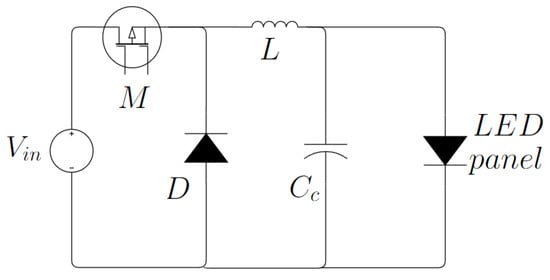
The relationship between estimating traffic flow and evaluating pollutant emissions lies in understanding how vehicular traffic patterns affect air quality. Traffic flow estimation is a complex field that involves a variety of analytical techniques to understand, predict, and manage the flow of vehicles on road networks. Different types of analyses commonly employed in this area are statistical analysis (e.g., descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, time series analysis), mathematical modeling (macroscopic models, microscopic models, mesoscopic models), computational methods (e.g., simulation modeling, machine learning, and AI techniques), geospatial analysis (e.g., geographic information systems (GISs), spatial data analysis), network analysis (e.g., graph theory and network flow models). In sensor network setups, the strategic placement of sensors is crucial, primarily due to the challenges posed by limited energy supplies, restricted storage capabilities, and the demands on processing and communication, all of which significantly impact maintenance costs and hardware limitations. To mitigate the burden on processing and communication, it is essential to deploy a limited number of sensors strategically. In practical applications, achieving an optimal layout of physical sensors (i.e., placing sensors within the network in such a way as to meet a specific optimality criterion, such as identifying the minimum number of sensors required to ensure the ability to design reliable state observers capable of reconstructing the network’s state based on the available data) is essential for the accurate monitoring of large-scale systems, including traffic flow or the distribution networks of water and gas. In the context of traffic systems, addressing the challenge of full link flow observability, that is, the ability to accurately monitor and assess the flow of entities (i.e., vehicles) across all the links or pathways within a network, entails selecting the smallest number of traffic sensors from a larger set to install. The goal is to choose a subset of
p sensors, which may include redundancies, from a pool of
potential sensors. This is conducted to maintain the structural observability of the entire traffic network. This concept pertains to deducing the complete internal state (traffic volume on each road link in the network) from external outputs and inputs (measurements from sensors). The traditional concept of system observability serves as a criterion for sensor placement. This article presents the development of a simulated annealing heuristic to address the selection problem. The selected sensors are then applied to construct a Luenberger observer, a mathematical construct used in control theory to accurately estimate the internal state of a dynamic system based on its inputs and outputs. Numerical simulations are carried out to demonstrate the effectiveness of this method, and a performance analysis using a digital twin of a transport network, designed using the Aimsun Next software, are also carried out to assess traffic flow and associated pollutant emissions. In particular, we examine a traffic network comprising 21 roads. We address the sensor selection problem by identifying an optimal set of six sensors, which facilitates the design of a Luenberger observer. This observer enables the reconstruction of traffic flow across the network with minimal estimation error. Furthermore, by integrating this observer with data from the Aimsun Next software, we assess the pollutant emissions related to traffic flow. The results indicate a high accuracy in estimating pollutant levels.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT