Summary
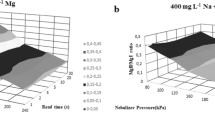
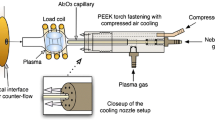
An analytical procedure for the determination of Se, as well as of other trace elements of clinical interest, in undiluted blood serum samples is presented. This procedure allows the on-line wet ashing of the sample, the hydride generation and the determination of the SeH2 formed in one step. For this purpose, carrier solution and the injected sample (300 μl) were merged with an acid stream (80% H2SO4, 12% HClO4, 8% HNO3) and passed through a reaction coil heated up to 240°C. To increase the dispersion, the wet digestion was carried out in an ultrasonic field. After trapping of the gas bubbles, 5 mol/l HCl and 0.053 mol/l NaBH4 solutions were added via T-junctions for Se-hydride generation. The nebulizing system of the ICP-OES was used as gas/liquid separator. The hydride was swept from the spray chamber into the plasma by an argon gas flow with droplets containing other sample constituents. This allows the simultaneous determination of other trace elements of clinical interest, for example Fe, Cu and Zn. The relative detection limit for Se in blood serum was 5 μg/l. The quality of the developed procedure was verified in two ways: by measuring SRM Seronorm 116 and by comparing the results for different serum samples with the results obtained with ETAAS. Our results were in good agreement in both cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brätter P, Negretti de Brätter VE, Rösick U, v Stockhausen HB (1987) In: Brätter P, Schramel P (eds) Trace element analytical chemistry in medicine and biology, Vol. 4. Gryter, Berlin New York, pp 133–143
Gramm HJ, Goecke J, Brätter P, Stoltenberg-Didinger G, Waldschmidt J, Eyrich K (1988) Infusionstherapie 15:11–12
Vinton N, Dahlstrom KA, Strobel CT, Ament ME (1987) Pediatrics 111:711–717
Brätter P, Gercken B, Tomiak A, Rösick U (1988) In: Brätter P, Schramel P (eds) Trace element analytical chemistry in medicine and biology, Vol. 5. de Gruyter, Berlin New York, pp 119–135
Tomiak A (1992) GIT Fachzeitschrift für das Laboratorium 8:812–813
Thompson M, Pahlavanpour B, Walton SJ, Kirkbright GF (1978) Analyst 103:568–579
Wolnik KA, Fricke FL, Hahn MH, Caruso JA (1981) Anal Chem 53:1030–1035
Nygaard D, Lowry J (1982) Anal Chem 54:803–807
Nakahara T, Kikui N (1985) Spectrochimica Acta 40b:21–28
Rösick U, Nowak F, Melchert D, Brätter P (1991) In: Welz B (ed) 6. CAS Colloquium Atomspektrometrische Spurenanalytik, Bodenseewerk Perkin Elmer GmbH, Überlingen, pp 49–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Dr. Wilhelm Fresenius on the occasion of his 80th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Recknagel, S., Brätter, P., Tomiak, A. et al. Determination of selenium in blood serum by ICP-OES including an on-line wet digestion and Se-hydride formation procedure. Fresenius J Anal Chem 346, 833–836 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321300
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00321300