Abstract
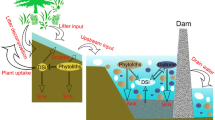
We tested the hypothesis that reservoirs with low water residence time and autochthonous production influence river biogeochemistry in eutrophied river systems draining cultivated watersheds. The effect of a single artificial water reservoir and consecutive reservoirs on silica (Si) river fluxes is exemplified by the moderately dammed Vistula River and the heavily regulated Daugava River that are compared with the practically undammed Oder River. The sum of the discharge weighted annual mean biogenic silica (BSi) and dissolved silicate (DSi) concentrations in the rivers Oder, Vistula and Daugava were about 160 μ M (40 + 120 μ M), 150 μ M (20 + 130 μ M) and 88 μ M (6 + 82 μ M), respectively. Assuming BSi and DSi concentrations as observed in the Oder River as typical for eutrophied but undammed rivers, complete trapping of this BSi could have lowered Si fluxes to the Baltic Sea from rivers with cultivated watersheds by 25%. The superimposed effect of hydrological alterations on reduced Si land–sea fluxes is demonstrated by studies in the boreal/subarctic and oligotrophic rivers Kalixälven and Lueälven. The DSi yield of the heavily dammed Luleälven (793 kg km−2 yr−1) constituted only 63% of that was found in the unregulated Kalixälven (1261 kg km−2 yr−1), despite the specific runoff of the Luleälven (672 mm m−2 yr−1) being 19% higher than that of theKalixälven (563 mm m−2 yr−1); runoff normalized DSi yield of the former, regulated watershed, was only half the DSi yield of the latter, unperturbed watershed. Based on these findings, it is hypothesized here that perturbed surface water–groundwater interactions are the major reasons for the reduced annual fluctuations in DSi concentrations as also seen in the heavily dammed and eutrophic river systems such as the Daugava and Danube.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Admiraal P. Breugem D. Jacobs E.D.D. Vansteveninck (1990) ArticleTitleFixation of dissolved silicate and sedimentation of biogenic silicate in the lower River Rhine during diatom blooms Biogeochemistry 9 175–185 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00692170
V. Almazov (1961) ArticleTitleStock rastverennykh veschestv kotorye vynoseatsya rekami USSR v. Chernoe More Naukovi Zapiski Odes. Biol. St., Kiev 3 99–107
Anon. 2001. Studium kompleksowego rozwiazania problemów stopnia i zbiornika Włocławek – Prognoza skutków społeczno-ekonomicznych – Synteza. Światowy Fundusz na Rzecz Przyrody (WWF), pp. 13–14.
K.D. Bidle M. Manganelli F. Azam (2002) ArticleTitleRegulation of oceanic silicon and carbon preservation by temperature control on bacteria Science 298 1980–1984 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1076076
D.E. Canfield (1993) Organic matter oxidation in marine sediments R. Wollast F.T. Mackenzie L. Chou (Eds) Interactions of C, NP and S Biogeochemical Cycles and Global Change Springer Berlin, Heidelberg 333–363
D.J. Conley (1997) ArticleTitleRiverine contribution of biogenic silica to the oceanic silica budget Limnolo. Oceanogr. 42 774–777
Conley D.J. 2002. Terrestrial ecosystems and the global biogeochemical silica cycle. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16: Art. No. 1121.
D.J. Conley C.L. Schelske E.F. Stoermer (1993) ArticleTitleModification of the Biogeochemical Cycle of Silica with Eutrophication Mar. Ecol.-Progr. Ser. 101 179–192
W.E. Dean E. Gorham (1998) ArticleTitleMagnitude and significance of carbon burial in lakes, reservoirs, and peatlands Geology 26 535–538 Occurrence Handle10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0535:MASOCB>2.3.CO;2
DeMaster D.J. 1979. The marine budgets of silica and Si-32. Ph.D. thesis, Yale University.
Drever J.I. 1997. The Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Prentice Hall.
M. Dynesius C. Nilsson (1994) ArticleTitleFragmentation and flow regulation of river systems in the northern 3rd of the world Science 266 753–762
J.K. Egge D.L. Aksnes (1992) ArticleTitleSilicate as a regulating nutrient in phytoplankton competition Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 83 281–289
Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) 2001. FAOSTAT: FAO Statistical Databases Accessible through the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://apps.fao.org/.
G. Friedl C. Teodoru B. Wehrli (2004) ArticleTitleIs the Iron Gate I reservoir on the Danube River a sink for dissolved silica? Biogeochemistry 68 21–32 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:BIOG.0000025738.67183.c0
J. Gaillardet B. Dupre P. Louvat C.J. Allegre (1999) ArticleTitleGlobal silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers Chem. Geol. 159 3–30 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5
J. Garnier B. Leporcq N. Sanchez X. Philippon (1999) ArticleTitleBiogeochemical mass-balances (C, NP, Si) in three large reservoirs of the Seine Basin (France) Biogeochemistry 47 119–146
L. Granat (1990) Luft och nederbördskemiska stationsnätet inom PMK Swedish Environmental Protection Agency Stockholm (in Swedish)
M.N. Gooseff D.M. McKnight W.B. Lyons A.E. Blum (2002) ArticleTitleWeathering reactions and hyporheic exchange controls on stream water chemistry in a glacial meltwater stream in the McMurdo Dry Valleys Water Res. Res. 38 1279 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2001WR000834
C. Humborg S. Smedberg S. Blomqvist C.M. Mörth J. Brink L. Rahm Å. Danielson J. Sohlberg (2004) ArticleTitleNutrient variations in subarctic Swedish rivers: Landscape control of land-sea fluxes Limnol. Oceanogr. 49 1871–1883
C. Humborg S. Blomqvist E. Avsan Y. Bergensund E. Smedberg J. Brink C.M. Mörth (2002) ArticleTitleHydrological alterations with river damming in northern Sweden: Implications for weathering and river biogeochemistry Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16 1039 Occurrence Handle10.1029/2000GB001369
C. Humborg D.J. Conley L. Rahm F. Wulff A. Cociasu V. Ittekkot (2000) ArticleTitleSilicon retention in river basins: Far-reaching effects on biogeochemistry and aquatic food webs in coastal marine environments Ambio 29 45–50
C. Humborg V. Ittekkot A. Cociasu B. von Bodungen (1997) ArticleTitleEffect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure Nature 386 385–388 Occurrence Handle10.1038/386385a0
V. Ittekkot (2003) ArticleTitleA new story from the ol’ man river Science 301 56–58 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1086419
R. Jansson C. Nilsson M. Dynesius E. Andersson (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of river regulation on river-margin vegetation: A comparison of eight boreal rivers Ecol. Applicat. 10 203–224
J. Karlsson A. Jonsson M. Jansson (2001) ArticleTitleBacterioplankton production in lakes along an altitude gradient in the subarctic north of Sweden Microbial Ecol. 42 372–382 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00248-001-0009-9
F. Koroleff (1983) Determination of silicon K. Grasshoff M. Ehrhardt K. Kremling (Eds) Methods of Seawater Analyses Verlag Chemie Weinheim 174–183
Lasaga A. 1998. Kinetic Theory in the Earth Science. Princeton University Press.
M. Li H.Q. Cheng (2001) ArticleTitleChanges of dissolved silicate flux from the Changjiang River into sea and its influence over the last 50 years Chin. Environ. Sci. 21 IssueID3 193–197
P.A. Maurice D.M. McKnight L. Leff J.E. Fulghum M.N. Gooseff (2002) ArticleTitleDirect observations of aluminosilicate weathering in the hyporheic zone of an Antarctic Dry Valley stream Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 66 1335–1347 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00890-0
M. Meybeck (1981) Pathways of nutrients and organic matter from land to ocean through rivers J.-M. Martin J.D. Burton D. Eisma (Eds) River Inputs to Ocean Systems UNEP, IOC, SCOR United Nations, New York 18–30
Milliman J.D., Rutkowski C. and Meybeck M. 1995. River Discharge to the Sea – A Global River Index (GLORI). LOICZ Reports and Studies.
N. Panin D. Jipa (2002) ArticleTitleDanube River sediment input and its interaction with the northwestern Black Sea Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 54 551–562 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.2000.0664
Raducu M.C. 2002. Transfer des nutriments dans le basin du Danube et apports a la Mer Noire: Modelisation et bilans. Ph.D. thesis, University of Paris 6.
O. Ragueneau C. Lancelot V. Egorov J. Vervlimmeren A. Cociasu G. Deliat A. Krastev N. Daoud V. Rousseau V. Popovitchev N. Brion L. Popa G. Cauwet (2002) ArticleTitleBiogeochemical transformations of inorganic nutrients in the mixing zone between the Danube River and the north-western Black Sea Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 54 321–336 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.2000.0650
Rahm P. Sandén F. Wulff P. Stålnacke D.J. Conley (1995) ArticleTitleA time series analysis of nutrient inputs to the Baltic Sea and changing DSi/N ratios Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 130 221–228
P.A. Raymond J.J. Cole (2003) ArticleTitleIncrease in the export of alkalinity from North America’s largest river Science 301 88–91 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1083788
S. Reschke V. Ittekkot N. Panin (2002) ArticleTitleThe nature of organic matter in the Danube River particles and north-western Black Sea seiments Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 54 563–574 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.2000.0665
Reschke S. 1999. Biogeochemische Variabilitäten in der Schwebstofffracht der Donau und deren Einfluss auf das Sedimentationsgeschehen im nordwestlichen Schwarzen Meer. Ph.D. thesis, Hamburg University.
R.E. Turner N.N. Rabalais (2003) ArticleTitleLinking landscape and water quality in the Mississippi river basin for 200 years BioScience 53 563–572
A.J. Bennekom Particlevan W. Salomons (1981) Pathways of nutrients and organic matter from land to ocean through rivers J.-M. Martin J.D. Burton D. Eisma (Eds) River Inputs to Ocean Systems UNEP, IOC, SCOR United Nations, New York 33–51
C.J. Vörösmarty D. Sahagian (2000) ArticleTitleAnthropogenic disturbance of the terrestrial water cycle BioScience 50 753–765
D.S. White (1993) ArticleTitlePerspectives on defining and delineating hyporheic zones J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 12 61–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Humborg, C., Pastuszak, M., Aigars, J. et al. Decreased Silica Land–sea Fluxes through Damming in the Baltic Sea Catchment – Significance of Particle Trapping and Hydrological Alterations. Biogeochemistry 77, 265–281 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-1533-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-1533-3