Background and Objectives: Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by
Burkholderia pseudomallei, and it has a wide range of clinical symptoms. It is endemic in tropical areas, including Southeast Asia. Despite the availability of effective treatment, the mortality rate is still high, especially in patients presenting with septic shock. The aim of this study was to determine and explore clinical characteristics, microbiology, treatment outcomes, and factors associated with in-hospital mortality which could predict prognosis and provide a guide for future treatment.
Materials and Methods: The population in this retrospective cohort study included all 262 patients with a diagnosis of melioidosis who were hospitalized at Surin Hospital, Surin, Thailand, from April 2014 to March 2017. We included patients older than 15 years with a positive culture for
B. pseudomallei. Data regarding the clinical characteristics, microbiology, and treatment outcomes of the patients were collected and analyzed. The patients were divided into two groups dependent on outcome, specifically non-survival and survival. Logistic regression was performed to determine the risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality.
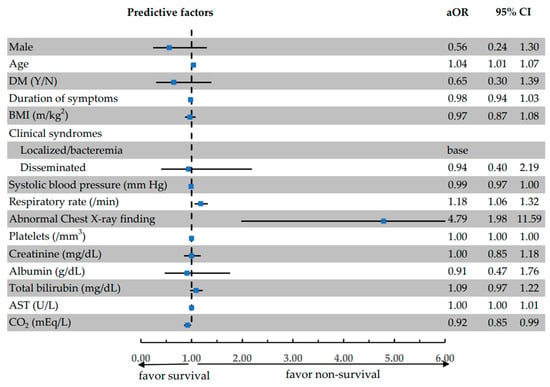
Results: Out of the 262 patients with melioidosis during the study period, 117 (44.7%) patients died. The mean age was 57.2 ± 14.4 years, and 193 (73.7%) patients were male. The most common comorbidity was diabetes (123, 46.9%), followed by chronic kidney disease (35, 13.4%) and chronic liver disease (31, 11.8%). Four risk factors were found to be associated with in-hospital mortality, including age (adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 1.04, 95%CI: 1.01–1.07), respiration rate (aOR 1.18, 95%CI: 1.06–1.32), abnormal chest X-ray finding (aOR 4.79, 95%CI: 1.98–11.59), and bicarbonate levels (CO
2) (aOR 0.92, 95%CI: 0.85–0.99).
Conclusions: Our study identified age, respiration rate, abnormal chest X-ray finding, and CO
2 levels are predictive factors associated with in-hospital mortality in melioidosis patients. Physicians should be aware of these factors, have access to aggressive treatment options, and closely monitor patients with these risk factors.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT