Abstract
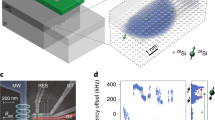
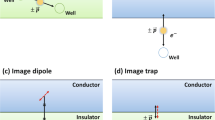
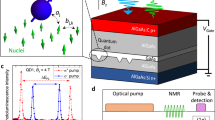
The interaction of an electronic spin with its nuclear environment, an issue known as the central spin problem, has been the subject of considerable attention due to its relevance for spin-based quantum computation using semiconductor quantum dots. Independent control of the nuclear spin bath using nuclear magnetic resonance techniques and dynamic nuclear polarization using the central spin itself offer unique possibilities for manipulating the nuclear bath with significant consequences for the coherence and controlled manipulation of the central spin. Here we review some of the recent optical and transport experiments that have explored this central spin problem using semiconductor quantum dots. We focus on the interaction between 104–106 nuclear spins and a spin of a single electron or valence-band hole. We also review the experimental techniques as well as the key theoretical ideas and the implications for quantum information science.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petta, J. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006).
Brunner, D. et al. A coherent single-hole spin in a semiconductor. Science 325, 70–72 (2009).
Mikkelsen, M. H., Berezovsky, J., Stoltz, N. G., Coldren, L. A. & Awschalom, D. D. Optically detected coherent spin dynamics of a single electron in a quantum dot. Nature Phys. 3, 770–773 (2007).
Press, D. et al. Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot. Nature Photon. 4, 367–370 (2010).
De Greve, K. et al. Ultrafast coherent control and suppressed nuclear feedback of a single quantum dot hole qubit. Nature Phys. 7, 872–878 (2011).
Greilich, A., Carter, S. G., Kim, D., Bracker, A. S. & Gammon, D. Optical control of one and two hole spins in interacting quantum dots. Nature Photon. 5, 703–709 (2011).
Godden, T. M. et al. Coherent optical control of the spin of a single hole in an InAs/GaAs quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 017402 (2012).
Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120–126 (1998).
Khaetskii, A. V., Loss, D. & Glazman, L. Electron spin decoherence in quantum dots due to interaction with nuclei. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 186802 (2002).
Merkulov, I. A., Efros, A. L. & Rosen, M. Electron spin relaxation by nuclei in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 65, 205309 (2002).
Gammon, D. et al. Nuclear spectroscopy in single quantum dots: Nanoscopic Raman scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance. Science 277, 85–88 (1997).
Abragam, A. The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism (Oxford Univ. Press, 1961).
Meier, F. & Zakharchenya, B. P. (eds) Optical Orientation (Elsevier, 1984).
Taylor, J. M., Marcus, C. M. & Lukin, M. D. Long-lived memory for mesoscopic quantum bits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 206803 (2003).
Makhonin, M. N. et al. Optically tunable nuclear magnetic resonance in a single quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 82, 161309 (2010).
Makhonin, M. N. et al. Fast control of nuclear spin polarization in an optically pumped single quantum dot. Nature Mater. 10, 844–848 (2011).
Takahashi, R., Kono, K., Tarucha, S. & Ono, K. Voltage-selective bidirectional polarization and coherent rotation of nuclear spins in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 026602 (2011).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Structural analysis of strained quantum dots using nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature Nanotech. 7, 646–650 (2012).
Tartakovskii, A. (ed.) Quantum Dots: Optics, Electron Transport and Future Applications (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2012).
Lai, C. W., Maletinsky, P., Badolato, A. & Imamoglu, A. Knight-field-enabled nuclear spin polarization in single quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 167403 (2006).
Eble, B. et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization of a single charge-tunable InAs/GaAs quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 74, 081306 (2006).
Tartakovskii, A. I. et al. Nuclear spin switch in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 026806 (2007).
Braun, P-F. et al. Bistability of the nuclear polarization created through optical pumping in InGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 74, 245306 (2006).
Urbaszek, B. et al. Efficient dynamical nuclear polarization in quantum dots: Temperature dependence. Phys. Rev. B 76, 201301 (2007).
Koppens, F. H. L., Nowack, K. C. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spin echo of a single spin in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 236802 (2008).
Xu, X. et al. Optically controlled locking of the nuclear field via coherent dark-state spectroscopy. Nature 459, 1105–1109 (2009).
Bluhm, H. et al. Dephasing time of GaAs electron-spin qubits coupled to a nuclear bath exceeding 200 μs. Nature Phys. 7, 109–113 (2010).
De Sousa, R. & Das Sarma, S. Theory of nuclear-induced spectral diffusion: Spin decoherence in phosphorus donors in Si and GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 68, 115322 (2003).
Yao, W., Lui, R-B. & Sham, L. J. Restoring coherence lost to a slow interacting mesoscopic spin bath. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 077602 (2007).
Shchukin, V. A. & Bimberg, D. Spontaneous ordering of nanostructures on crystal surfaces. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 1125–1171 (1999).
Warburton, R. J. et al. Optical emission from a charge-tunable quantum ring. Nature 405, 926–929 (2000).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Pumping of nuclear spins by optical excitation of spin-forbidden transitions in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 066804 (2010).
Bracker, A. S. et al. Optical pumping of the electronic and nuclear spin of single charge-tunable quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 047402 (2005).
Maletinsky, P., Lai, C. W., Badolato, A. & Imamoglu, A. Nonlinear dynamics of quantum dot nuclear spins. Phys. Rev. B 75, 035409 (2007).
Maletinsky, P., Badolato, A. & Imamoglu, A. Dynamics of quantum dot nuclear spin polarization controlled by a single electron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 056804 (2007).
Chekhovich, E. A., Krysa, A. B., Skolnick, M. S. & Tartakovskii, A. I. Direct measurement of the hole–nuclear spin interaction in single InP/GaInP quantum dots using photoluminescence spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 027402 (2011).
Latta, C. et al. Confluence of resonant laser excitation and bidirectional quantum-dot nuclear-spin polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 758–763 (2009).
Fallahi, P., Yilmaz, S. T. & Imamoglu, A. Measurement of a heavy-hole hyperfine interaction in InGaAs quantum dots using resonance fluorescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 257402 (2010).
Oulton, R. et al. Subsecond spin relaxation times in quantum dots at zero applied magnetic field due to a strong electron-nuclear interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 107401 (2007).
Greilich, A. et al. Nuclei-induced frequency focusing of electron spin coherence. Science 317, 1896–1899 (2007).
Hanson, R., Kouwenhoven, L. P., Petta, J. R., Tarucha, S. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 1217–1265 (2007).
Hanson, R. & Awschalom, D. D. Coherent manipulation of single spins in semiconductors. Nature 453, 1043–1049 (2008).
Bluhm, H., Foletti, S., Mahalu, D., Umansky, V. & Yacoby, A. Enhancing the coherence of a spin qubit by operating it as a feedback loop that controls its nuclear spin bath. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 216803 (2010).
Vink, I. et al. Locking electron spins into magnetic resonance by electron–nuclear feedback. Nature Phys. 5, 764–768 (2009).
Nowack, K. C., Koppens, F. H. L., Nazarov, Y. V. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Coherent control of a single electron spin with electric fields. Science 318, 1430–1433 (2007).
Laird, E. A. et al. Hyperfine-mediated gate-driven electron spin resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 246601 (2007).
Ono, K., Austing, D. G., Tokura, Y. & Tarucha, S. Current rectification by Pauli exclusion in a weakly coupled double quantum dot system. Science 297, 1313–1317 (2002).
Petta, J. R. et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization with single electron spins. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 067601 (2008).
Reilly, D., Marcus, C., Hanson, M. & Gossard, A. Fast single-charge sensing with a rf quantum point contact. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 162101 (2007).
Barthel, C., Reilly, D., Marcus, C., Hanson, M. & Gossard, A. Rapid single-shot measurement of a singlet–triplet qubit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 160503 (2009).
Baugh, J., Kitamura, Y., Ono, K. & Tarucha, S. Large nuclear Overhauser fields detected in vertically coupled double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 096804 (2007).
Foletti, S., Bluhm, H., Mahalu, D., Umansky, V. & Yacoby, A. Universal quantum control of two-electron spin quantum bits using dynamic nuclear polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 903–908 (2009).
Brown, S. W., Kennedy, T. A., Gammon, D. & Snow, E. S. Spectrally resolved Overhauser shifts in single GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 54, R17339–R17342 (1996).
Kloeffel, C. et al. Controlling the interaction of electron and nuclear spins in a tunnel-coupled quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 046802 (2011).
Dyakonov, M. I. (ed.) Spin Physics in Semiconductors (Springer, 2008).
Makhonin, M. N. et al. Nuclear spin pumping under resonant optical excitation in a quantum dot. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 073113 (2008).
Klotz, F. et al. Asymmetric optical nuclear spin pumping in a single uncharged quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 82, 121307 (2010).
Korenev, V. L. Nuclear spin nanomagnet in an optically excited quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 256405 (2007).
Latta, C., Srivastava, A. & Imamoğlu, A. Hyperfine interaction-dominated dynamics of nuclear spins in self-assembled InGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 167401 (2011).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Dynamics of optically induced nuclear spin polarization in individual InP/GaInP quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 81, 245308 (2010).
Makhonin, M. N. et al. Long nuclear spin polarization decay times controlled by optical pumping in individual quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 77, 125307 (2008).
Nikolaenko, A. E. et al. Suppression of nuclear spin diffusion at a GaAs/AlGaAs interface measured with a single quantum-dot nanoprobe. Phys. Rev. B 79, 081303 (2009).
Dzhioev, R. I. & Korenev, V. L. Stabilization of the electron–nuclear spin orientation in quantum dots by the nuclear quadrupole interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 037401 (2007).
Maletinsky, P., Kroner, M. & Imamoglu, A. Breakdown of the nuclear-spin-temperature approach in quantum-dot demagnetization experiments. Nature Phys. 5, 407–411 (2009).
Bulutay, C. Quadrupolar spectra of nuclear spins in strained InxGa1− xAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 85, 115313 (2012).
Belhadj, T. et al. Controlling the polarization eigenstate of a quantum dot exciton with light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 086601 (2009).
Ono, K. & Tarucha, S. Nuclear-spin-induced oscillatory current in spin-blockaded quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 256803 (2004).
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Control and detection of singlet–triplet mixing in a random nuclear field. Science 309, 1346–1350 (2005).
Rudner, M. S. & Levitov, L. S. Electrically driven reverse Overhauser pumping of nuclear spins in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 246602 (2007).
Rudner, M. S., Koppens, F. H. L., Folk, J. A., Vandersypen, L. M. K. & Levitov, L. S. Nuclear spin dynamics in double quantum dots: Fixed points, transients, and intermittency. Phys. Rev. B 84, 075339 (2011).
Danon, J. et al. Multiple nuclear polarization states in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 046601 (2009).
Cywiński, L., Witzel, W. M. & Das Sarma, S. Electron spin dephasing due to hyperfine interactions with a nuclear spin bath. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 057601 (2009).
Coish, W. A., Fischer, J. & Loss, D. Exponential decay in a spin bath. Phys. Rev. B 77, 125329 (2008).
Reilly, D. J. et al. Measurement of temporal correlations of the Overhauser field in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 236803 (2008).
Reilly, D. et al. Exchange control of nuclear spin diffusion in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 236802 (2010).
Hahn, E. L. Spin echoes. Phys. Rev. 80, 580 (1950).
Witzel, W. M. & Das Sarma, S. Quantum theory for electron spin decoherence induced by nuclear spin dynamics in semiconductor quantum computer architectures: Spectral diffusion of localized electron spins in the nuclear solid-state environment. Phys. Rev. B 74, 035322 (2006).
Yao, W., Lui, R-B. & Sham, L. J. Theory of electron spin decoherence by interacting nuclear spins in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 74, 195301 (2006).
Heiss, D. et al. Observation of extremely slow hole spin relaxation in self-assembled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 76, 241306 (2007).
Gerardot, B. D. et al. Optical pumping of a single hole spin in a quantum dot. Nature 451, 441–444 (2008).
Gryncharova, E. I. & Perel, V. I. Relaxation of nuclear spins interacting with holes in semiconductors. Sov. Phys. Semicond. 11, 997 (1977).
Testelin, C., Bernardot, F., Eble, B. & Chamarro, M. Hole–spin dephasing time associated with hyperfine interaction in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 79, 195440 (2009).
Fischer, J., Coish, W. A., Bulaev, D. V. & Loss, D. Spin decoherence of a heavy hole coupled to nuclear spins in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 78, 155329 (2008).
Eble, B. et al. Hole–nuclear spin interaction in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 146601 (2009).
Chekhovich, E. A. et al. Element-sensitive measurement of the hole–nuclear spin interaction in quantum dots. Nature Phys. 9, 74–78 (2013).
Desfonds, P. et al. Electron and hole spin cooling efficiency in InAs quantum dots: The role of nuclear field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 172108 (2010).
Li, Y. et al. Intrinsic spin fluctuations reveal the dynamical response function of holes coupled to nuclear spin baths in (In, Ga)As quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 186603 (2012).
Glazov, M. M., Yugova, I. A. & Efros, A. L. Electron spin synchronization induced by optical nuclear magnetic resonance feedback. Phys. Rev. B 85, 041303 (2012).
Reilly, D. J. et al. Suppressing spin qubit dephasing by nuclear state preparation. Science 321, 817–821 (2008).
Ribeiro, H. & Burkard, G. Nuclear state preparation via Landau–Zener–Stuckelberg transitions in double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 216802 (2009).
Barthel, C. et al. Relaxation and readout visibility of a singlet–triplet qubit in an Overhauser field gradient. Phys. Rev. B 85, 035306 (2012).
Flisinski, K. et al. Optically detected magnetic resonance at the quadrupole-split nuclear states in In-GaAs/GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 82, 081308 (2010).
Cherbunin, R. V. et al. Resonant nuclear spin pumping in InGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 84, 041304 (2011).
Krebs, O. et al. Anomalous Hanle effect due to optically created transverse Overhauser field in single InAs/GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 056603 (2010).
Simon, P., Braunecker, B. & Loss, D. Magnetic ordering of nuclear spins in an interacting two-dimensional electron gas. Phys. Rev. B 77, 045108 (2008).
Kondo, Y. et al. Multipulse operation and optical detection of nuclear spin coherence in a GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 207601 (2008).
Rudner, M. S., Vandersypen, L. M. K., Vuletic, V. & Levitov, L. S. Generating entanglement and squeezed states of nuclear spins in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 206806 (2011).
Kessler, E. M. et al. Dissipative phase transition in a central spin system. Phys. Rev. A 86, 012116 (2012).
Kitagawa, M. & Ueda, M. Squeezed spin states. Phys. Rev. A 47, 5138–5143 (1993).
Sørensen, A. S. & Mølmer, K. Entanglement and extreme spin squeezing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4431–4434 (2001).
Gullans, M. et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization in double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 226807 (2010).
Schuetz, M. J. A., Kessler, E. M., Cirac, J. I. & Giedke, G. Superradiance-like electron transport through a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 86, 085322 (2012).
Kessler, E. M., Yelin, S., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Giedke, G. Optical superradiance from nuclear spin environment of single-photon emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 143601 (2010).
Kuemmeth, F., Churchill, H. O. H., Herring, P. K. & Marcus, C. M. Carbon nanotubes for coherent spintronics. Mater. Today 13, 18–26 (March, 2010).
Abe, E. et al. Electron spin coherence of phosphorus donors in silicon: Effect of environmental nuclei. Phys. Rev. B 82, 121201 (2010).
Morton, J. J. L. et al. Solid-state quantum memory using the 31P nuclear spin. Nature 455, 1085–1088 (2008).
Shaji, N. et al. Spin blockade and lifetime-enhanced transport in a few-electron Si/SiGe double quantum dot. Nature Phys. 4, 540–544 (2008).
Dutt, M. V. G. et al. Quantum register based on individual electronic and nuclear spin qubits in diamond. Science 316, 1312–1316 (2007).
Pfund, A., Shorubalko, I., Ensslin, K. & Leturcq, R. Spin state mixing in InAs double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 76, 161308(R) (2007).
Nadj-Perge, S., Frolov, S. M., Bakkers, E. P. A. M. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. Spin–orbit qubit in a semiconductor nanowire. Nature 468, 1084–1087 (2010).
Acknowledgements
E.A.C., M.N.M. and A.I.T. acknowledge support by the EPSRC Programme grants (EP/G001642/1 and EP/J007544/1), ITN Spin-Optronics and the Royal Society. A.Y. acknowledges support by IARPA. L.M.K.V. acknowledges support by a European Research Council starting grant, the Dutch Foundation for Fundamental Research on Matter (FOM), and the Office of the Director of National Intelligence, Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), through the Army Research Office grant W911NF-12-1-0354. H. B. thanks the Alfried Krupp von Bohlen und Halbach Foundation. K.C.N. acknowledges support from the Center for Probing the Nanoscale, an NSF NSEC, supported under grant no. PHY-0830228, and from NSF grant no. DMR-0803974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chekhovich, E., Makhonin, M., Tartakovskii, A. et al. Nuclear spin effects in semiconductor quantum dots. Nature Mater 12, 494–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3652
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3652
This article is cited by
-
Wigner-molecularization-enabled dynamic nuclear polarization
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Coherence protection of spin qubits in hexagonal boron nitride
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Optimal operation points for ultrafast, highly coherent Ge hole spin-orbit qubits
npj Quantum Information (2021)
-
Quantum sensing of a coherent single spin excitation in a nuclear ensemble
Nature Physics (2021)
-
Non-Markovian Speedup Dynamics in Markovian and Non-Markovian Channels
International Journal of Theoretical Physics (2021)