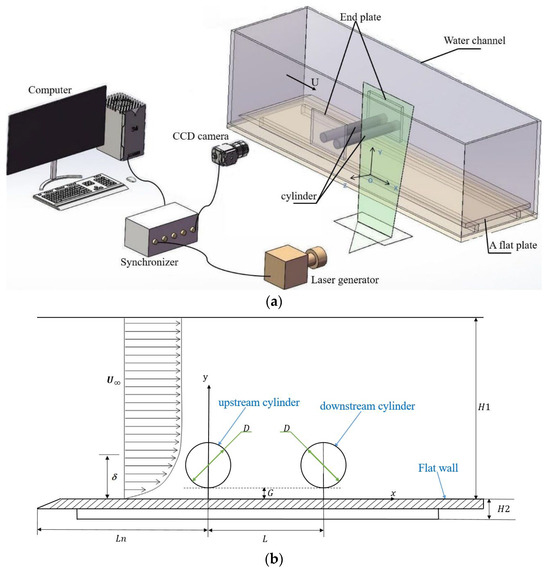
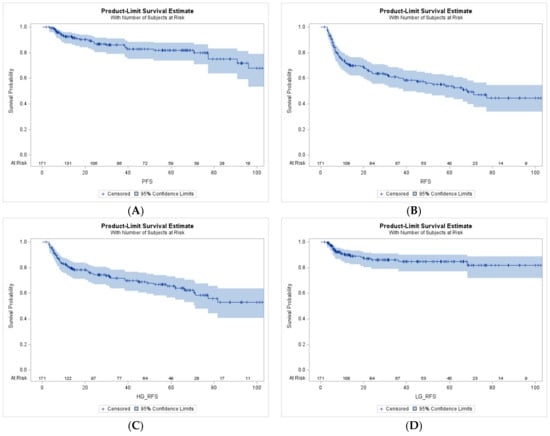
The flow around two tandem circular cylinders in proximity to a wall is investigated using particle image velocimetry (PIV) for
Re = 2 × 10
3. The spacing ratios
L/
D are 1, 2, and 5, and the gap ratios
G/
D are 0.3, 0.6, and 1. The proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) method and λci vortex identification method are used to investigate the evolution of flow structure, and the influences of
L/
D and
G/
D on flow physics are shown. At
L/
D = 2 and
G/
D = 0.3, a “pairing” process occurs between the wall shear layer and the upstream cylinder’s lower shear layer, resulting in a small separation bubble behind the upstream cylinder. At
L/
D = 1, the Strouhal number (
St) increases with decreasing
G/D. At three gap ratios, the
St gradually decreases as
L/
D increases. At
G/
D = 0.3, there is nearly a 49.98% decrease from
St = 0.3295 at
L/
D = 1 to
St = 0.1648 at
L/
D = 5, which is larger than the reductions in cases of
G/
D = 0.6 and
G/
D = 1. The effects of
L/
D on the evolution of flow structure at
G/
D = 0.6 are revealed in detail. At
L/
D = 1, the vortex shedding resembles that of the single cylinder. As
L/
D increases to 2, a squarish flow structure is formed between two cylinders, and a small secondary vortex is formed due to induction of the lower shear layer of the upstream cylinder. At
L/
D = 5, there is a vortex merging process between the upper wake vortices of the upstream and downstream cylinders, and the lower wake vortex of the upstream cylinder directly impinges the downstream cylinder. In addition, the shear layers and wake vortices of the upstream cylinder interact with the wake of the downstream cylinder as L/D increases, resulting in reductions in velocity fluctuations, and the production and turbulent diffusion of turbulent kinetic energy are decreased behind the downstream cylinder.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT