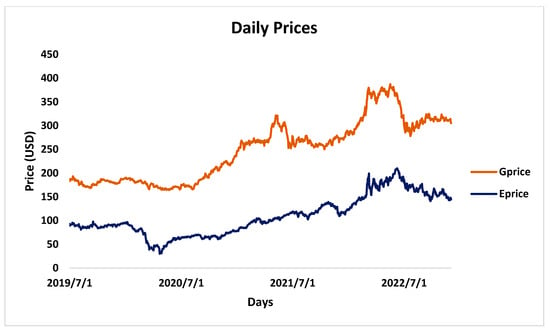
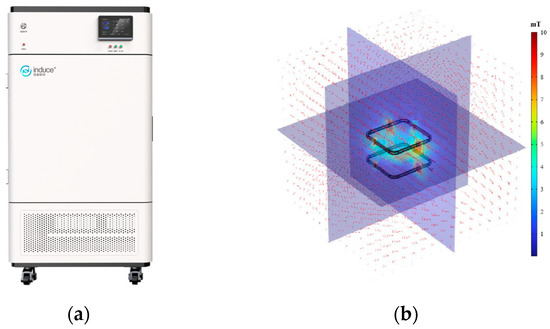
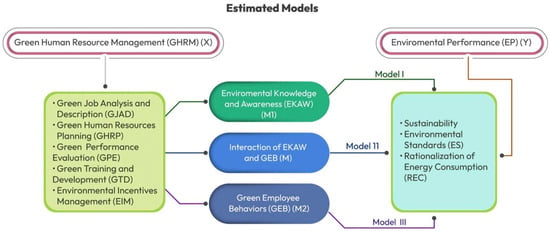
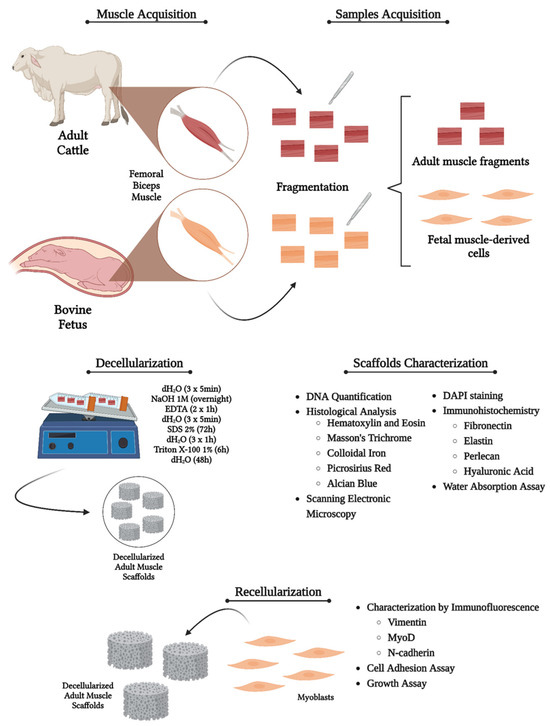
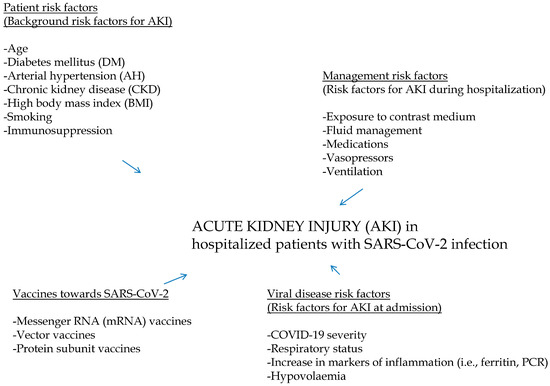
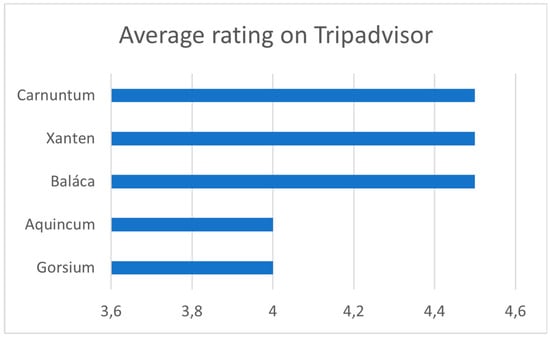
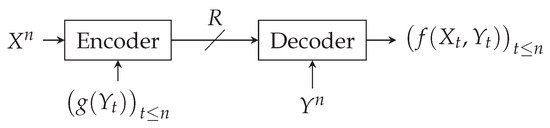
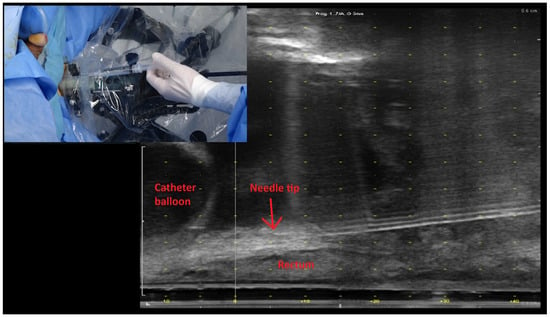
The rise in contaminated sites presents a significant issue for the environment and human health, necessitating the decontamination of the surroundings and the adoption of effective decontamination strategies. This investigation was initiated to assess the potential aspects of
Acacia karroo in conjunction with enzyme activity, a method that shows promise for mitigating soil contamination.
Acacia karroo, with its hyperaccumulator traits, demonstrates great capacity. Enzymes significantly efficiently convert and detoxify harmful substances to a non-toxic level. ICP-MS quantified the concentrations of trace elements in
Acacia karroo, while colorimetric assays were used to determine the activity levels of the enzymes. Ten toxic elements were identified in leaf samples of
Acacia karroo in the following sequence: Sr > Zn > Cr > V > Rb > Cu > Ni > Y > Sc > Co; concentrations ranged between 203.86 ± 4.48 ppm (Zn) and 10.12 ± 0.09 ppm (Sc). The concentration of these metals was very high, posing a potential risk of harming the environment. Meanwhile, the three identified enzymes, invertase (INV), phosphatase (PHO), and catalase (CAT), have high and average activity levels, respectively. PHO and CAT showed a positive correlation with Zn, Rb, Sr, and Y, while INV correlated positively with Sc, V, Cr, Co, Cu, and Ni content. The principal component analysis (PCA) findings in this study demonstrated an inconclusive correlation between soil enzyme activity and soil heavy metal content. Both positive and negative correlations between soil enzyme activity and heavy metals were observed. This investigation revealed
Acacia karroo as an optimal botanical species for phytoremediation. Consequently, a correlation analysis demonstrated that incorporating the
Acacia karroo species along with enzyme activity seems to be a highly promising environmentally friendly technique for remediating soil pollution. The
Acacia species can also be used in phytoremediation efforts to help conserve biodiversity. Subsequent investigations should focus on the operational mechanisms of different plant parts used as herbal remedies, isolated compounds, their efficacy, adverse effects, and practical implications.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT