Abstract
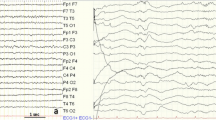
A new method for analyzing the time-frequency dynamics of brain’s background electrical activity is described. It is used to detect at least three main features of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in its early stages: (1) hemispheric asymmetry in the time-frequency characteristics (EEG) in the central recording areas of the motor cortex, (2) the emergence in these recording areas of EEG rhythms in the frequency range of 4–6 Hz and its relation to electromyograms (EMG) and the mechanical tremor of contralateral limbs in the case of tremor-dominant PD, and (3) the disruption of the dominant rhythm corresponding to views generally held on the disorganization of different systems in PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. England, R. S. Schwab, and E. Peterson, “The electroencephalogram in Parkinson’s syndrome,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 11, 723–721 (1959).
J. A. Ganglberger, “The EEG in parkinsonism and its alteration by stereotaxically produced lesions in pallidum,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 13, 82 (1961).
R. Soikkeli, J. Partenen, H. Soininen, et al., “Slowing of EEG in Parkinson’s disease,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 79, 159–165 (1991).
N. Fogelson, D. Williams, M. Tijssen, et al., “Different functional loops between cerebral cortex and subthalamic area in Parkinson disease,” Cerebral Cortex 16, 64–75 (2006).
D. Stoffers, J. L. W. Bosboom, J. B. Dejen, et al., “Slowing of oscillatory brain activity is a stable characteristic of Parkinson’s disease without dementia,” Brain 130, 1847–1860 (2007).
M. Moazami-Gourdarzi, J. Sarnthein, L. Michels, et al., “Enhanced frontal low and high frequency power and synchronization in the resting EEG of parkinsonian patients,” Neuroimage 41, 985–997 (2008).
L. Pezard, R. Jech, and E. Ruzicka, “Investigation of non-linear properties of multichannel EEG in the early stages of Parkinson’s disease,” Clin. Neuriphysiol. 112, 38–45 (2001).
C. E. d’Atellis, S. I. Isaacson, and R. O. Sime, “Detection of epileptic events in electroencephalograms using wavelet analysis,” Ann. Biomed. Eng. 25, 286–293 (1997).
A. V. Gabova, D. Yu. Bosnyakova, M. S. Bosnyakov, et al., “Time-frequency structure of peak-wave discharges of genetic absence-epilepsy,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk 396, 557–560 (2004).
D. Yu. Bosnyakova and Yu. V. Obukhov, “Extraction of dominant feature in biomedical signals,” Pattern Recogn. Image Anal. 15, 513–515 (2005).
Yu. V. Obukhov, A. V. Antsiperov, A. B. Gekht, G.R. Popov, A. V. Gabova, A. V. Zharikova, and G. D. Kuznetsova, “Time-frequency analysis of brain electrical activity for Parkinson disease,” in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Theory and Practice, Ed. by M. V. Ugryumov (Nauka, Moscow, 2010), pp. 112–129 [in Russian].
A. M. Vein, V. L. Golubev, and N. N. Yakhno, “Parkinson’s disease in terms of functional-neurological analysis,” in Parkinson’s Disease: Problems on Clinical Picture, Pathogenesis, and Treatment (Moscow, 1974), pp. 57–65 [in Russian].
V. L. Golubev, Ya. I. Levin, and A. M. Vein, Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonian Syndrome (MEDpress, Moscow, 1999) [in Russian].
L. Senhadji and F. Wendling, “Epileptic transient detection wavelet and time-frequency approaches,” Neurophysiol. Clin. 32, 175–192 (2002).
S. J. Siff, A. Aldroubi, M. Unser, et al., “Fast wavelet transformation of the EEG,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 91, 442–445 (1994).
A. J. Gabor, R. R. Leach, and F. U. Dowla, “Automated seizure detection using a self-organizing neuronal network,” EEG Clin. Neurophysiol. 66, 257–266 (1996).
S. Blanko, R. Quian-Quiroga, O. A. Rosso, and E. Serrano, “Time-frequency analysis of electroencephalogram series. III. Wavelet packets and information cost function,” Phys. Rev. E 57, 932–940 (1998).
M. Sun, M. I. Scheuer, and R. J. Sclabbassi, “Extraction and analysis of early ictal activity in subdural electroen cephalogram,” Ann. Biomed. Eng. 29, 878–896 (2001).
J. J. Battiston, T. M. Darcey, A. M. Sigel, et al., “Statistical mapping of scalp-recorded ictal EEG records using wavelet analysis,” Epilepsia 44, 664–672 (2003).
H. Adeli, Z. Zhou, and N. Dadmehr, “Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform,” J. Neurosci. Meth. 123, 69–87 (2003).
D. Bosnyakova, A. Gabova, A. Zharikova, et al., “Some peculiarities of time-frequency dynamics of spike-wave discharges in human and rats,” Clin. Neuriphysiol. 118, 1736–1743 (2007).
A. Oswal, V. Litvak, and P. Brown, “Syncronized neural oscillations and the parkinsonian state,” in Parkinson Disease and other Movement Disorders, Ed. by E. Wolters and C. Baumann (Int. Ass. of Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, VU University Press, 2014), pp. 163–181.
Yu. V. Obukhov, M. S. Korolev, A. V. Gabova, G. D. Kuznetsova, and M. V. Ugryumov, RF Patent 2484766 (20.06.2013).
M. S. Korolev and Yu. V. Obukhov, “The way to find signs of early Parkinson’s disease at EEG,” Nelin. Mir, No. 2, 131–132 (2012).
Yu. V. Obukhov, M. S. Korolev, and K. Yu. Obukhov, “The way to estimate numerically EEG rhythms nonstationarirty for normal and for early Parkinson’s disease,” in Proc. 16th All-Russian Conf. Mathematical Method for Pattern Recognition MMPR-10, Kazan, Oct. 6–12, 2013 (Tezaurus Press, Moscow, 2013), p. 79.
Yu. V. Obukhov, M. S. Korolev, K. Yu. Obukhov, O. S. Sushkova, R. R. Nigmatullina, Z. A. Zaljalova, A. V. Gabova, G. D. Kuznetsova, and M. V. Ugrumov, “Time-frequency spontaneous EEG features of early stage Parkinson’s disease,” in Proc. 11th Int. Conf. on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis: New Information Technologies (PRIA-11-2013) (IPSI RAS, Samara, Sept. 23–28, 2013), Vol. 1, pp. 50–53.
Yu. V. Obukhov, M. S. Korolev, K. Yu. Obukhov, O. S. Sushkova, R. R. Nigmatullina, Z. A. Zaljalova, A.V. Karabanov, A. V. Gabova, G. D. Kuznetsova, and M. V. Ugrumov, “Some EEG features in early-stage Parkinson disease patients,” in Proc. 20th World Congress on Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders (Geneva, Dec. 8–11, 2013), p. 37. http://www2.kenes.com/parkinson/abs/Pages/AbstractSubmission.aspx
K. Brockmann and D. Berg, “Diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” in Parkinson Disease and other Movement Disorders, Ed. by E. Wolters and C. Baumann (Int. Ass. of Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, VU University Press, 2014), pp. 229–242.
E. A. Andreeva and O. E. Khutorskaya, Spectral Way for Analyzing Muscles Electromyographical Activity (Nauka, Moscow, 1987) [in Russian].
D. E. Vakman and L. A. Vainshtein, “Amplitude, phase, frequency, are the main concepts of oscillation theory,” Usp. Fiz. Nauk 123(4), 657–682 (2000).
L. Timmermann, J. Gross, M. Dirks, J. Volkmann, H. J. Freund, and A. Schnitzel, “The cerebral oscillatory network of parkinsonian resting tremor,” Brain 126, 199–212 (2003).
R. Levy, J. O. Dostrovsky, A. E. Lang, E. Sime, W. D. Hutchison, and A. M. Lozano, “Effects of apomorphine in sibthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus neurons in patients with Parkinsons disease,” J. Neurophysiol. 86, 249–260 (2001).
H. Bergman, T. Wihmann, B. Karmon, and R. De Long, “The primate subthalamic nucleus. II. Neuronal activity in parkinsonism,” J. Neurophysiol. 72, 507–520 (1999).
W. R. Gibb and A. J. Lees, “The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease,” J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 51, 745–752 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper uses the materials of the report submitted at the 11th International Conference “Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis: New Information Technologies,” Samara, The Russian Federation, September 23–28, 2013.
Yurii Vladimirovich Obukhov. Born in 1950. Graduated from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology in 1974. Received degree of doctor of physical and mathematical sciences in 1992. Currently holds the position of the head of the laboratory of the Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Academy of Sciences. Scientific interests: visualization, processing and analysis of images, biomedical informatics, and information systems. Author of more than 100 papers. Member of the editorial board of the journals Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis and Biomedical Radioelectronics.
Aleksandra Vasil’evna Gabova. Born in 1953. Graduated from Moscow Regional Pedagogical Institute in 1979. Received degree of candidate of biological sciences in 1990. Currently holds the position of senior researcher in the General Physiology of Temporary Connections Lab at the Institute of Higher Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology. Scientific interests: electroencephalography, processing, and analysis of EEG in neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy). Author of about 30 papers.
Razina Ramazanovna Nigmatullina. Born in 1959. Graduated from the Faculty of Natural Sciences and Geography of Kazan State Pedagogical University in 1983. Received degree of doctor of biological sciences in 1999. Professor of the Kazan State Medical University since 2006. Currently holds the position of Professor in the Department of Normal Physiology at the Kazan State Medical University. Scientific interests: neurohumoral regulation of heart functions, chronic heart failure, and peripheral markers of Parkinson’s disease. Author of more than 50 scientific papers.
Mikhail Sergeevich Korolev. Born in 1988. Graduated from the Faculty of Physical and Quantum Electronics of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology in 2011. From 2011 until the present time he has been a full-time graduate student at the Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics. Author of 11 papers. Scientific interests: information technology and processing of biomedical signals of electroencephalography and electromyography.
Aleksei Aleksandrovich Morozov. Born in 1968. Graduated from the Moscow State Technical University in 1991. Received degree of candidate of physical and mathematical sciences in 1998. Currently works as a senior researcher at the Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Author of 90 papers. Scientific interests: logic programming, intelligent video surveillance, and processing of biomedical signals (EEG, EMG, MEG).
Konstantin Yur’evich Obukhov. Born in 1993. A fifth year student at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Author of 7 papers. Scientific interests: information technology and processing of biomedical signals of electroencephalography and electromyography.
Olga Sergeevna Sushkova. Born in 1990. Graduated from the Faculty of Information Technology in Education of the Moscow Humanitarian Pedagogical Institute in 2012. From 2012 until the present time she has been a full-time graduate student at the Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics. Author of 7 papers. Scientific interests: information technology and processing of biomedical signals of electroencephalography and electromyography.
Zuleikha Abdullazyanovna Zaljalova. Born in 1966. Graduated with honors from Kazan Medical Institute with a specialization in pediatrics in 1989. Received doctoral degree in 2005. Professor in the Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation of the Kazan State Medical University under the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, head of the Republican Clinical Diagnostic Centre for Extrapyramidal Pathology and Botulinum Therapy and Kazan Consultative and Diagnostic Centre for Extrapyramidal Pathology, member of the Presidium of the National Society for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders, and member of the Presidium of the Russian Interregional Public Organization of Experts of Botulinotherapy. Scientific interests: new anticonvulsants in the treatment of essential tremor and dynamics of pain syndrome in the treatment of spasmodic torticollis by injections of botulinum toxin. Author of more than 140 scientific papers.
Aleksei Vyacheslavovich Karabanov. Born in 1960. Graduated from First Moscow State Medical University in 1986. In 1992, completed clinical residency at the Moscow Medical Academy with a specialization in neurological diseases. Received the degree of Candidate of Medical Science in 2000. Currently holds the position of Senior Researcher at the Neurology Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. Scientific interests: genetic disorders of the nervous system and extrapyramidal diseases. Author of more than 80 papers.
Sergei Nikolaevich Illarioshkin. Born in 1963. Graduated from the Second Faculty of General Medicine the First Moscow State Medical University in 1986. Completed clinical residency (1986–1988) and postgraduate studies (1988–1991) at the Research Institute of Neurology of the Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR (Moscow). Received degree of Doctor of Medicine in 1997. Since 2003 till present holds the position of the Deputy Director for Science at the Neurology Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. Concurrently, from 2006 to present Head of the Brain Research Department at the Neurology Research Center. Scientific interests: Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Author of more than 350 scientific papers.
Galina Dmitrievna Kuznetsova. Born in 1928. Graduated from Moscow State Lomonosov University. Doctor of Sciences. Professor of the Institute of Higher Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology RAS. Scientific interests: neurophysiology, brain pathophysiology, electroencephalography. Author of 200 scientific papers and 3 monographs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obukhov, Y.V., Gabova, A.V., Zaljalova, Z.A. et al. Electroencephalograms features of the early stage Parkinson’s disease. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 24, 593–604 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054661814040166
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1054661814040166