Abstract
For a ground-level continuous release of a trace substance like 222Rn, for which the vertical profile of concentrations is exponential, a quantity, ‘equivalent mixing height’ h, is defined in this paper in the following way. If the substance were to be redistributed uniformly through a layer such that the concentration were to be equal to that at the surface, then the top of the layer would be h.
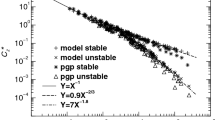
Relative values of h can be obtained from surface measurements of Radon concentrations, but absolute values require estimates of the vertical fluxes of Radon. A comparison is given of the estimates of h obtained from surface measurements with estimates derived from the vertical profile of Radon from the surface to 100 m.
Practical methods are proposed for estimating the surface flux of Rn.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Birot, A., Adroguer, B., and Fontan, J.: 1970, ‘Vertical Distribution of Radon-222 in the Atmosphere and its Use for Study of Exchange in the Lower Troposphere’, J. Geophys. Res. 75, 2373.
Clements, W. E. and Wilkening, M. H.: 1974, ‘Atmospheric Pressure Effects on Radon Transport Across the Earth-Air Interface’, J. Geophys. Res. 20, 5025–5029.
Cros, B.: ‘Contribution à 1'étude des noyaux d'Aitken en Afrique Equatoriale’. Thèse de doctorat d'état. Université Paul Sabatier Toulouse 1977. no. 789.
Druilhet, A.: 1973, ‘Etude des transferts turbulents de matière dans l'atmosphère au voisinage du sol’. Thèse doctorat ès sciences. Université Paul Sabatier Toulouse no. 527.
Druilhet, A. and Fontan, J.: 1972, ‘Détermination des coefficients de diffusion verticale entre 0 et 100 mètres à l'aide du radon et du ThB’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 476.
Druilhet, A. and Fontan, J.: 1974, ‘Utilisation du Radon comme indicateur de l'intensité des échanges près du sol’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 6, pp. 387–412.
Fontan, J., Druilhet, A., Lopez, A., Bernis, M. J., and Cautenet, G.: 1976, ‘Surveillance de la stabilité verticale dans un site urbain’. Pollution atmosphérique', no. 1 pp. 231, 240.
Garland, J. A. and Branson, J. R.: 1976, ‘The Mixing Height and Mass Balance of SO2 in the Atmosphere above Great Britain’, Atm. Env. 10, pp. 353–362.
Gonzales, F. C.: 1977, ‘Contribucion àl estudio de la eslabilidad vertical de la atmosfera de un nucleo urbano’. Thèse doctorat es
Guedalia, D., Allet, C., and Fontan, J.: 1974, ‘Vertical Exchanges Measurements in the Lower Troposphere Using ThB and Radon’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 13, p. 27.
Guedalia, D., Druilhet, A., Fontan, J., et A. N'Tsila: 1978, ‘The Variation of Vertical Atmospheric Stability by Means of Radon Measurements and of Sodar Monitoring’, In III Natural Radiation Environment, Houston, April. (in Press).
Hosler: 1969, ‘Vertical Diffusivity from Radon Profiles’, J. Geophys. Res. 74, p. 7018.
Hosler: 1978, ‘Urban-Rural Climatology of Atmospheric Radon Concentration’, J. Geophys. Res. 73, pp. 1155–1156.
Kraner, H. W., Schroeder, G. L., Evans, R. D.: 1964, ‘Measurements of the Effects of Atmospheric Variables on Radon 222 Flux and Soil-Gas Concentrations’, The Natural Radiation Environment, University of Chicago Pres. pp. 191, 215.
Meetham, A. R.: 1950, ‘Natural Removal of Pollution from the Atmosphere’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 76, 359–371.
N'Tsila, A.: 1977, ‘Surveillance de la stabilité verticale de l'atmosphère à l'aide, du radon et du sodar. Comparaison des deux méthodes’. Thèse de 3ℴ cycle, Université Paul Sabatier no. 2063.
Pasquill: 1961, ‘The estimation of the Dispersion of Wind-Borne Material’, Meteorol. Mag. 90, 33–49.
Pearson, J. E. and Jones, G. E.: 1966, ‘Soil Concentration of Emanating Radium 226 and the Emanation of Radon 222 from Soils and Plants’, Tellus 18, 655.
Servant, J.: 1967, ‘La détermination du coefficient de diffusion turbulente verticale dans la basse atmosphère à l'aide du Radon’, La Météorologie I, p. 3.
Sutton, O. G.: 1953, Micrométéorology, McGraw-Hill p. 131.
Tanner, A. B.: 1964, Radon Migration in the Ground: a Review; the Natural Radiation Environment, University of Chicago Press, pp. 161, 190.
Turner, B.: 1969, Workbook on atmospheric dispersion estimates, Env. Prot. Agency, Research Triangle. NC 84pp.
Wilkening, M. H., Clements, W. E. and Stanley, D.: 1974, ‘Radon 222 Flux in Widely Parted Regions’, Natural Radiation Environemnt II. Technical Information Division US Atomic Energy Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontan, J., Guedalia, D., Druilhet, A. et al. Une methode de mesure de la stabilite verticale de l'atmosphere pres du sol. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 17, 3–14 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121933
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121933