Objectives: This study aimed to identify predictors of remission or low disease activity (LDA) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and low-ultrasound inflammation.
Methods: A total of 80 patients with RA who fulfilled the 1987 ACR criteria for RA with a disease activity score of 28 joints (DAS28) > 3.2 were recruited. Over 1 year of therapy, we conducted blood tests every 6 months to examine erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), neuraminidase 3 (Neu3), and α-2,3-sialyltrasnferse I (ST3Gal-1) levels in B cells and monocytes. Additionally, we evaluated physical function by using the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Data on demographic and clinical parameters were collected, and musculoskeletal ultrasonography was performed twice a year on 12 specific joints to assess synovial changes. One year later, we compared all collected data and laboratory or ultrasound results between patients achieving remission or LDA and those who did not in order to determine the predictors.
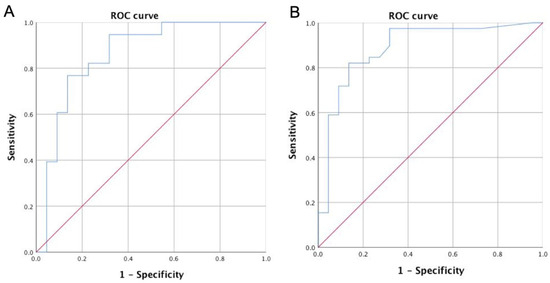
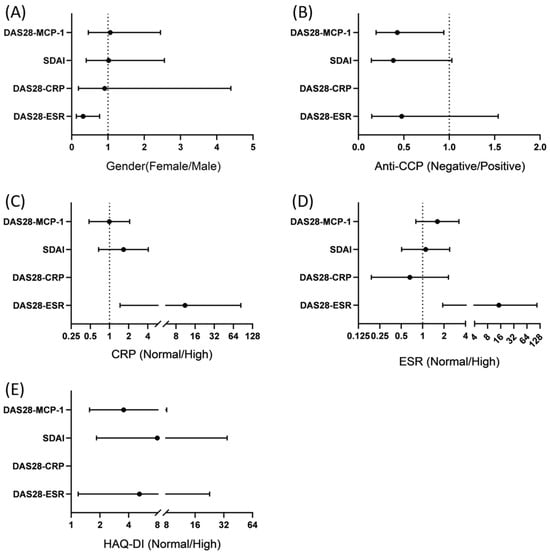
Results: Age, the presence or absence of rheumatoid factor, and the number of conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs used were not correlated with remission or LDA for DAS28 or Simplified Disease Activity Index formulas. However, male sex, low CRP levels, low ESR levels, and low HAQ-DI scores were associated with a higher likelihood of achieving remission or LDA for DAS28-ESR. Negative anticyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) and low HAQ-DI scores were predictors of remission or LDA for DAS28-MCP-1. Interestingly, having less than two comorbidities is a good predictor of a combined remission/low disease activity state for SDAI and DAS28-MCP-1. Furthermore, Neu3 and ST3Gal-1 levels and ST3Gal-1/Neu3 ratios in B cells and monocytes had no significant correlation with total ultrasound scores. Nevertheless, monocyte ST3Gal-1 and Neu3 correlated significantly with DAS28-ESR >5.1 and DAS-MCP-1 >4.8 (both categories belong to high disease activity), respectively (rho = 0.609 with
p = 0.012, and rho = 0.727 with
p = 0.011, respectively). Monocyte ST3Gal-1/Neu3 ratios connected with DAS28-ESR >5.1 and 3.3 < SDAI ≦ 11 (low disease activity), respectively (rho = 0.662 with
p = 0.005, and rho = 0.342 with
p = 0.048, respectively).
Conclusions: In patients with RA in Taiwan, male sex, low CRP levels, low ESR levels, and low HAQ-DI scores are predictors of remission or LDA for DAS28-ESR, which differ from the predictors for DAS28-MCP-1. Moreover, monocyte ST3Gal-1, Neu3, and their ratios correlated with different disease activity categories of DAS28-ESR, DAS28-MCP-1, and SDAI scores.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT