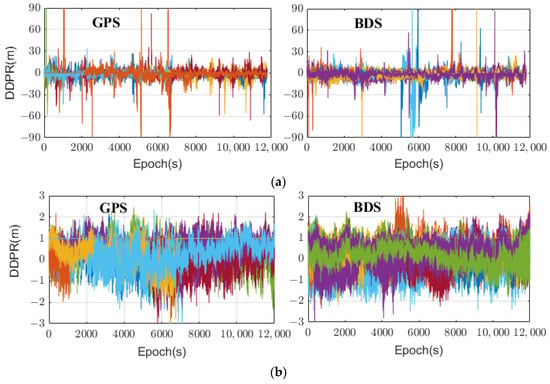
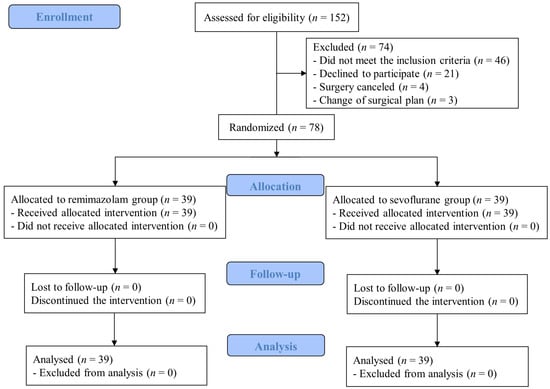
A new analytical formula for
H0, one of the three parameters (
H0,
g, and
r) on which the NeQuick model is based to describe the altitude profile of the electron density above the F2-layer peak height
hmF2, has recently been proposed. This new analytical representation of
H0, called
H0,corr, relies on numerical grids based on two different types of datasets. On one side, electron density observations by the Swarm satellites over Europe from December 2013 to September 2018, and on the other side, IRI UP (International Reference Ionosphere UPdate) maps over Europe of the critical frequency of the ordinary mode of propagation associated with the F2 layer,
foF2, and
hmF2, at 15 min cadence for the same period. The new NeQuick topside representation based on
H0,corr, hereafter referred to as NeQuick-corr, improved the original NeQuick topside representation. This work updates the numerical grids of
H0,corr by extending the underlying Swarm and IRI UP datasets until December 2021, thus allowing coverage of low solar activity levels, as well. Moreover, concerning Swarm, besides the original dataset, the calibrated one is considered, and corresponding grids of
H0,corr calculated. At the same time, the role of
g is investigated, by considering values different from the reference one, equal to 0.125, currently adopted. To understand what are the best
H0,corr grids to be considered for the NeQuick-corr topside representation, vertical total electron content data for low, middle, and high latitudes, recorded from five low-Earth-orbit satellite missions (COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3, GRACE, METOP, TerraSAR-X, and Swarm) have been analyzed. The updated
H0,corr grids based on the original Swarm dataset with a value for
g = 0.15, and the updated
H0,corr grids based on the calibrated Swarm dataset with a value for
g = 0.14, are those for which the best results are obtained. The results show that the performance of the different NeQuick-corr models is reliable also for low latitudes, even though these are outside the spatial domain for which the
H0,corr grids were obtained, and are dependent on solar activity.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT