Abstract
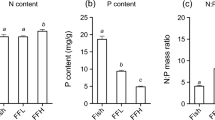
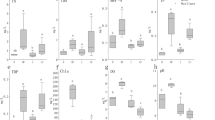
Epiphytes are important components of the biomass and productivity of Posidonia oceanica meadows. Bottom-up mechanisms may promote epiphyte biomass through a bottom-up mechanism. At the same time, epiphytes represent an essential resource for higher trophic levels of seagrass food webs. Posidonia oceanica meadows host a diverse assemblage of fish that feed directly on the leaves, on the epiphytes, and on the mesograzers inhabiting the meadows. In this study, we experimentally evaluate the overall effect of fish community and increased water column nutrient availability on seagrass and the associated epiphytes. Our results show a large increase of epiphyte biomass in P. oceanica shoots after 2 months of nutrient addition. Increased nutrient concentrations also resulted in a reduction of shoot size. Fish exclusion did not affect epiphyte biomass under ambient or increased nutrient availability. Although herbivorous fish bites were present in 6% of the shoots, the percentage of shoots with fish bites did not respond to the higher leaf nutrient content found in the increased nutrient treatments. Consumption marks of gastropod herbivores in the leaves were present in 78% of the shoots; however, grazer activity did not modify the response of epiphytic biomass to nutrient addition. These results highlight the importance of nutrient impact in oligotrophic meadows, where bottom-up processes seem to be more relevant in the control of epiphyte and seagrass growth than top-down processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcoverro, T., C. M. Duarte & J. Romero, 1995. Annual growth dynamics of Posidonia oceanica. Contribution of largescale versus local factors to seasonality. Marine Ecology Progress Series 120: 203–210.
Alcoverro, T., C. M. Duarte & J. Romero, 1997. The influence of herbivores on Posidonia oceanica epiphytes. Aquatic Botany 56: 93–104.
Alcoverro, T., M. Manzanera & J. Romero, 2000. Nutrient mass balance of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: the importance of nutrient retranslocation. Marine Ecology Progress Series 194: 13–21.
Antolié, B., 1985. Distribution of epiphytic flora on Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile (National Park “Kornati”—Central Adriatic). Acta Adriatica 26: 135–143.
Bethoux, J. P. & G. Copin-Montegut, 1986. Biological fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in the Mediterranean Sea. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 1353–1358.
Borowitzka, M. A., P. S. Lavery & M. Van Keulen, 2006. Epiphytes of seagrasses. In Larkum, A. W. D., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Dordrecht: 441–561.
Borum, J., 1987. Dynamics of epiphyton on eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) leaves: relative roles of algal growth, herbivory, and substratum turnover. Limnology and Oceanography 32: 986–992.
Buia, M. C., M. C. Gambi & M. Dappiano, 2003. I sistemi a fanerogame marine. In Gambi, M. C. & M. Dappiano (eds), Manuale di Metodologie di Campionamento e Studio del Benthos Marino Mediterraneo. Società Italiana di Biologia Marina, Livorno: 145–198.
Burkepile, D. E. & M. E. Hay, 2006. Herbivore vs. nutrient control of marine primary producers: context-dependent effects. Ecology 87: 3128–3139.
Burkholder, J. M., K. M. Mason & H. B. Glasgow Jr., 1992. Water-column nitrate enrichment promotes decline of eelgrass Zostera marina : evidence from seasonal mesocosm experiments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 81: 163–178.
Burkholder, J. M., H. B. Glasgow Jr. & J. E. Cooke, 1994. Comparative effects of water-column nitrate enrichment on eelgrass Zostera marina, shoalgrass Halodule wrightii, and widgeongrass Ruppia maritime. Marine Ecology Progress Series 105: 121–138.
Burkholder, J. M., D. A. Tomasko & B. W. Touchette, 2007. Seagrasses and eutrophication. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 46–72.
Castejon-Silvo, I., 2011. Grazing on the epiphytic community of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile: an assessment of its relevance as a buffering process of eutrophication effects. PhD dissertation. Balearic Islands University.
Cornelisen, C. D. & F. I. M. Thomas, 2004. Ammonium and nitrate uptake by leaves of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum: impact of hydrodynamic regime and epiphyte cover on uptake rates. Journal of Marine Systems 49: 177–194.
Deudero, S., G. Morey, A. Frau, J. Moranta & I. Moreno, 2008. Temporal trends of littoral fishes at deep Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows in a temperate coastal zone. Journal of Marine Systems 70: 182–195.
Fourqurean, J. W., J. C. Zieman & G. V. N. Powell, 1992. Relationships between porewater nutrients and seagrasses in a subtropical carbonate environment. Marine Biology 114: 57–65.
Gambi, M. C., M. Lorenti, G. F. Russo, M. B. Scipione & V. Zupo, 1992. Depth and seasonal distribution of some groups of the vagile fauna of the Posidonia oceanica leaf stratum—structural and trophic analyses. Marine Ecology 13: 17–39.
Giovannetti, E., M. Montefalcone, C. Morri, C. N. Bianchi & G. Albertelli, 2010. Early warning response of Posidonia oceanica epiphyte community to environmental alterations (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). Marine Pollution Bulletin 60: 1031–1039.
Guidetti, P., 2000. Differences among nearshore fish assemblages associated with shallow water Posidonia oceanica seagrass beds, rocky-algal reefs and unvegetated sand habitats in the Adriatic Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 50: 515–529.
Hemminga, M. A., N. Marbà & J. Stapel, 1999. Leaf nutrient resorption, leaf lifespan and the retention of nutrients in seagrass systems. Aquatic Botany 65: 141–158.
Hughes, A. R., K. J. Bando, L. F. Rodriguez & S. L. Williams, 2004. Relative effects of grazers and nutrients on seagrasses: a meta-analysis approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 282: 87–99.
Invers, O., G. P. Kraemer, M. Pérez & J. Romero, 2004. Effects of nitrogen addition on nitrogen metabolism and carbon reserves in the temperate seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 303: 97–114.
Jennings, S., O. Renones, B. Morales-Nin, N. V. C. Polunin, J. Moranta & J. Coll, 1997. Spatial variation in the N-15 and C-13 stable isotope composition of plants, invertebrates and fishes on Mediterranean reefs: implications for the study of trophic pathways. Marine Ecology Progress Series 146: 109–116.
Keuskamp, D., 2004. Limited effects of grazer exclusion on the epiphytes of Posidonia sinuosa in South Australia. Aquatic Botany 78: 3–14.
Leoni, V., A. Vela, V. Pasqualini, C. Pergent-Martini & G. Pergent, 2008. Effects of experimental reduction of light and nutrient enrichments (N and P) on seagrasses: a review. Aquatic Conservation: Marine Freshwater Ecosystem 18: 202–220.
Lepoint, G., J. Jacquemart, J. M. Bouquegneau, V. Demoulin & S. Gobert, 2007. Field measurements of inorganic nitrogen uptake by epiflora components of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica (Monocotyledons, Posidoniaceae). Journal of Phycology 43: 208–218.
McClelland, J. W. & I. Valiela, 1998. Linking nitrogen in estuarine producers to land-derived sources. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 577–585.
McGlathery, K., 1995. Nutrient and grazing influences on a subtropical seagrass community. Marine Ecology Progress Series 122: 239–252.
Moksnes, P. O., M. Gullström, K. Tryman & S. Baden, 2008. Trophic cascades in a temperate seagrass community. Oikos 117: 763–777.
Morales-Nin, B., G. Morey, J. Moranta, A. Ruiz, M. Palmer, F. Ordines & P. Tugores, 2004. Monitoring the Effect of Protection Measures on the Fish Community of the Marine Protected Areas in the Balearic Islands. Balearic Islands Government.
Moranta, J., M. Palmer, G. Morey, A. Ruiz & B. Morales-Nin, 2006. Multi-scale spatial variability in fish assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica meadows in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 68: 579–592.
Neckles, H., R. Wetzel & R. J. Orth, 1993. Relative effects of nutrient enrichment and grazing on epiphyte-macrophyte (Zostera marina L.) dynamics. Oecologia 93: 285–295.
Pasqualini, V., C. Pergent-Martini, P. Clabaut & G. Pergent, 1998. Mapping of Posidonia oceanica using aerial photographs and side scan sonar: application off the Island of Corsica (France). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 47: 359–367.
Perez, M., T. Garcia, O. Invers & J. M. Ruiz, 2008. Physiological responses of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica as indicators of fish farm impact. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56: 869–879.
Piazzi, L., D. Balata, F. Cinelli & L. Benedetti-Cecchi, 2004. Patterns of spatial variability in epiphytes of Posidonia oceanica—differences between a disturbed and two reference locations. Aquatic Botany 79: 345–356.
Pinnegar, J. K., N. V. C. Polunin, P. Francour, F. Badalamenti, R. Chemello, M. L. Harmelin-Vivien, B. Hereu, M. Milazzo, M. Zabala, G. D’Anna & C. Pipitone, 2000. Trophic cascades in benthic marine ecosystems: lessons for fisheries and protected-area management. Environmental Conservation 27: 179–200.
Prado, P., T. Alcoverro, B. Martínez-Crego, A. Vergés, J. L. Pérez-Llorens & J. Romero, 2007. Macrograzers strongly influence patterns of epiphytic assemblages in seagrass meadows. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 130–143.
Prado, P., T. Alcoverro & J. Romero, 2008a. Seasonal response of Posidonia oceanica epiphyte assemblages to nutrient increase. Marine Ecology Progress Series 359: 89–98.
Prado, P., S. Farina, F. Tomas, J. Romero & T. Alcoverro, 2008b. Marine protection and meadow size alter fish herbivory in seagrass ecosystems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 371: 11–21.
Prado, P., J. Romero & T. Alcoverro, 2010. Nutrient status, plant availability and seasonal forcing mediate fish herbivory in temperate seagrass beds. Marine Ecology Progress Series 409: 229–239.
Reñones, O., E. Massuti, J. Moranta, J. Coll & I. Moreno, 1995. Fish fauna of Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows is Palma Bay. Cibium 19: 201–206.
Rueda, J. L. & C. Salas, 2007. Trophic dependence of the emerald neritid Smaragdia viridis (Linnaeus, 1758) on two seagrasses from European coasts. Journal of Molluscan Studies 73: 211–214.
Shepherd, S. A., A. J. McComb, D. A. Bulthuis, V. Neverauskas, D. A. Steffensen & R. West, 1989. Decline of seagrasses. In Larkum, A. W. D., A. J. McComb & S. A. Shepherd (eds), Biology of Seagrasses. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 346–359.
Short, F. T., D. M. Burdick & J. E. Kaldy III, 1995. Mesocosm experiments quantify the effects of eutrophication on eelgrass, Zostera marina. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 740–749.
Sieben, K., L. Ljunggren, U. Bergstrom & B. K. Eriksson, 2011a. A meso-predator release of stickleback promotes recruitment of macroalgae in the Baltic Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 397: 79–84.
Sieben, K., A. Rippen & B. Eriksson, 2011b. Cascading effects from predator removal depend on resource availability in a benthic food web. Marine Biology 158: 391–400.
StatSoft, Inc., 2005. STATISTICA (data analysis software system), version 7.1 www.statsoft.com.
Stergiou, K. I. & V. S. Karpouzi, 2001. Feeding habits and trophic levels of Mediterranean fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 11: 217–254.
Tomas, F., X. Turon & J. Romero, 2005a. Seasonal and small-scale spatial variability of herbivory pressure on the temperate seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Marine Ecology Progress Series 301: 95–107.
Tomas, F., X. Turon & J. Romero, 2005b. Effects of herbivores on a Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow: importance of epiphytes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 287: 115–125.
Tomas, F., D. Alvarez-Cascos, X. Turon & J. Romero, 2006. Differential element assimilation by sea urchins Paracentrotus lividus in seagrass beds: implications for trophic interactions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 306: 125–131.
Tomasko, D. & B. E. Lapointe, 1991. Productivity and biomass of Thalassia testudinum as related to water column nutrient availability and epiphyte levels: field observations and experimental studies. Marine Ecology Progress Series 75: 9–17.
Valentine, J. F. & J. E. Duffy, 2006. The central role of grazing in seagrass ecology. In Larkum, A. W. D., R. J. Orth & C. M. Duarte (eds), Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Dordrecht: 463–501.
Vasapollo, C., 2009. Spatio-temporal variability of plant features and motile invertebrates in Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows. PhD dissertation. The Open University Milton Keynes.
Acknowledgments
Research funds were provided by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (project CTM2005-23775-E), by the Government of the Balearic Islands (project UGIZC) and by the European Commission (VII Framework Programme; Project Conflict CGL2008-958). I. Castejón-Silvo was supported by an I3P-FSE studentship awarded by Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas. We thank Francisco Javier Medina Pons and Eduardo Infantes Oanes for their help during fieldwork; Miquel Ribas-Carbó (Department of Biology, University of the Balearic Islands) for facilitating the use of the ball mill; and Gabriel Martorell (Scientific & Techniques Services, University of the Balearic Islands) for his help in the analyses of nitrogen in epiphytes. We also thank Direcció General de Pesca (Govern de les Illes Balears) for granting us permission to perform this study inside the Palma Bay Marine Reserve, and Club Náutico S’Arenal for allowing us to use the club facilities, making our work easier.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Luis Mauricio Bini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castejón-Silvo, I., Terrados, J., Domínguez, M. et al. Epiphyte response to in situ manipulation of nutrient availability and fish presence in a Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile meadow. Hydrobiologia 696, 159–170 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1190-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1190-1