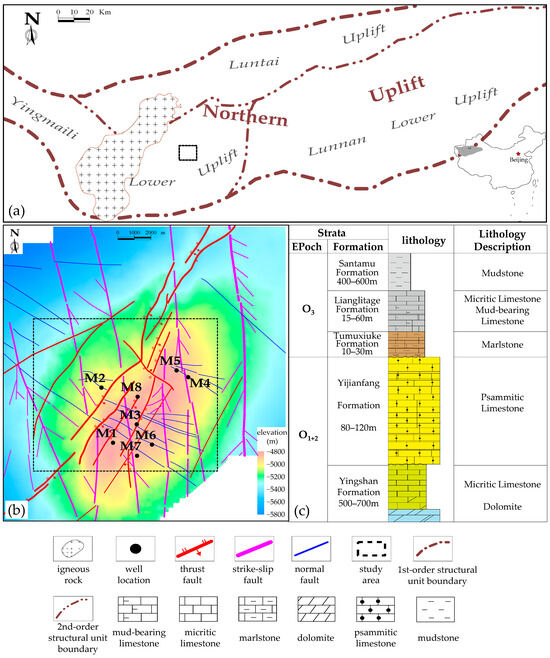
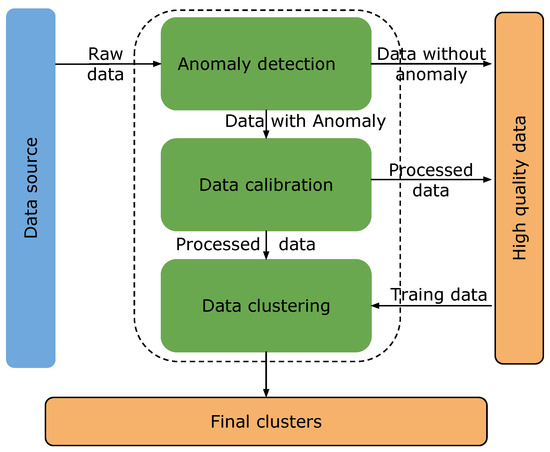
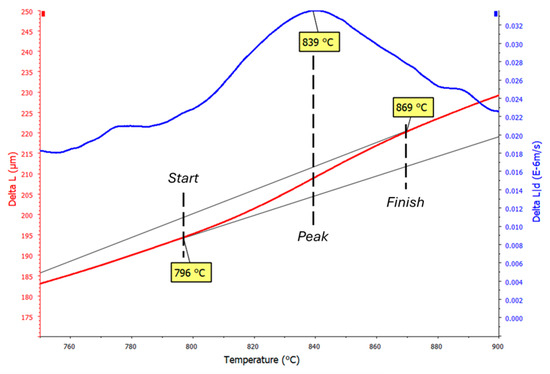
The exploration of novel biomarkers to assess poultry health is of paramount importance, not only to enhance our understanding of the pathogenicity of zoonotic agents but also to evaluate the efficacy of novel treatments as alternatives to antibiotics. The present study aimed to investigate potential gut health biomarkers in broiler chicks challenged by
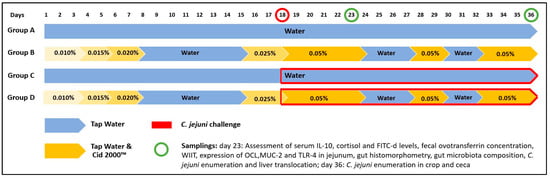
Campylobacter jejuni and subjected to a continuous water disinfection program. A total of 144 one-day-old hatched broiler chicks were randomly allocated to four treatment groups with four replicates each, according to the following experimental design: Group A received untreated drinking water; Group B received drinking water treated with 0.01–0.05%
v/
v Cid 2000™ (hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid and paracetic acid); Group C was challenged by
C. jejuni and received untreated drinking water; and Group D was challenged by
C. jejuni and received drinking water treated with 0.01–0.05%
v/
v Cid 2000™. The use of Cid 2000™ started on day 1 and was applied in intervals until the end of the experiment at 36 days, while the
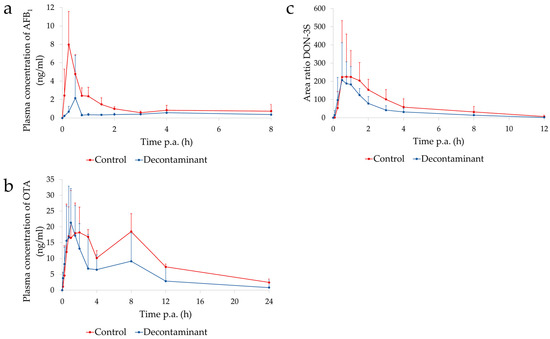
C. jejuni challenge was applied on day 18. Potential biomarkers were investigated in serum, feces, intestinal tissue, intestinal content, and liver samples of broilers. Statistical analysis revealed significant increases (
p < 0.001) in serum cortisol levels in
C. jejuni-challenged broilers. Serum fluorescein isothiocyanate dextran (FITC-d) increased significantly (
p = 0.004) in broilers challenged by
C. jejuni and treated with drinking water disinfectant, while fecal ovotransferrin concentration also increased significantly (
p < 0.001) in broilers that received the drinking water disinfectant alone. The gene expression levels of
occludin (
p = 0.003) and
mucin-2 (
p < 0.001) were significantly upregulated in broilers challenged by
C. jejuni, while mucin-2 significantly increased in birds that were challenged and received the drinking water disinfectant (
p < 0.001).
TLR-4 expression levels were significantly (
p = 0.013) decreased in both groups that received the drinking water disinfectant, compared to the negative control group. Finally, the
C. jejuni challenge significantly increased (
p = 0.032) the crypt depth and decreased (
p = 0.021) the villus height-to-crypt-depth ratio in the ileum of birds, while the tested disinfectant product increased (
p = 0.033) the villus height in the jejunum of birds. Furthermore, the counts of
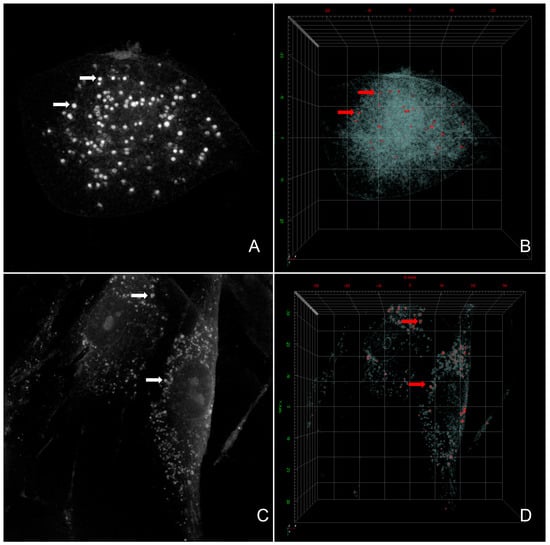
C. jejuni in the ceca of birds (
p = 0.01), as well as its translocation rate to the liver of broilers (
p = 0.001), were significantly reduced by the addition of the water disinfectant. This research contributes to novel insights into the intricate interplay of water disinfection and/or
C. jejuni challenge with potential intestinal biomarkers. In addition, it emphasizes the need for continued research to unveil the underlying mechanisms, expands our understanding of broiler responses to these challenges and identifies breakpoints for further investigations.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT