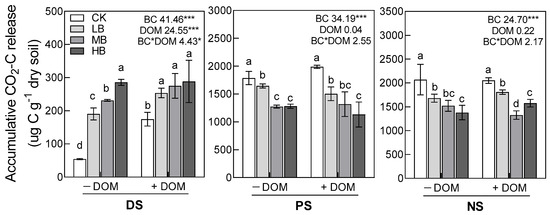
Biochar, as a soil amendment, has been widely confirmed to increase soil carbon sequestration. However, how biochar addition affects soil carbon changes during the vegetation restoration process is still unclear, which constrains our ability to explore biochar’s application in the technology of soil carbon sequestration in forests. We conducted an incubation experiment on biochar and dissolved organic matter (DOM) addition to soil at three stages of revegetation (degraded land (DS), plantation forest (PS), and secondary natural forest (NS) in Changting County in Fujian province, China) to investigate the effects of vegetation restoration, biochar, DOM, and their interaction on soil CO
2 emission and its relative mechanisms. We found that the accumulative release of CO
2-C in the NS and PS soils was 7.6 and 6.8 times higher, respectively, in comparison to that from the DS soil. In the DS, biochar addition significantly increased the accumulative release of CO
2-C, soil pH, NH
4+-N content,
qCO
2, phenol oxidase, and peroxidase activities. Peroxidase activities were positively correlated with the accumulative release of CO
2-C, and oxidase was the most important direct factor influencing the accumulative release of CO
2-C in the DS. However, the accumulative release of CO
2-C, soil NH
4+-N content,
qCO
2, β-glucosidase, and N-acetylglucosaminidase activities was significantly reduced after the application of biochar in the PS and NS. These two hydrolases were positively associated with the accumulative release of CO
2-C, and hydrolase was the most vital direct factor influencing the accumulative release of CO
2-C from the PS and NS soils. The positive effect of DOM addition on CO
2 emission under biochar application declined with a vegetation restoration age increase. Our results indicated that biochar could alter microbial physiological processes, inhibit
qCO
2 and hydrolase activities, and further decrease CO
2 emission in relatively fertile soil from the PS and NS; but in the relatively barren soil from the DS, biochar might promote CO
2 emission by stimulating microorganisms to enhance
qCO
2 and oxidase activities.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT