Cossu, G. Di Maida, B. Dural, P. Francour, S. Gobert, G. Lepoint, A. Meinesz, H. Molenaar, H. M. Mansour, P. Panayotidis, A. Peirano, G. Pergent, L. Piazzi, M. Pirrotta, G. Relini, J. Romero, J. L. Sanchez-Lizaso, R. Semroud, P. Shembri, A. Shili, A. Tomasello & B. Velimirov, 2005. Descriptors of Posidonia oceanica meadows: use and application. Ecological Indicators 5: 213–230.
Pergent-Martini, C., C.-F. Boudouresque, V. Pasqualini & G. Pergent, 2006. Impact of fish farming facilities on Posidonia oceanica meadows: a review. Marine Ecology 27: 310–319.
Qu, W. C., R. J. Morrison & R. J. West, 2003. Inorganic nutrient and oxygen fluxes across the sediment–water interface in the inshore macrophyte areas of a shallow estuary (Lake Illawarra, Australia). Hydrobiologia 492: 119–127.
Raimbault, P., W. Pouvesle, F. Diaz, N. Garcia & R. Sempere, 1999. Wet-oxidation and automated colorimetry for simultaneous determination of organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus dissolved in seawater. Marine Chemistry 66: 161–169.
Risgaard-Petersen, N., T. Dalsgaard, S. Rysgaard, P. B. Christensen, J. Borum, K. J. McGlathery & L. P. Nielsen, 1998. Nitrogen balance of a temperate eelgrass Zostera marina bed. Marine Ecology Progress Series 174: 281–291.
Ruiz, J. M., M. Perez & J. Romero, 2001. Effects of fish farm loadings on seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) distribution, growth and photosynthesis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42: 749–760.
Strickland, J. D. & T. R. Parsons, 1972. A practical handbook of sea-water analysis. Bulletin of Fisheries Research Board of Canada 167: 311.
Sugimura, Y. & Y. Suzuki, 1988. A high-temperature catalytic oxidation method for the determination of non-volatile dissolved organic carbon in seawater by direct injection of a liquid sample. Marine Chemistry 24: 105–131.
Welsh, D. T., M. Bartoli, D. Nizzoli, G. Castaldelli, S. A. Riou & P. Viaroli, 2000. Denitrification, nitrogen fixation, community primary productivity and inorganic-N and oxygen fluxes in an intertidal Zostera noltii meadow. Marine Ecology Progress Series 208: 65–77.
Yarbro, L. A. & P. R. Carlson, 2008. Community oxygen and nutrient fluxes in seagrass beds of Florida Bay, USA. Estuaries and Coasts 31: 877–897.
Ziegler, S. & R. Benner, 1999a. Dissolved organic carbon cycling in a subtropical seagrass-dominated lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 180: 149–160.
Ziegler, S. & R. Benner, 1999b. Nutrient cycling in the water column of a subtropical seagrass meadow. Marine Ecology Progress Series 188: 51–62.
Ziegler, S., E. Kaiser & R. Benner, 2004. Dynamics of dissolved organic carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a seagrass meadow of Laguna Madre, Texas. Bulletin of Marine Science 75: 391–407.
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the IBIS Project, co-financed by E.U.-European Social Fund (75%) and the Greek Ministry of Development-GSRT (25%). Thanks are due to T. Tsagaraki, I. Glabedakis, V. Pefanis-Vassilatos, N. Kouroubalis, V. Stasinos and S. Kiparissis for assistance with sampling, M. Delefose, E. Dafnomili, S. Zivanovic, S. Iliakis, M. Anthoula, Y. Zachioti, A. Androni, E. Krasakopoulou, A. Pavlidou and K. Giamalaki for assistance in chemical analyses, K. Lika for advice in statistical analysis and two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and criticism on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: M. Holmer & N. Marbà / Dynamics and functions of seagrass ecosystems
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Apostolaki, E.T., Holmer, M., Marbà, N. et al. Degrading seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) ecosystems: a source of dissolved matter in the Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia 649, 13–23 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0255-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0255-2